CH 14 – Copy
... Work of weight The particle moves along the path s, from s 1 to s 2 .At the immediate point, the displacement dr = dx i + dy j + dz k . ...
... Work of weight The particle moves along the path s, from s 1 to s 2 .At the immediate point, the displacement dr = dx i + dy j + dz k . ...
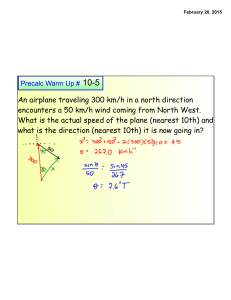
An airplane traveling 300 km/h in a north direction
... direction, are applied at a point A. What is the resulting FORCE at A? (You need a direction AND a magnitude) ...
... direction, are applied at a point A. What is the resulting FORCE at A? (You need a direction AND a magnitude) ...
Answers to Data Analysis Assessment Task for Unit 3
... 5. Describe how the shape of this graph relates to the motion of the spring. (3 marks) Negative values as it is dropping from start point Each trough then crest in the wave shape indicated an oscillation Turning points indicate zero velocity, where the spring stops and starts changing directio ...
... 5. Describe how the shape of this graph relates to the motion of the spring. (3 marks) Negative values as it is dropping from start point Each trough then crest in the wave shape indicated an oscillation Turning points indicate zero velocity, where the spring stops and starts changing directio ...
Document
... body (physical object) is an identifiable collection of matter, which may be more or less constrained to move together by translation or rotation, rigid body is an idealization of a solid body in which deformation is neglected, barycentre is is the center of mass of two or more bodies that are orbit ...
... body (physical object) is an identifiable collection of matter, which may be more or less constrained to move together by translation or rotation, rigid body is an idealization of a solid body in which deformation is neglected, barycentre is is the center of mass of two or more bodies that are orbit ...
Lecture04d
... The window washer pulls down on the rope with a tension force so the rope pulls up on her hands with a tension force The tension in The rope is also applied at the other end of the rope, where it FT attaches to the bucket. So there is another force pulling up on the bucket. The bucket-washer combina ...
... The window washer pulls down on the rope with a tension force so the rope pulls up on her hands with a tension force The tension in The rope is also applied at the other end of the rope, where it FT attaches to the bucket. So there is another force pulling up on the bucket. The bucket-washer combina ...
18.034 Honors Differential Equations
... The spring-mass system and the electric circuit. If a mass m is attached to one end of a sus pended spring, it will produce an elongation, say y0 , which, according to Hooke’s law, is propor tional to the force of gravity ky0 = mg, where k > 0 is the stiffness constant of spring and g > 0 is the g ...
... The spring-mass system and the electric circuit. If a mass m is attached to one end of a sus pended spring, it will produce an elongation, say y0 , which, according to Hooke’s law, is propor tional to the force of gravity ky0 = mg, where k > 0 is the stiffness constant of spring and g > 0 is the g ...
Chapter 13
... Assume the object is initially pulled to a distance A and released from rest As the object moves toward the equilibrium position, F and a decrease, but v increases At x = 0, F and a are zero, but v is a maximum The object’s momentum causes it to overshoot the equilibrium position ...
... Assume the object is initially pulled to a distance A and released from rest As the object moves toward the equilibrium position, F and a decrease, but v increases At x = 0, F and a are zero, but v is a maximum The object’s momentum causes it to overshoot the equilibrium position ...
Springs and Hooke`s Law
... from an object’s mass and velocity. KE = ½ mv2 • A 2 kg object moving at 3 m/s has a kinetic energy of…KE = ½(2)(3)2 = 9 J • Mass doesn’t change. This means that when strain energy is released, either the end of the spring or an object attached to it undergoes an increase in velocity. • The power is ...
... from an object’s mass and velocity. KE = ½ mv2 • A 2 kg object moving at 3 m/s has a kinetic energy of…KE = ½(2)(3)2 = 9 J • Mass doesn’t change. This means that when strain energy is released, either the end of the spring or an object attached to it undergoes an increase in velocity. • The power is ...
Chapter 9 Linear Momentum Linear Momentum and Kinetic Energy
... between hard balls. Later, Newton conducted carefully experiments on collision between all kinds of substances, such as glass, wood, steel, and putty. Newton found the vector mv was always conserved, but that the scalar quantity mv2 was conserved only in special case of collisions between hard spher ...
... between hard balls. Later, Newton conducted carefully experiments on collision between all kinds of substances, such as glass, wood, steel, and putty. Newton found the vector mv was always conserved, but that the scalar quantity mv2 was conserved only in special case of collisions between hard spher ...
Chapter 3
... Measuring mass and measuring weight. • An object’s mass is the same everywhere. • An object’s weight varies with gravity. ...
... Measuring mass and measuring weight. • An object’s mass is the same everywhere. • An object’s weight varies with gravity. ...