Law of conservation of linear momentum
... Law of inertia, law of acceleration, law of action and reaction Law of inertia: A body is at rest or in uniform rectilinear motion unless made to change its state by external forces Inertia is a property of matter by which it remains at rest or continues moving uniformly in a straight line unless ac ...
... Law of inertia, law of acceleration, law of action and reaction Law of inertia: A body is at rest or in uniform rectilinear motion unless made to change its state by external forces Inertia is a property of matter by which it remains at rest or continues moving uniformly in a straight line unless ac ...
chapter7
... Introduction to Energy A variety of problems can be solved with Newton’s Laws and associated principles. Some problems that could theoretically be solved with Newton’s Laws are very difficult in practice. These problems can be made easier with other techniques. The concept of energy is one of the ...
... Introduction to Energy A variety of problems can be solved with Newton’s Laws and associated principles. Some problems that could theoretically be solved with Newton’s Laws are very difficult in practice. These problems can be made easier with other techniques. The concept of energy is one of the ...
Y12 Mechanics Notes - Cashmere
... Forces A force causes the motion or shape of an object to change. Force is a vector quantity so must have both a size and a direction Force is measured in Newtons N. A resultant (or net) force is produced when 2 or more forces act on an object. These forces can be added to find the resultant. ...
... Forces A force causes the motion or shape of an object to change. Force is a vector quantity so must have both a size and a direction Force is measured in Newtons N. A resultant (or net) force is produced when 2 or more forces act on an object. These forces can be added to find the resultant. ...
Work Done By Forces Conservative vs. Nonconservative Forces
... have to different) ○ The collision has to be elastic ○ I don’t have a proof of this, and I am interested in proving it at some point. ...
... have to different) ○ The collision has to be elastic ○ I don’t have a proof of this, and I am interested in proving it at some point. ...
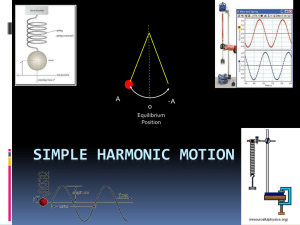
Simple Harmonic Motion
... mechanical energy of a harmonic oscillator at a particular point in its motion is true? a) The mechanical energy depends on the acceleration at that point. b) The mechanical energy depends on the velocity at that point. c) The mechanical energy depends on the position of that point. d) The mechanica ...
... mechanical energy of a harmonic oscillator at a particular point in its motion is true? a) The mechanical energy depends on the acceleration at that point. b) The mechanical energy depends on the velocity at that point. c) The mechanical energy depends on the position of that point. d) The mechanica ...
Chapter 1 Two-Body Orbital Mechanics 1.1
... The Equation of Relative Motion is usually written in the very simple form ...
... The Equation of Relative Motion is usually written in the very simple form ...
Lecture07
... A Typical Problem An object displaced by force F on a frictionless, horizontal surface. Free body diagram is shown Normal force FN & weight mg do no work in the process, since both are perpendicular to the displacement. Angles for forces: ...
... A Typical Problem An object displaced by force F on a frictionless, horizontal surface. Free body diagram is shown Normal force FN & weight mg do no work in the process, since both are perpendicular to the displacement. Angles for forces: ...
Cross Products
... rule to find the direction of vu, it points in the opposite direction as the direction of uv. (2) This follows from the fact that the angle between u and itself is zero. (3) Consider the case t > 0. Note that both tu and u have the same direction. Therefore (tu)v and uv have the same direction. ...
... rule to find the direction of vu, it points in the opposite direction as the direction of uv. (2) This follows from the fact that the angle between u and itself is zero. (3) Consider the case t > 0. Note that both tu and u have the same direction. Therefore (tu)v and uv have the same direction. ...
Section 7.5
... required to produce an acceleration of 1 centimeter per second per second on a mass of 1 gram. In this system, work is typically expressed in dyne-centimeters (ergs) or newton-meters (joules), where 1 joule = 107 ergs. ...
... required to produce an acceleration of 1 centimeter per second per second on a mass of 1 gram. In this system, work is typically expressed in dyne-centimeters (ergs) or newton-meters (joules), where 1 joule = 107 ergs. ...
Physics 141 Mechanics Yongli Gao Lecture 4 Motion in 3-D
... • You may not know it, but every atom/molecule in your body is oscillating. • For any system, there's at least one state that the system is of the lowest potential energy. This is a point of stable equilibrium, or the bottom of the valley in a potential vs. position curve. • If the system is of a sm ...
... • You may not know it, but every atom/molecule in your body is oscillating. • For any system, there's at least one state that the system is of the lowest potential energy. This is a point of stable equilibrium, or the bottom of the valley in a potential vs. position curve. • If the system is of a sm ...