41 HW#2 Key
... side. An object of mass m at a distance r from the center of the Earth is pulled toward the center of the Earth only by the mass within the sphere of radius r. (a) Write Newton's law of gravitation for an object at the distance r from the center of the Earth, and show that the force on it is of Hook ...
... side. An object of mass m at a distance r from the center of the Earth is pulled toward the center of the Earth only by the mass within the sphere of radius r. (a) Write Newton's law of gravitation for an object at the distance r from the center of the Earth, and show that the force on it is of Hook ...
Mass-spring system Simple Model Application of the momentum
... the stiffness of a spring, and we understand that the force required to stretch an ideal spring a distance s from its unstretched position is F = ks s ...
... the stiffness of a spring, and we understand that the force required to stretch an ideal spring a distance s from its unstretched position is F = ks s ...
a p course audit
... measurement. Draw the free body diagram and analyze the forces and determine which measurements you would take. Can you calculate acceleration due to earth’s gravity by this method? Explain 4. Design the experiment to measure the acceleration due to earth’s gravity in this lab. Verify by different m ...
... measurement. Draw the free body diagram and analyze the forces and determine which measurements you would take. Can you calculate acceleration due to earth’s gravity by this method? Explain 4. Design the experiment to measure the acceleration due to earth’s gravity in this lab. Verify by different m ...
A P COURSE AUDIT
... measurement. Draw the free body diagram and analyze the forces and determine which measurements you would take. Can you calculate acceleration due to earth’s gravity by this method? Explain 4. Design the experiment to measure the acceleration due to earth’s gravity in this lab. Verify by different m ...
... measurement. Draw the free body diagram and analyze the forces and determine which measurements you would take. Can you calculate acceleration due to earth’s gravity by this method? Explain 4. Design the experiment to measure the acceleration due to earth’s gravity in this lab. Verify by different m ...
Oscillations Problems
... 1988M2. A 5-kilogram object initially slides with speed vo in a hollow frictionless pipe. The end of the pipe contains two springs. one nested inside the other, as shown above. The object makes contact with the inner spring at point A, moves 0.1 meter to make contact with the outer spring at point ...
... 1988M2. A 5-kilogram object initially slides with speed vo in a hollow frictionless pipe. The end of the pipe contains two springs. one nested inside the other, as shown above. The object makes contact with the inner spring at point A, moves 0.1 meter to make contact with the outer spring at point ...
Physics Midterm Study Guide
... resolving vectors into x and y components put the tail of the vector at the origin of an x-y coordinate system measure the angle from the positive x-axis to the vector. This is called the “standard position” the vector, the x-component and the y-component form a right triangle the height of the tria ...
... resolving vectors into x and y components put the tail of the vector at the origin of an x-y coordinate system measure the angle from the positive x-axis to the vector. This is called the “standard position” the vector, the x-component and the y-component form a right triangle the height of the tria ...
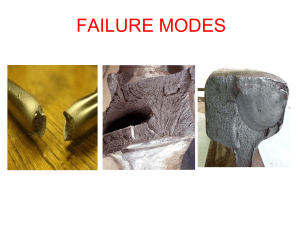
Failure Modes
... • The stress at which the material starts to behave in a non-elastic manner is called the elastic limit. • Between A & B, the material behaves elastically & regains the original position after removal of load. • Point ‘B’ denotes the elastic limit • As the load is increased beyond point B, there com ...
... • The stress at which the material starts to behave in a non-elastic manner is called the elastic limit. • Between A & B, the material behaves elastically & regains the original position after removal of load. • Point ‘B’ denotes the elastic limit • As the load is increased beyond point B, there com ...
Physics - Harmonic Motion
... The drawing above gives you an idea of the sequential motion of the system. Initially the spring is compressed. This is shown in the first drawing. The ball is released and the spring pushes it outward. In the second drawing, the spring has reached its normal displacement and is no longer exerting a ...
... The drawing above gives you an idea of the sequential motion of the system. Initially the spring is compressed. This is shown in the first drawing. The ball is released and the spring pushes it outward. In the second drawing, the spring has reached its normal displacement and is no longer exerting a ...
Student AP Physics 1 Date Oscillations – MC 1. A mass m, attached
... (A) The potential energy of the spring is at a minimum at x = 0 (B) The potential energy of the spring is at a minimum at x = A (C) The kinetic energy of the block is at a minimum at x =0 (D) The kinetic energy of the block is at a maximum at x = A 23. A simple pendulum consists of a l.0 kilogram br ...
... (A) The potential energy of the spring is at a minimum at x = 0 (B) The potential energy of the spring is at a minimum at x = A (C) The kinetic energy of the block is at a minimum at x =0 (D) The kinetic energy of the block is at a maximum at x = A 23. A simple pendulum consists of a l.0 kilogram br ...
chapter13
... A longitudinal wave can also be represented as a sine curve Compressions correspond to crests and stretches correspond to troughs Also called density waves or pressure waves ...
... A longitudinal wave can also be represented as a sine curve Compressions correspond to crests and stretches correspond to troughs Also called density waves or pressure waves ...
SUMMARY Phys 2113 (General Physics I) Compiled by Prof
... • As the notion of potential energy comes from work performed by an external conservative force, there can be potential energy, as before, associated with M at the position of the center of mass. For example, the gravitational potential energy is M ghcm . ...
... • As the notion of potential energy comes from work performed by an external conservative force, there can be potential energy, as before, associated with M at the position of the center of mass. For example, the gravitational potential energy is M ghcm . ...
PHYS 1405 Sample Questions (1-4)
... As done in class, add the vectors in the force diagram shown below. Is the NetForce zero or non-zero? _____________ If the NetForce is not zero, draw the arrow representing its size and direction and label it “NetForce”. ...
... As done in class, add the vectors in the force diagram shown below. Is the NetForce zero or non-zero? _____________ If the NetForce is not zero, draw the arrow representing its size and direction and label it “NetForce”. ...