Work-Energy Principle
... Not conservative. m experiences same force as long as velocity is same. Position independent. The constant c meanst this is linear dashpot behavior. If all forces are potentiall or the ones that are not do work (e.g. always perpendicular to motion) we call the particle motion ”conservative” because ...
... Not conservative. m experiences same force as long as velocity is same. Position independent. The constant c meanst this is linear dashpot behavior. If all forces are potentiall or the ones that are not do work (e.g. always perpendicular to motion) we call the particle motion ”conservative” because ...
Cellular materials made of stacked tubes : influence of the
... 3. Experimental results The strains measured by both the strain gauge and the optical extensometer delivered the same measurements until the failure of the strain gauge. The stress time history shows high frequency oscillations for the tests performed at a displacement rate of 1m.s-1. These oscilla ...
... 3. Experimental results The strains measured by both the strain gauge and the optical extensometer delivered the same measurements until the failure of the strain gauge. The stress time history shows high frequency oscillations for the tests performed at a displacement rate of 1m.s-1. These oscilla ...
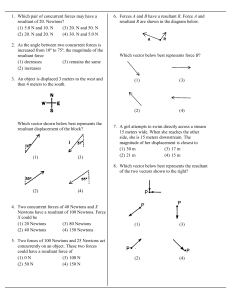
Physics B AP Review Packet: Mechanics Name
... Periodic motion described by sine or cosine function. Springs and pendulums are Simple Harmonic Oscillators (SHOs) that obey Hooke’s Law. Restoring Force (Hooke’s Law) F = -kx (negative sign indicates force is restoring) Restoring force is greatest at maximum displacement and zero at equilibrium Equ ...
... Periodic motion described by sine or cosine function. Springs and pendulums are Simple Harmonic Oscillators (SHOs) that obey Hooke’s Law. Restoring Force (Hooke’s Law) F = -kx (negative sign indicates force is restoring) Restoring force is greatest at maximum displacement and zero at equilibrium Equ ...
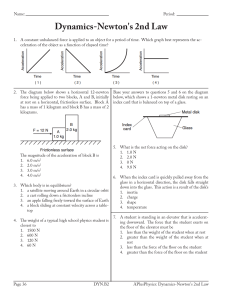
AP 1st Qtr Exam Review Key
... Analyze static situations involving friction to determine under what circumstances a body will start to slip, or to calculate the magnitude of the force of static friction. above problem address this Students should understand the effect of fluid friction on the motion of a body so they can: a. Find ...
... Analyze static situations involving friction to determine under what circumstances a body will start to slip, or to calculate the magnitude of the force of static friction. above problem address this Students should understand the effect of fluid friction on the motion of a body so they can: a. Find ...
Document
... A 2.5 kg box is released from rest 1.5 m above the ground and slides down a frictionless ramp. It slides across a floor that is frictionless, except for a small section 0.5 m wide that has a coefficient of kinetic friction of 0.2. At the left end, is a spring with spring constant 250 N/m. The box co ...
... A 2.5 kg box is released from rest 1.5 m above the ground and slides down a frictionless ramp. It slides across a floor that is frictionless, except for a small section 0.5 m wide that has a coefficient of kinetic friction of 0.2. At the left end, is a spring with spring constant 250 N/m. The box co ...
Identification of an average temperature and a dynamical
... We present a classical approach of a mixture of compressible fluids when each constituent has its own temperature. The introduction of an average temperature together with the entropy principle dictates the classical Fick law for diffusion and also novel constitutive equations associated with the di ...
... We present a classical approach of a mixture of compressible fluids when each constituent has its own temperature. The introduction of an average temperature together with the entropy principle dictates the classical Fick law for diffusion and also novel constitutive equations associated with the di ...
Work and Energy
... 2. In Part II you did work to stretch the spring. The graph of force vs. distance depends on the particular spring you used, but for most springs will be a straight line. This corresponds to Hooke’s law, or F = – kx, where F is the force applied by the spring when it is stretched a distance x. k is ...
... 2. In Part II you did work to stretch the spring. The graph of force vs. distance depends on the particular spring you used, but for most springs will be a straight line. This corresponds to Hooke’s law, or F = – kx, where F is the force applied by the spring when it is stretched a distance x. k is ...
Lecture18-11
... initial and final positions of the mass are the same (it ends up back at its original position), then the displacement is zero. ...
... initial and final positions of the mass are the same (it ends up back at its original position), then the displacement is zero. ...
Harmonic Oscillators and Sound Quiz
... 28. Using the graph of acceleration as a function of time for a harmonic oscillator. What is the equation for the velocity of the harmonic oscillator as a function of time? (Assume the velocity at time 0 is 0) a. V=.5sin(8t) ...
... 28. Using the graph of acceleration as a function of time for a harmonic oscillator. What is the equation for the velocity of the harmonic oscillator as a function of time? (Assume the velocity at time 0 is 0) a. V=.5sin(8t) ...