File
... • The amount of work done, force and distance are related by the equation: work done = force applied × distance moved in direction of force • Work done against frictional forces is mainly transformed into heat. • Elastic potential is the energy stored in an object when work is done on the object to ...
... • The amount of work done, force and distance are related by the equation: work done = force applied × distance moved in direction of force • Work done against frictional forces is mainly transformed into heat. • Elastic potential is the energy stored in an object when work is done on the object to ...
Slide 1
... How is Energy Related to Work? • Energy is defined as the ability to do work. Recall that work is the product of force and distance. If a force acts through a greater distance, it has done more work. You can use work to measure changes in energy. • Place two identical books on the table so there is ...
... How is Energy Related to Work? • Energy is defined as the ability to do work. Recall that work is the product of force and distance. If a force acts through a greater distance, it has done more work. You can use work to measure changes in energy. • Place two identical books on the table so there is ...
Name:
... Energy stored in flammable substances like wood. Released during a forest fire. Energy that can be released by changing the number of protons and neutrons in an atom. Energy associated with the velocity of an object. ...
... Energy stored in flammable substances like wood. Released during a forest fire. Energy that can be released by changing the number of protons and neutrons in an atom. Energy associated with the velocity of an object. ...
Document
... There are two TYPES of energy: potential and kinetic. Energy can’t be created or destroyed so we need to convert energy we have into what we need. The energy we use comes from many sources: Fossil fuel (coal, oil, natural gas), nuclear power, sun, wind, geothermal, hydropower. Most of this we conver ...
... There are two TYPES of energy: potential and kinetic. Energy can’t be created or destroyed so we need to convert energy we have into what we need. The energy we use comes from many sources: Fossil fuel (coal, oil, natural gas), nuclear power, sun, wind, geothermal, hydropower. Most of this we conver ...
Physics 100 prac exam2
... 32. An 80-kg football player travels to the left at 10 m/s and a 120-kg player on the opposite team travels to the right at 4.0 m/s. The total momentum is A. 240 kg m/s to the left. B. 320 kg m/s to the right. C. zero. D. 320 kg m/s to the left. E. 1280 kg m/s to the right. 33. A 25-kg child runs a ...
... 32. An 80-kg football player travels to the left at 10 m/s and a 120-kg player on the opposite team travels to the right at 4.0 m/s. The total momentum is A. 240 kg m/s to the left. B. 320 kg m/s to the right. C. zero. D. 320 kg m/s to the left. E. 1280 kg m/s to the right. 33. A 25-kg child runs a ...
2. Work, Energy and Power
... Potential Energy (U) :- The energy possessed by a body by virtue of its specific position or changed configuration is called potential energy. Eg:- A body placed at a height above the ground, a wound up watch spring, a compressed spring, a bent bow, a stretched rubber etc. Forms of potential energy ...
... Potential Energy (U) :- The energy possessed by a body by virtue of its specific position or changed configuration is called potential energy. Eg:- A body placed at a height above the ground, a wound up watch spring, a compressed spring, a bent bow, a stretched rubber etc. Forms of potential energy ...
Chapter 9 Motion and Energy
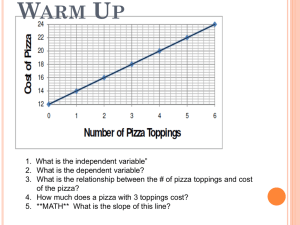
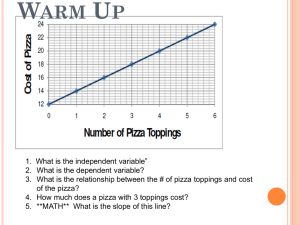
... The slope of a distance-versustime graph represents speed, that is, the rate that distance changes in relation to time. • Time is shown on the horizontal axis, or x-axis. • Distance, or position, is shown on the vertical axis, or y-axis. • A point on the line represents the distance an object has tr ...
... The slope of a distance-versustime graph represents speed, that is, the rate that distance changes in relation to time. • Time is shown on the horizontal axis, or x-axis. • Distance, or position, is shown on the vertical axis, or y-axis. • A point on the line represents the distance an object has tr ...
File
... Energy transformations also occur during projectile motion when an object moves in a curved path. However, the mechanical energy of the ball-Earth system remains constant as it rises and falls. ...
... Energy transformations also occur during projectile motion when an object moves in a curved path. However, the mechanical energy of the ball-Earth system remains constant as it rises and falls. ...
Conservation of Energy
... Mechanical Energy As the apple falls to the ground, its height decreases. Therefore, its GPE decreases. Potential energy that is dependent on height is called gravitational potential energy. The potential energy is not lost… it is converted into kinetic energy as the velocity of the apple inc ...
... Mechanical Energy As the apple falls to the ground, its height decreases. Therefore, its GPE decreases. Potential energy that is dependent on height is called gravitational potential energy. The potential energy is not lost… it is converted into kinetic energy as the velocity of the apple inc ...
Lesson 3: An Energy Mix Renewable and Nonrenewable Resources
... categorized as potential energy or having stored energy and require a chemical reaction to be used for our needs, whereas wind and hydropower are better classified under kinetic energy, and requires motion for us to utilize its energy. Utilizing the U.S. Energy Information Administration’s Energy Ki ...
... categorized as potential energy or having stored energy and require a chemical reaction to be used for our needs, whereas wind and hydropower are better classified under kinetic energy, and requires motion for us to utilize its energy. Utilizing the U.S. Energy Information Administration’s Energy Ki ...
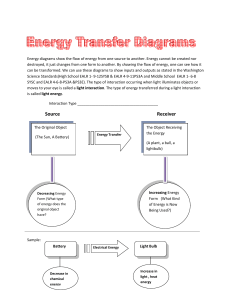
Energy Flow Introduction
... into work and heat. The work is used to carry on cell processes like growing, reproducing, moving molecules around, and getting rid of waste. The heat is a byproduct of the fuel "burning" process. Heat is always given off when fuel is burned, whether it is in a diesel engine or an animal cell. In an ...
... into work and heat. The work is used to carry on cell processes like growing, reproducing, moving molecules around, and getting rid of waste. The heat is a byproduct of the fuel "burning" process. Heat is always given off when fuel is burned, whether it is in a diesel engine or an animal cell. In an ...
Chapter 5 Work and Energy conclusion
... A ball is thrown upward with an initial speed v from the roof of a building. An identical ball is thrown downward with the same initial speed v. When the balls reach the ground, how do the kinetic energies of the two balls compare? Ignore air resistance effects. a) The kinetic energies of the two ba ...
... A ball is thrown upward with an initial speed v from the roof of a building. An identical ball is thrown downward with the same initial speed v. When the balls reach the ground, how do the kinetic energies of the two balls compare? Ignore air resistance effects. a) The kinetic energies of the two ba ...
P3 Forces for Transport
... For example, Rooney takes a free kick by kicking a stationary football with a force of 40N. If the ball has a mass of 0.5kg and his foot is in contact with the ball for 0.1s calculate: 1) The change in momentum of the ball (its impulse), 2) The speed the ball moves away with ...
... For example, Rooney takes a free kick by kicking a stationary football with a force of 40N. If the ball has a mass of 0.5kg and his foot is in contact with the ball for 0.1s calculate: 1) The change in momentum of the ball (its impulse), 2) The speed the ball moves away with ...