on-campus manual for Lab 8
... entertainment, and much more. Even though energy is said to be consumed, the truth is the energy was just converted to another form. For example, the plane started with thousands of gallons of fuel (chemical energy) that gets consumed in flight. However, that energy is not gone but remains as mostly ...
... entertainment, and much more. Even though energy is said to be consumed, the truth is the energy was just converted to another form. For example, the plane started with thousands of gallons of fuel (chemical energy) that gets consumed in flight. However, that energy is not gone but remains as mostly ...
Worked solutions Chapter 2: Collisions and
... p = mv = 1.0 103 × 10 = 1.0 104 kg m s–1 east For the station wagon: p = mv = 2.0 103 × 5.0 = 1.0 104 kg m s–1 west Total momentum = 1.0 104 kg m s–1 east + 1.0 104 kg m s–1 west = 0 p i = p f From Question 1c, p i = 0 so p f = 0 i.e. common velocity = 0 It hasn’t gone anywhere. The ...
... p = mv = 1.0 103 × 10 = 1.0 104 kg m s–1 east For the station wagon: p = mv = 2.0 103 × 5.0 = 1.0 104 kg m s–1 west Total momentum = 1.0 104 kg m s–1 east + 1.0 104 kg m s–1 west = 0 p i = p f From Question 1c, p i = 0 so p f = 0 i.e. common velocity = 0 It hasn’t gone anywhere. The ...
gravitational potential energy
... horizontal. Assuming that all three bears throw with the same speed, which rock will be traveling fastest when it hits the water?” Three students meet after the exam and discuss their answers. Emma: “Baby Bear’s rock will be going the fastest because it starts with a downward component of velocity.” ...
... horizontal. Assuming that all three bears throw with the same speed, which rock will be traveling fastest when it hits the water?” Three students meet after the exam and discuss their answers. Emma: “Baby Bear’s rock will be going the fastest because it starts with a downward component of velocity.” ...
Topic 10
... iii. The motion of the oscillator is then said to be steady-state motion. iv. In the steady state, the energy put into the system per cycle by the driving force equals the energy dissipated per cycle due to the damping. b. The amplitude, and therefore the energy, of a system in the steady state depe ...
... iii. The motion of the oscillator is then said to be steady-state motion. iv. In the steady state, the energy put into the system per cycle by the driving force equals the energy dissipated per cycle due to the damping. b. The amplitude, and therefore the energy, of a system in the steady state depe ...
Energy 1 Notes
... _______________________________ states that energy cannot be created or destroyed. It may be transformed from one form into another, but the total amount of energy _______________ changes. Energy can be changed from one form to another as follows: Mechanical energy transformations The mechanical ene ...
... _______________________________ states that energy cannot be created or destroyed. It may be transformed from one form into another, but the total amount of energy _______________ changes. Energy can be changed from one form to another as follows: Mechanical energy transformations The mechanical ene ...
Solution - American Association of Physics Teachers
... • Your answer to each question must be marked on the optical mark answer sheet. • Select the single answer that provides the best response to each question. Please be sure to use a No. 2 pencil and completely fill the box corresponding to your choice. If you change an answer, the previous mark must ...
... • Your answer to each question must be marked on the optical mark answer sheet. • Select the single answer that provides the best response to each question. Please be sure to use a No. 2 pencil and completely fill the box corresponding to your choice. If you change an answer, the previous mark must ...
Conservation of Energy - Bogazici University Physics Department
... A “physical system” consists of a well-defined set of bodies that are interacting by means of forces. Any bodies that lie outside the boundary of the system reside in the “surroundings”. A state of the system is a set of measurable physical quantities that completely characterize the system. Figure ...
... A “physical system” consists of a well-defined set of bodies that are interacting by means of forces. Any bodies that lie outside the boundary of the system reside in the “surroundings”. A state of the system is a set of measurable physical quantities that completely characterize the system. Figure ...
Do now! - mr badham`s physics locker
... Energy stored in 1 litre of petrol: Energy used by the human body for 1 day: Energy in a typical chocolate bar: Energy to boil 1 l of water, from freezing: Energy stored in a peanut: Kinetic energy of a fast-moving cricket ball: Energy stored in one new AA battery: Energy from burning one whole matc ...
... Energy stored in 1 litre of petrol: Energy used by the human body for 1 day: Energy in a typical chocolate bar: Energy to boil 1 l of water, from freezing: Energy stored in a peanut: Kinetic energy of a fast-moving cricket ball: Energy stored in one new AA battery: Energy from burning one whole matc ...
Introduction to Potential Energy Chapter 7 [ Edit ]
... Description: A m stone slides down a snowcovered hill (the figure ), leaving point A with a speed of v. There is no friction on the hill between points A and B, but there is friction on the level ground at the bottom of the hill, between B and the wall. After... A 10.0 kg stone slides down a snowc ...
... Description: A m stone slides down a snowcovered hill (the figure ), leaving point A with a speed of v. There is no friction on the hill between points A and B, but there is friction on the level ground at the bottom of the hill, between B and the wall. After... A 10.0 kg stone slides down a snowc ...
KE = ½ m v2
... electromagnetic energy - waves of electricity and magnetism, called electromagnetism. It is often called light. electron - negatively charged particles that orbit the nucleus of atoms. energy - in physics, work or the capacity for doing work. energy exchanges - process where energy changes or is rec ...
... electromagnetic energy - waves of electricity and magnetism, called electromagnetism. It is often called light. electron - negatively charged particles that orbit the nucleus of atoms. energy - in physics, work or the capacity for doing work. energy exchanges - process where energy changes or is rec ...
Lesson Plan Title: Transformations: The Many Forms of Energy
... followed by bubbles with examples, formulas, and SI units. In small groups, the students will be required to complete the L section of the KWL chart. They will use chart paper and a marker to report out to the whole class. Each student in the group will be assigned a role to ensure that everyone pa ...
... followed by bubbles with examples, formulas, and SI units. In small groups, the students will be required to complete the L section of the KWL chart. They will use chart paper and a marker to report out to the whole class. Each student in the group will be assigned a role to ensure that everyone pa ...
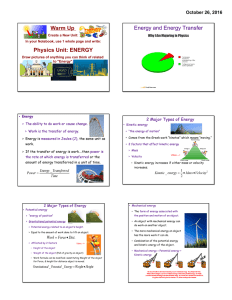
Warm Up Physics Unit: ENERGY Energy and Energy Transfer
... How much energy does different types of bouncy balls have? Which one is the bounciest? Let's find out! In your group, you will choose 3 types of bouncy balls to see which one has the most Gravitational potential energy. 1. First, you must know the mass of all 3 balls. 2. Then, you will calculate the ...
... How much energy does different types of bouncy balls have? Which one is the bounciest? Let's find out! In your group, you will choose 3 types of bouncy balls to see which one has the most Gravitational potential energy. 1. First, you must know the mass of all 3 balls. 2. Then, you will calculate the ...
















![Introduction to Potential Energy Chapter 7 [ Edit ]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/002485791_1-42fa032fe69c02e2c16b81d7409163a9-300x300.png)