forms of energy worksheet
... 1. Energy that is stored within an object is called ____________________ energy. 2. Compressed springs and stretched rubber bands store_______________________ energy. 3. The vibration and movements of the atoms and molecules within substances is called heat or ____________ energy. 4. The energy from ...
... 1. Energy that is stored within an object is called ____________________ energy. 2. Compressed springs and stretched rubber bands store_______________________ energy. 3. The vibration and movements of the atoms and molecules within substances is called heat or ____________ energy. 4. The energy from ...
What is Energy?
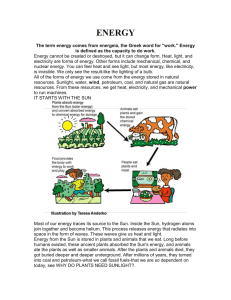
... change in itself or the world around it. Whenever work is done, energy is transformed or is transferred from one system to another. ...
... change in itself or the world around it. Whenever work is done, energy is transformed or is transferred from one system to another. ...
Slide 1
... 12.Which of the following is NOT true of kinetic energy? a.The faster something moves, the more kinetic energy it has b.The lower the mass is, the higher the kinetic energy c.Speed has a greater effect on kinetic energy than mass has ...
... 12.Which of the following is NOT true of kinetic energy? a.The faster something moves, the more kinetic energy it has b.The lower the mass is, the higher the kinetic energy c.Speed has a greater effect on kinetic energy than mass has ...
CONSERVATION OF MECHANICAL ENERGY (40 minutes) Exp
... In this exercise the student will verify that the total mechanical energy of a system is conserved, provided that the only forces doing work are conservative forces. Our system will be a particle swinging at the end of a string. Two forces act on the mass: Tension T, and weight W. Since T is always ...
... In this exercise the student will verify that the total mechanical energy of a system is conserved, provided that the only forces doing work are conservative forces. Our system will be a particle swinging at the end of a string. Two forces act on the mass: Tension T, and weight W. Since T is always ...
Name: Date: Chapter 8-Lesson 3-5: Energy Transformations and
... temperaturea measure of the average energy of motion of the particles of a substance Fahrenheit scaleThe temperature scale on which water freezes at 32 degrees and boils at 212 degrees Celsius scaleThe temperature scale on which water freezes at 0 degrees and boils at 100 degrees Kelvin scaleThe tem ...
... temperaturea measure of the average energy of motion of the particles of a substance Fahrenheit scaleThe temperature scale on which water freezes at 32 degrees and boils at 212 degrees Celsius scaleThe temperature scale on which water freezes at 0 degrees and boils at 100 degrees Kelvin scaleThe tem ...
Forces and COM - K
... Types of forces encountered by humans Force and motion relationships – Instantaneous effect – Newton’s law of acceleration (F=ma) – Force applied through time (Impulse-momentum) • Conservation of Momentum ...
... Types of forces encountered by humans Force and motion relationships – Instantaneous effect – Newton’s law of acceleration (F=ma) – Force applied through time (Impulse-momentum) • Conservation of Momentum ...
energy & energy transformations
... A 42 kg child runs and then slides 7.8m along an iced over pond. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the child's boots and the ice is 0.0050. a.) What is the force of kinetic friction acting on the child? b.) Calculate the work done by the kinetic ...
... A 42 kg child runs and then slides 7.8m along an iced over pond. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the child's boots and the ice is 0.0050. a.) What is the force of kinetic friction acting on the child? b.) Calculate the work done by the kinetic ...
Forces and COM - K
... • Identify Newton’s laws of motion and gravitation and describe practical illustrations of the laws • Explain what factors affect friction and discuss the role of friction in daily activities and sports • Define impulse and momentum and explain the relationship ...
... • Identify Newton’s laws of motion and gravitation and describe practical illustrations of the laws • Explain what factors affect friction and discuss the role of friction in daily activities and sports • Define impulse and momentum and explain the relationship ...
Kinetic and Potential Energy . ppt
... energy. You can’t run up the stairs (work) without energy! ...
... energy. You can’t run up the stairs (work) without energy! ...
Newtons 3 Laws of Motion - Saint Mary Catholic School
... What is the difference between potential energy and kinetic energy? ________________ When calculating a formula you are given g for gravity. What does g equal? _____________ What is gravity and how does the force of gravity affect objects on Earth and in our Solar System? ...
... What is the difference between potential energy and kinetic energy? ________________ When calculating a formula you are given g for gravity. What does g equal? _____________ What is gravity and how does the force of gravity affect objects on Earth and in our Solar System? ...
Energy Test Study Guide
... Explain the energy transformation between potential and kinetic energy o When juggling ...
... Explain the energy transformation between potential and kinetic energy o When juggling ...
THIS MS Word file
... Potential Energy, symbol U but then like force with a subscript for example Ug gravitational potential energy. There are other types of potential energy as well and we will discuss those as we go along. These are discussed in more detail below: Please read these notes and then complete the basic p ...
... Potential Energy, symbol U but then like force with a subscript for example Ug gravitational potential energy. There are other types of potential energy as well and we will discuss those as we go along. These are discussed in more detail below: Please read these notes and then complete the basic p ...