this powerpoint
... • Rayleigh (R) waves which are similar to ocean waves. These cause surface materials to move in a vertical circle just as a floating object would move as a sea wave passes under it. These waves are responsible for most of the damage to buildings. ...
... • Rayleigh (R) waves which are similar to ocean waves. These cause surface materials to move in a vertical circle just as a floating object would move as a sea wave passes under it. These waves are responsible for most of the damage to buildings. ...
Unit 3 - Mahalakshmi Engineering College
... (iii) Deep-focus earthquake: Here, the point of origin of the seismic wave is at a depth of greater than 300 km. 18. What is Seismograph? Seismograph is an instrument used to recording motions of the earth’s surface caused by seismic waves, as a function of time. A modern seismograph includes five b ...
... (iii) Deep-focus earthquake: Here, the point of origin of the seismic wave is at a depth of greater than 300 km. 18. What is Seismograph? Seismograph is an instrument used to recording motions of the earth’s surface caused by seismic waves, as a function of time. A modern seismograph includes five b ...
CPS Physics Final Study Guide site
... 42. What motion(s) would you see if the forces on an object are balanced? (constant speed, acceleration, at rest) 43. What motion(s) would you see if the forces on an object are unbalanced? (constant speed, acceleration, at rest) 44. What is Newton’s second law? ...
... 42. What motion(s) would you see if the forces on an object are balanced? (constant speed, acceleration, at rest) 43. What motion(s) would you see if the forces on an object are unbalanced? (constant speed, acceleration, at rest) 44. What is Newton’s second law? ...
8th grade Energy, Force and Motion Quiz 4 (M) Newton`s Laws of
... 2. Newton’s first law is also called the Law of __________________ because it says that objects resist changes in their motion. 3. A rocket with less _________ will have a greater acceleration during launch. 4.You need more __________ to accelerate when you have a larger mass. Multiple Choice 1. New ...
... 2. Newton’s first law is also called the Law of __________________ because it says that objects resist changes in their motion. 3. A rocket with less _________ will have a greater acceleration during launch. 4.You need more __________ to accelerate when you have a larger mass. Multiple Choice 1. New ...
Chapter 8 Earthquakes and Earth’s Interior
... reaching the surface Travel more slowly than body waves Move up-and-down and well as side to side Usually much larger than body waves, so they are the most destructive ...
... reaching the surface Travel more slowly than body waves Move up-and-down and well as side to side Usually much larger than body waves, so they are the most destructive ...
MYSTERIES OF PLANET EARTH
... composed of elastic/plastic solids; Changes in P& S-wave velocities reveal mantle layers; Pwave velocity from Moho to Asthenosphere: 88.3 km/s; P-wave velocity in Asthenosphere: < 8 km/s; Asthenosphere is partially molten because of unique temperature and pressure combination Transition Zone: Belo ...
... composed of elastic/plastic solids; Changes in P& S-wave velocities reveal mantle layers; Pwave velocity from Moho to Asthenosphere: 88.3 km/s; P-wave velocity in Asthenosphere: < 8 km/s; Asthenosphere is partially molten because of unique temperature and pressure combination Transition Zone: Belo ...
Name
... 2. What did Galileo learn from his “leaning tower of Pisa” experiment? 3. In Galileo’s Inclined plane experiment, He discovered If there is NO _______________, then NO _____________ are required to keep an object in motion. 4. An astronaut in outerspace away from frictional or gravitational forces t ...
... 2. What did Galileo learn from his “leaning tower of Pisa” experiment? 3. In Galileo’s Inclined plane experiment, He discovered If there is NO _______________, then NO _____________ are required to keep an object in motion. 4. An astronaut in outerspace away from frictional or gravitational forces t ...
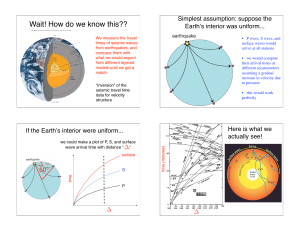
Wait! How do we know this??
... We get this picture by calculating arrival times for all seismic phases in a stratified model of the Earth, and making sure they match the observed arrival times at all points on the Earth ...
... We get this picture by calculating arrival times for all seismic phases in a stratified model of the Earth, and making sure they match the observed arrival times at all points on the Earth ...
Earthquakes PowerPoint
... rupture - breakage and fracturing of the rock, causing an earthquake. ...
... rupture - breakage and fracturing of the rock, causing an earthquake. ...
center of mass
... integration expression, but not to evaluate it, however… we’ll look at how to do it… ...
... integration expression, but not to evaluate it, however… we’ll look at how to do it… ...
Newton’s Laws of Motion - Montville Township School District
... Because of inertia, objects (including you) resist changes in their motion. When the car going 80 km/hour is stopped by the brick wall, your body keeps moving at 80 m/hour. ...
... Because of inertia, objects (including you) resist changes in their motion. When the car going 80 km/hour is stopped by the brick wall, your body keeps moving at 80 m/hour. ...
Newtons Laws - Cardinal Newman High School
... For example: When you kick a soccer ball, do you feel anything in your foot? ...
... For example: When you kick a soccer ball, do you feel anything in your foot? ...
Standard EPS Shell Presentation
... Show how force is required to change the motion of an object. Use a graph to identify the relationships between variables. Explain and discuss Newton's second law and the relationship between force, mass and acceleration. Describe how changing the mass of the ca affects its ...
... Show how force is required to change the motion of an object. Use a graph to identify the relationships between variables. Explain and discuss Newton's second law and the relationship between force, mass and acceleration. Describe how changing the mass of the ca affects its ...
Earthquakes
... Seismic Waves • Surface waves – Seismic waves that travel along the surface of the Earth. Slowest moving waves collectively referred to as L or Long waves. • Love waves - transverse side-to-side wave motion in a horizontal plane parallel to Earth’s surface. • Rayleigh waves - backward rotating, cir ...
... Seismic Waves • Surface waves – Seismic waves that travel along the surface of the Earth. Slowest moving waves collectively referred to as L or Long waves. • Love waves - transverse side-to-side wave motion in a horizontal plane parallel to Earth’s surface. • Rayleigh waves - backward rotating, cir ...
laws of motion - WordPress.com
... Exercise: Law of acceleration 1. The combined mass of a stretcher & a patient is 100 kg. If the force applied in pushing the stretcher carrying the patient is 300 N then what is the acceleration of the stretcher? 2. The acceleration of a stretcher towards the emergency room is 1.2 m/s2. Find the fo ...
... Exercise: Law of acceleration 1. The combined mass of a stretcher & a patient is 100 kg. If the force applied in pushing the stretcher carrying the patient is 300 N then what is the acceleration of the stretcher? 2. The acceleration of a stretcher towards the emergency room is 1.2 m/s2. Find the fo ...
Document
... wapparent = wreal – ma The apparent weight of a mass m is its real weight minus its mass times the acceleration of the frame (vector addition). In outer space, where wreal = 0, wapparent = – ma ...
... wapparent = wreal – ma The apparent weight of a mass m is its real weight minus its mass times the acceleration of the frame (vector addition). In outer space, where wreal = 0, wapparent = – ma ...