Insert Figure 4.1 from Force and Motion book
... quantity that goes factor, such as changes but on the right side of 2.2 pounds per your mass F=ma. Weight is a kilogram. remains the force, and it goes on same. the left side of F=ma. ...
... quantity that goes factor, such as changes but on the right side of 2.2 pounds per your mass F=ma. Weight is a kilogram. remains the force, and it goes on same. the left side of F=ma. ...
mass wasting
... The downslope movement of surface material under the direct influence of gravity is called "Mass Wasting." Mass wasting plays a vital role in transferring the products of weathering from their original sites to lower lying places where the agents of erosion can pick them up for transporting a longer ...
... The downslope movement of surface material under the direct influence of gravity is called "Mass Wasting." Mass wasting plays a vital role in transferring the products of weathering from their original sites to lower lying places where the agents of erosion can pick them up for transporting a longer ...
Seism shop
... Fund for providing facilities and generous funding to make this event possible. The Seismology Student Workshop is an event designed by graduate students, for graduate students. We aim to foster a convivial environment where young researchers connect with peers in their field and present active rese ...
... Fund for providing facilities and generous funding to make this event possible. The Seismology Student Workshop is an event designed by graduate students, for graduate students. We aim to foster a convivial environment where young researchers connect with peers in their field and present active rese ...
Volcanoes and Igneous Activity Earth
... • Three station recordings are needed to locate an epicenter • Circle equal to the epicenter distance is drawn around each station • Point where three circles intersect is the epicenter ...
... • Three station recordings are needed to locate an epicenter • Circle equal to the epicenter distance is drawn around each station • Point where three circles intersect is the epicenter ...
Newton`s Laws of Motion
... Acceleration= Net Force/ Mass Acceleration is measured in meter per second per second (m/s²) ...
... Acceleration= Net Force/ Mass Acceleration is measured in meter per second per second (m/s²) ...
Juniata College Shake, Rattle, and Roll Earthquake Board and
... Tsunami - A tsunami is a series of very long wavelength ocean waves caused by the sudden displacement of water by earthquakes, landslides, or submarine slumps. Ordinarily, tsunamis are produced only by earthquakes exceeding magnitude 7.5. In the open ocean, tsunami waves travel at speeds of 600-800 ...
... Tsunami - A tsunami is a series of very long wavelength ocean waves caused by the sudden displacement of water by earthquakes, landslides, or submarine slumps. Ordinarily, tsunamis are produced only by earthquakes exceeding magnitude 7.5. In the open ocean, tsunami waves travel at speeds of 600-800 ...
Gravity, Weight, Mass, Falling Objects, and Centripetal Force
... exerted on an object by the Earth. Weight is a force, and mass is a measure of the amount of matter an object contains. Your mass is the same no matter where in the universe you are, but your weight will vary because of gravity. ...
... exerted on an object by the Earth. Weight is a force, and mass is a measure of the amount of matter an object contains. Your mass is the same no matter where in the universe you are, but your weight will vary because of gravity. ...
Non-Inertial Frames
... We are now going to discuss accelerating frames where the non-inertial frame is rotating (relative to the inertial frames). Before we can discuss these, we must introduce some concepts and notation for handling rotation. Many rotation problems involve axes fixed in a rigid body (e.g. the rotation of ...
... We are now going to discuss accelerating frames where the non-inertial frame is rotating (relative to the inertial frames). Before we can discuss these, we must introduce some concepts and notation for handling rotation. Many rotation problems involve axes fixed in a rigid body (e.g. the rotation of ...
Section 2-1 chapter 2
... Friction: A force opposing motion a. Whenever 2 forces touch, there is friction b. Friction will cause an object to slow down and finally stop c. The amount of friction depends on how hard the surface is and the material that the object is made of. d. Friction moves in the opposite direction of the ...
... Friction: A force opposing motion a. Whenever 2 forces touch, there is friction b. Friction will cause an object to slow down and finally stop c. The amount of friction depends on how hard the surface is and the material that the object is made of. d. Friction moves in the opposite direction of the ...
2016 sample exam
... new equations of motion for the coupled circuits. (iv) Now suppose that we let the resistance R2 → ∞. Show from the equations of motion that the current in circuit 2 is then zero, so that the charge Q2 is frozen to be Q̄2 for all time. Then from this write down the equation of motion for the charge ...
... new equations of motion for the coupled circuits. (iv) Now suppose that we let the resistance R2 → ∞. Show from the equations of motion that the current in circuit 2 is then zero, so that the charge Q2 is frozen to be Q̄2 for all time. Then from this write down the equation of motion for the charge ...
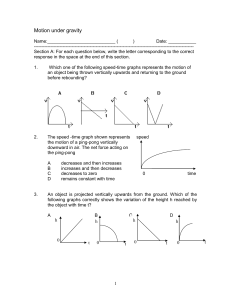
Quiz on Motion under gravity
... The acceleration of the object decreases as the object rises up; The acceleration is positive for the upward motion and negative for the downward motion; At maximum height, the velocity of the object is zero; If air resistance is negligible, the time for the upward motion is equal to the time for th ...
... The acceleration of the object decreases as the object rises up; The acceleration is positive for the upward motion and negative for the downward motion; At maximum height, the velocity of the object is zero; If air resistance is negligible, the time for the upward motion is equal to the time for th ...
Car Push Lab - SchemmScience.com
... Bathroom Scale (calibrated in Newtons) Discussion: Newton was the first to realize that the acceleration produced when we move something depends not only on how hard we push or pull, but also on the object’s mass. He devised one of the most important rules of nature ever proposed, his second law of ...
... Bathroom Scale (calibrated in Newtons) Discussion: Newton was the first to realize that the acceleration produced when we move something depends not only on how hard we push or pull, but also on the object’s mass. He devised one of the most important rules of nature ever proposed, his second law of ...