
Physics Worksheet Work and Energy
... 7. An escalator is used to move 20 passengers every minute from the first floor of a department store to the second. The second floor is located 5-meters above the first floor. The average passenger's mass is 60 kg. Determine the power requirement of the escalator in order to move this number of pas ...
... 7. An escalator is used to move 20 passengers every minute from the first floor of a department store to the second. The second floor is located 5-meters above the first floor. The average passenger's mass is 60 kg. Determine the power requirement of the escalator in order to move this number of pas ...
F - coach iwan
... – Attractive forces exist between bodies (e.g. a body and the Earth) that are proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the distance between them ...
... – Attractive forces exist between bodies (e.g. a body and the Earth) that are proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the distance between them ...
NEWTONS LAW`S OF MOTION
... velocity (acceleration )of an object is proportional to the force and in the direction of force. • Similarly it takes less stopping force to stop an object moving with less velocity (acceleration) ...
... velocity (acceleration )of an object is proportional to the force and in the direction of force. • Similarly it takes less stopping force to stop an object moving with less velocity (acceleration) ...
Earthquakes
... S waves, but they can produce violent ground movements Some of them make the ground roll like ocean waves Other surface waves move buildings from side to side ...
... S waves, but they can produce violent ground movements Some of them make the ground roll like ocean waves Other surface waves move buildings from side to side ...
AAAAA
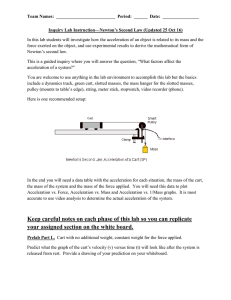
... This is a guided inquiry where you will answer the question, “What factors affect the acceleration of a system?” You are welcome to use anything in the lab environment to accomplish this lab but the basics include a dynamics track, green cart, slotted masses, the mass hanger for the slotted masses, ...
... This is a guided inquiry where you will answer the question, “What factors affect the acceleration of a system?” You are welcome to use anything in the lab environment to accomplish this lab but the basics include a dynamics track, green cart, slotted masses, the mass hanger for the slotted masses, ...
Newton`s Three Laws
... If the force from the Earth moves the apple, why doesn’t the Earth move? • The force on the apple is large compared to the small mass of an apple. • Therefore, the apple accelerates with a big acceleration I’m so little I have large acceleration! ...
... If the force from the Earth moves the apple, why doesn’t the Earth move? • The force on the apple is large compared to the small mass of an apple. • Therefore, the apple accelerates with a big acceleration I’m so little I have large acceleration! ...
Practice Questions on Forces and Velocity
... d. None of the above 6. Burl and Paul have a total weight of 1300 N. The tensions in the ropes that support the scaffold they stand on add to 1700 N. The weight of the scaffold itself must be: (400N) 7. When you stand at rest on a pair of bathroom scales, the readings on the scales will always a. ea ...
... d. None of the above 6. Burl and Paul have a total weight of 1300 N. The tensions in the ropes that support the scaffold they stand on add to 1700 N. The weight of the scaffold itself must be: (400N) 7. When you stand at rest on a pair of bathroom scales, the readings on the scales will always a. ea ...
7-8 Center of Mass In - mrhsluniewskiscience
... 7-8 Center of Mass (CM) Practice Problem Example 7-12: CM of three guys on a raft. Three people of roughly equal masses m on a lightweight (air-filled) banana boat sit along the x axis at positions xA = 1.0 m, xB = 5.0 m, and xC = 6.0 m, measured from the left-hand end. Find the position of the CM. ...
... 7-8 Center of Mass (CM) Practice Problem Example 7-12: CM of three guys on a raft. Three people of roughly equal masses m on a lightweight (air-filled) banana boat sit along the x axis at positions xA = 1.0 m, xB = 5.0 m, and xC = 6.0 m, measured from the left-hand end. Find the position of the CM. ...
Ch. 22.5 EQ study guide
... •Deaths & Injuries – but mostly from collapsing structures •Damage to buildings & structures (collapse) •Underground water and gas pipes break – floods & fires ...
... •Deaths & Injuries – but mostly from collapsing structures •Damage to buildings & structures (collapse) •Underground water and gas pipes break – floods & fires ...
Forces and Motion Lab Results Example
... 1. What happens to the bubble when the bottle starts to move? Why? What happens to the bubble when the bottle slows down? Why? a. The bubble initially moves in the same direction as that of the force applied to the car. If the force is forward, the bubble moves forward initially. Once the car has ma ...
... 1. What happens to the bubble when the bottle starts to move? Why? What happens to the bubble when the bottle slows down? Why? a. The bubble initially moves in the same direction as that of the force applied to the car. If the force is forward, the bubble moves forward initially. Once the car has ma ...
Newtons 3 Laws of Motion - Saint Mary Catholic School
... Acceleration – change in velocity over time Motion – an object changing position or distance in time Rate of Change – amount of time it takes to change position or motion Inertia - tendency of a still object to stay still or miving object to keep moving unless acted on by an unbalanced force Force – ...
... Acceleration – change in velocity over time Motion – an object changing position or distance in time Rate of Change – amount of time it takes to change position or motion Inertia - tendency of a still object to stay still or miving object to keep moving unless acted on by an unbalanced force Force – ...
Kinematics - Gymnázium Slovanské náměstí
... If there is a frame of reference at rest or in uniform rectilinear motion relative (with respect) to an inertial frame of reference, then it is inertial too! So a train going at constant velocity (at constant speed on a straight track) can be taken as an inertial frame of reference ...
... If there is a frame of reference at rest or in uniform rectilinear motion relative (with respect) to an inertial frame of reference, then it is inertial too! So a train going at constant velocity (at constant speed on a straight track) can be taken as an inertial frame of reference ...
Lecture-VII
... An empty coal car of mass m0 starts from rest under an applied force of magnitude F . At the same time coal begins to run into the car at a steady rate b from a coal hopper at rest along the track. Find the speed when a mass mc of coal has been transferred. Because the falling coal does not have any ...
... An empty coal car of mass m0 starts from rest under an applied force of magnitude F . At the same time coal begins to run into the car at a steady rate b from a coal hopper at rest along the track. Find the speed when a mass mc of coal has been transferred. Because the falling coal does not have any ...
Newton`s Second Law
... Newton’s second law states that the acceleration of an object is directly related to the force on it, and inversely related to the mass of the object. You need more force to move or stop an object with a lot of mass (or inertia) than you need for an object with less mass. The formula for the sec ...
... Newton’s second law states that the acceleration of an object is directly related to the force on it, and inversely related to the mass of the object. You need more force to move or stop an object with a lot of mass (or inertia) than you need for an object with less mass. The formula for the sec ...
Potential Energy - McMaster University
... 2) A paddler in a stationary canoe (floating on the water, no friction) walks from the rear seat to the front seat. The CM of the canoe plus paddler moves relative to the canoe, but not relative to the land (the canoe moves backwards). Here there is no external force. ...
... 2) A paddler in a stationary canoe (floating on the water, no friction) walks from the rear seat to the front seat. The CM of the canoe plus paddler moves relative to the canoe, but not relative to the land (the canoe moves backwards). Here there is no external force. ...



















![PhysRozz Midterm 2012 [via06-07] Version 18](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/014722455_1-33f5b15b25beb94441904fea997b655c-300x300.png)

