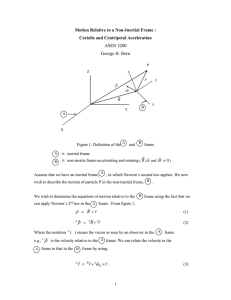
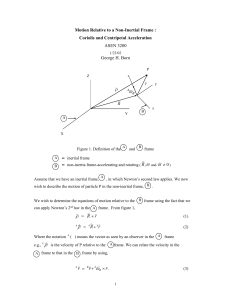
m/s
... are not moving. (Couch Potato) Sliding Friction - force that opposes the direction of motion of an object as it slides over a surface. (Ice skating or bobsledding) Rolling Friction – friction force that acts on ...
... are not moving. (Couch Potato) Sliding Friction - force that opposes the direction of motion of an object as it slides over a surface. (Ice skating or bobsledding) Rolling Friction – friction force that acts on ...
Managing Acceleration
... F – Force m – mass (how much matter or atoms make up the object) a – acceleration (rate at which speed or direction changes) ...
... F – Force m – mass (how much matter or atoms make up the object) a – acceleration (rate at which speed or direction changes) ...
what is a force?
... diameter, and a steel ball the size of a baseball has more mass than both balls. ...
... diameter, and a steel ball the size of a baseball has more mass than both balls. ...
the january 25th, 1999 earthquake in the coffee growing region of
... near the epicentre recorded the main shock in three-component digital recorders. Figure 8 shows an isoacceleration map for the area. Readings for peak accelerations decrease rapidly. Hence, 50 km away from the epicentre, peak accelerations as low as 50 gals were found [INGEOMINAS, 1999a]. In the cit ...
... near the epicentre recorded the main shock in three-component digital recorders. Figure 8 shows an isoacceleration map for the area. Readings for peak accelerations decrease rapidly. Hence, 50 km away from the epicentre, peak accelerations as low as 50 gals were found [INGEOMINAS, 1999a]. In the cit ...
Mass - Effingham County Schools
... (mathematic principles of natural philosophy) in 1687. Today these laws are known as Newton’s Laws of Motion and describe the motion of all objects on the scale we experience in our everyday lives. ...
... (mathematic principles of natural philosophy) in 1687. Today these laws are known as Newton’s Laws of Motion and describe the motion of all objects on the scale we experience in our everyday lives. ...
Friction, Work, and Energy in the Inclined Plane
... A machine can be defined as any device that multiplies forces or changes the direction of forces in order to do work. Consider the machine in figure II, which shows a system of two masses connected by a pulley, where work done on m 2 is used to lift m 1 up the plane. For the object with a given mass ...
... A machine can be defined as any device that multiplies forces or changes the direction of forces in order to do work. Consider the machine in figure II, which shows a system of two masses connected by a pulley, where work done on m 2 is used to lift m 1 up the plane. For the object with a given mass ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Newton’s Laws of Motion
... takes a large force to change their motion. Once they are moving, it takes a large force to stop them. ...
... takes a large force to change their motion. Once they are moving, it takes a large force to stop them. ...
Tri A Final Review Packet
... a) How long does it take for the swimmer to cross the river?__________ b) If the current pushes the swimmer downstream at 6 m/s, how far down river will the swimmer be when they reach the other side? ___________ ...
... a) How long does it take for the swimmer to cross the river?__________ b) If the current pushes the swimmer downstream at 6 m/s, how far down river will the swimmer be when they reach the other side? ___________ ...
Force and Motion Force: a push or a pull that causes a change in
... 1) Friction: A force that resists the motion of 2 surfaces/objects touching each other; slows down or prevents motion. Example: car tires on a road surface 2) Gravity: Force of attraction between 2 or more objects; Weight is a measure of the force of gravity on an object. Rate of acceleration (fre ...
... 1) Friction: A force that resists the motion of 2 surfaces/objects touching each other; slows down or prevents motion. Example: car tires on a road surface 2) Gravity: Force of attraction between 2 or more objects; Weight is a measure of the force of gravity on an object. Rate of acceleration (fre ...
Physics Review #1
... If the direction of a moving car changes and its speed remains constant, which quantity must remain the same? (A) velocity (B) displacement (C) momentum (D) kinetic energy ...
... If the direction of a moving car changes and its speed remains constant, which quantity must remain the same? (A) velocity (B) displacement (C) momentum (D) kinetic energy ...
Examine the forces exerted on objects by gravity
... On Uranus (8) the mass of 16kg = On Neptune (11) the mass of 11kg = On Pluto (0.4) the mass of 50kg = On Mercury (3) the mass of 70kg = On Venus (9) the mass of 45kg = On Earth (10) the mass of 12kg = On Mars (4) the mass of 60kg = On Jupiter (23) the mass of 5kg = On Saturn (9) the mass of 52kg = O ...
... On Uranus (8) the mass of 16kg = On Neptune (11) the mass of 11kg = On Pluto (0.4) the mass of 50kg = On Mercury (3) the mass of 70kg = On Venus (9) the mass of 45kg = On Earth (10) the mass of 12kg = On Mars (4) the mass of 60kg = On Jupiter (23) the mass of 5kg = On Saturn (9) the mass of 52kg = O ...