Problem Set #2a
... can be used in any one of the four vertical equations, and Vh is used in the horizontal equation (Dh = Vh * time). 10.) It doesn’t. Acceleration only effects an objects vertical motion, and neglecting air resistance leaves no forces in the horizontal direction to effect motion. 11.) Because looking ...
... can be used in any one of the four vertical equations, and Vh is used in the horizontal equation (Dh = Vh * time). 10.) It doesn’t. Acceleration only effects an objects vertical motion, and neglecting air resistance leaves no forces in the horizontal direction to effect motion. 11.) Because looking ...
Widely separated binary systems of very low mass stars Phan Bao
... frame. + We choose the ground to be our inertial frame (stationary), so using Newton’s second law for the passenger with a mass m : ...
... frame. + We choose the ground to be our inertial frame (stationary), so using Newton’s second law for the passenger with a mass m : ...
Conceptual Physics
... 12. y-axis 38. vertical component 60. inelastic collision 13. slope 39. range 61. system 14. scalar 40. inertia 62. law of conservation of 15. vector 41. mass momentum 16. magnitude 42. force 63. energy 17. relative 43. net force 64. kinetic energy 18. frame of reference 44. balanced forces 65. pote ...
... 12. y-axis 38. vertical component 60. inelastic collision 13. slope 39. range 61. system 14. scalar 40. inertia 62. law of conservation of 15. vector 41. mass momentum 16. magnitude 42. force 63. energy 17. relative 43. net force 64. kinetic energy 18. frame of reference 44. balanced forces 65. pote ...
Dynamics Rewrite Problems 1. A 0.40 kg toy car moves at constant
... 1. A 0.40 kg toy car moves at constant acceleration of 2.3 m/s 2. Determine the net applied force that is responsible for that acceleration. 2. If a net horizontal force of 175 N is applied to a bike whose mass is 43.0 kg what acceleration is produced? 3. What average net force is required to stop a ...
... 1. A 0.40 kg toy car moves at constant acceleration of 2.3 m/s 2. Determine the net applied force that is responsible for that acceleration. 2. If a net horizontal force of 175 N is applied to a bike whose mass is 43.0 kg what acceleration is produced? 3. What average net force is required to stop a ...
Newton`s laws - netBlueprint.net
... “To every action (force) there is always opposed an equal reaction (force): or, the mutual actions of two bodies upon each other are always equal, and directed to contrary parts. ” ...
... “To every action (force) there is always opposed an equal reaction (force): or, the mutual actions of two bodies upon each other are always equal, and directed to contrary parts. ” ...
Air Pressure, Forces, and Motion
... of uniform motion in a straight line, unless it is compelled to change that state by forces impressed upon it. acceleration = 0.0 unless the objected is acted on by an unbalanced force ...
... of uniform motion in a straight line, unless it is compelled to change that state by forces impressed upon it. acceleration = 0.0 unless the objected is acted on by an unbalanced force ...
Insurance Portfolio Analysis
... An insurance portfolio means a set of policies retained by an insurance company. The estimation of payment for the entire portfolio is one of the most important issues for an insurance company. In general, when the numbers of polices is large the total amount of the payment for the portfolio converg ...
... An insurance portfolio means a set of policies retained by an insurance company. The estimation of payment for the entire portfolio is one of the most important issues for an insurance company. In general, when the numbers of polices is large the total amount of the payment for the portfolio converg ...
PDF#10
... A friction force between two objects in contact opposes the sliding of one object over the surface of the adjacent one. It is tangent to the surface of the adjacent object and opposite in direction to the velocity of the moving object. The magnitude of the frictional force is assumed to be proportio ...
... A friction force between two objects in contact opposes the sliding of one object over the surface of the adjacent one. It is tangent to the surface of the adjacent object and opposite in direction to the velocity of the moving object. The magnitude of the frictional force is assumed to be proportio ...
5. Forces and Motion-I Newton's First Law:
... e.g. a powerless spacecraft far away from all planets (good example) or close to the surface of the Earth (good approximation). Any frame that ...
... e.g. a powerless spacecraft far away from all planets (good example) or close to the surface of the Earth (good approximation). Any frame that ...
Ballistic Pendulum
... 2. Prepare the ballistic pendulum for firing and measure the height of the pendulum from its center of mass (CM). Let this height be the reference height (h = 0). If your pendulum can be measured in degrees of swing, then record the starting angle. 2. Fire the projectile, then record the Δh of the p ...
... 2. Prepare the ballistic pendulum for firing and measure the height of the pendulum from its center of mass (CM). Let this height be the reference height (h = 0). If your pendulum can be measured in degrees of swing, then record the starting angle. 2. Fire the projectile, then record the Δh of the p ...
Kinematics Multiples
... d. independent of amplitude and never greater than for spring 1. e. independent of amplitude and never less than for spring 1. *A. This one is tricky. Because the spring is nonlinear, the solution to the differential equation is not a sine function and the period does depend on the amplitude. If you ...
... d. independent of amplitude and never greater than for spring 1. e. independent of amplitude and never less than for spring 1. *A. This one is tricky. Because the spring is nonlinear, the solution to the differential equation is not a sine function and the period does depend on the amplitude. If you ...
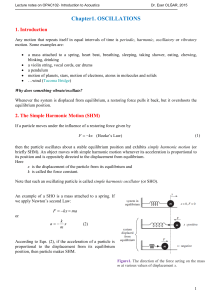
Chapter1. OSCILLATIONS
... We know that in reality, a spring won't oscillate for ever. Frictional forces will diminish the amplitude of oscillation until eventually the system is at rest. When dissipative forces such as friction are not negligible, the amplitude of oscillations will decrease with time. The oscillations are da ...
... We know that in reality, a spring won't oscillate for ever. Frictional forces will diminish the amplitude of oscillation until eventually the system is at rest. When dissipative forces such as friction are not negligible, the amplitude of oscillations will decrease with time. The oscillations are da ...