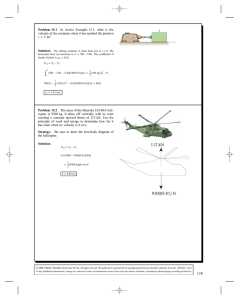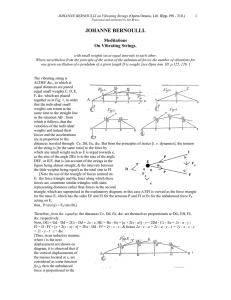
Chapter 14
... stretched from its equilibrium position. Not all springs obey Hooke’s law, but many do. Those that do are called elastic. Potential energy When a force is applied to stretch a spring, such as by hanging an object on its end, there is a direct linear relationship between the exerted force and the dis ...
... stretched from its equilibrium position. Not all springs obey Hooke’s law, but many do. Those that do are called elastic. Potential energy When a force is applied to stretch a spring, such as by hanging an object on its end, there is a direct linear relationship between the exerted force and the dis ...
Mass times velocity.
... What we now call momentum, Newton referred to as “quantity of motion.” The linear momentum of an object equals the product of its mass and velocity. (In this chapter, we focus on linear momentum. Angular momentum, or momentum due to rotation, is a topic in another chapter.) Momentum is a useful conc ...
... What we now call momentum, Newton referred to as “quantity of motion.” The linear momentum of an object equals the product of its mass and velocity. (In this chapter, we focus on linear momentum. Angular momentum, or momentum due to rotation, is a topic in another chapter.) Momentum is a useful conc ...
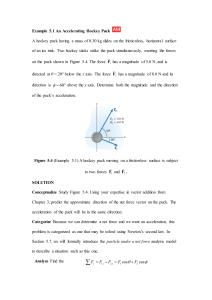
Example 5.1 An Accelerating Hockey Puck A hockey puck having a
... Finalize Note that the acceleration component ax is independent of the mass of the car! It depends only on the angle of inclination and on g. From Equation (2), we conclude that the component of Fg perpendicular to the incline is balanced by the normal force; that is, n = mg cos θ. This situation is ...
... Finalize Note that the acceleration component ax is independent of the mass of the car! It depends only on the angle of inclination and on g. From Equation (2), we conclude that the component of Fg perpendicular to the incline is balanced by the normal force; that is, n = mg cos θ. This situation is ...
CHAPTER 17 - The Sine and Cosine Function
... more confusion to your understanding of Sines and Cosines. At such a point your mind must have justifiably asked, . What do Indian Tribal Chiefs and Circles have to do with the study of the Sine function, a function whose application arises everywhere from the ten second swaying period of the Worlds ...
... more confusion to your understanding of Sines and Cosines. At such a point your mind must have justifiably asked, . What do Indian Tribal Chiefs and Circles have to do with the study of the Sine function, a function whose application arises everywhere from the ten second swaying period of the Worlds ...
m/s - James M. Hill High School
... 12. A 14.7 kg box is pressed up against the wall using an applied force of 600 N. For the box not to fall, calculate the minimum coefficient of static friction necessary between the wall and the box. (0.24) 13. A 22 kg box held up against a wall. The coefficients of friction are µs = 0.39 and µk = 0 ...
... 12. A 14.7 kg box is pressed up against the wall using an applied force of 600 N. For the box not to fall, calculate the minimum coefficient of static friction necessary between the wall and the box. (0.24) 13. A 22 kg box held up against a wall. The coefficients of friction are µs = 0.39 and µk = 0 ...
Ch 10 Solutions Glencoe 2013
... 36. A satellite orbits Earth in a circular orbit. Does Earth’s gravity do work on the satellite? Explain. SOLUTION: No, the force of gravity is directed toward Earth and is perpendicular to the direction of displacement of the satellite. 37. An object slides at constant speed on a frictionless sur ...
... 36. A satellite orbits Earth in a circular orbit. Does Earth’s gravity do work on the satellite? Explain. SOLUTION: No, the force of gravity is directed toward Earth and is perpendicular to the direction of displacement of the satellite. 37. An object slides at constant speed on a frictionless sur ...
Problem 15.1 In Active Example 15.1, what is the velocity of the
... Problem 15.17 At the instant shown, the 160-N vaulter’s center of mass is 8.5 m above the ground, and the vertical component of his velocity is 4 m/s. As his pole straightens, it exerts a vertical force on the vaulter of magnitude 180 + 2.8y 2 N, where y is the vertical position of his center of ma ...
... Problem 15.17 At the instant shown, the 160-N vaulter’s center of mass is 8.5 m above the ground, and the vertical component of his velocity is 4 m/s. As his pole straightens, it exerts a vertical force on the vaulter of magnitude 180 + 2.8y 2 N, where y is the vertical position of his center of ma ...
POP4e: Ch. 10 Problems
... cylindrical wall of the ring, with radius 100 m. At rest when constructed, the ring is set rotating about its axis so that the people inside experience an effective free-fall acceleration equal to g. (Fig. P10.44 shows the ring together with some other parts that make a negligible contribution to th ...
... cylindrical wall of the ring, with radius 100 m. At rest when constructed, the ring is set rotating about its axis so that the people inside experience an effective free-fall acceleration equal to g. (Fig. P10.44 shows the ring together with some other parts that make a negligible contribution to th ...
Chap4
... and then looked at positions, velocities, and accelerations as functions of time. We weren’t concerned with the forces that caused the objects’ motions. We will now deal with dynamics, where the goal is to understand why objects move the way they do. This chapter and the following ones will therefor ...
... and then looked at positions, velocities, and accelerations as functions of time. We weren’t concerned with the forces that caused the objects’ motions. We will now deal with dynamics, where the goal is to understand why objects move the way they do. This chapter and the following ones will therefor ...