Objective Assignment - PRADEEP KSHETRAPAL PHYSICS
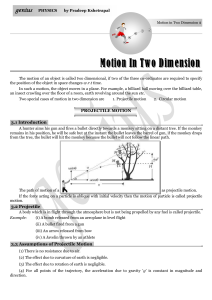
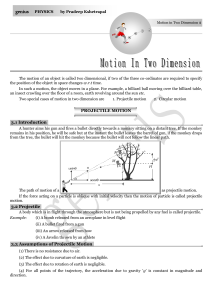
... When body projected with initial velocity u by making angle with the horizontal. Then after time t, (at point P) it’s direction is perpendicular to u . Magnitude of velocity at point P is given by v u cot . (from sample problem no. 9) For vertical motion : Initial velocity (at point O) u sin ...
... When body projected with initial velocity u by making angle with the horizontal. Then after time t, (at point P) it’s direction is perpendicular to u . Magnitude of velocity at point P is given by v u cot . (from sample problem no. 9) For vertical motion : Initial velocity (at point O) u sin ...
PHY101 - National Open University of Nigeria
... 3.1.1 Rest and motion To help us to understand the concept of frame of reference we need to note certain observations that have been made by physicists about this physical world we are living in. One of such observations is that a body is said to be at rest when it does not change its position with ...
... 3.1.1 Rest and motion To help us to understand the concept of frame of reference we need to note certain observations that have been made by physicists about this physical world we are living in. One of such observations is that a body is said to be at rest when it does not change its position with ...
Chapter 19 - Aerostudents
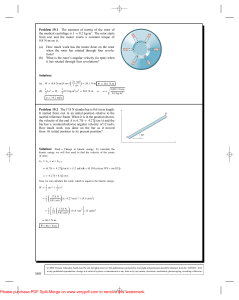
... Problem 19.2 The 17.8 N slender bar is 0.61 m in length. It started from rest in an initial position relative to the inertial reference frame. When it is in the position shown, the velocity of the end A is 6.71i + 4.27 j (m/s) and the bar has a counterclockwise angular velocity of 12 rad/s. How much ...
... Problem 19.2 The 17.8 N slender bar is 0.61 m in length. It started from rest in an initial position relative to the inertial reference frame. When it is in the position shown, the velocity of the end A is 6.71i + 4.27 j (m/s) and the bar has a counterclockwise angular velocity of 12 rad/s. How much ...
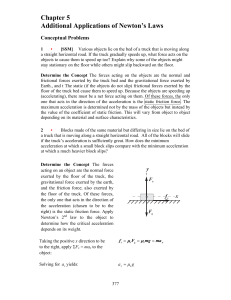
Chapter 5 Additional Applications of Newton`s Laws
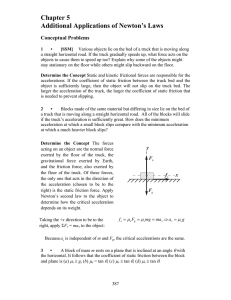
... conclude that the magnitude of its _____ is constant. (a) velocity, (b) acceleration, (c) net force, (d) apparent weight. Determine the Concept A particle traveling in a vertical circle experiences a downward gravitational force plus an additional force that constrains it to move along a circular pa ...
... conclude that the magnitude of its _____ is constant. (a) velocity, (b) acceleration, (c) net force, (d) apparent weight. Determine the Concept A particle traveling in a vertical circle experiences a downward gravitational force plus an additional force that constrains it to move along a circular pa ...
Problem 16.1 The 20-kg crate is stationary at time t = 0. It is
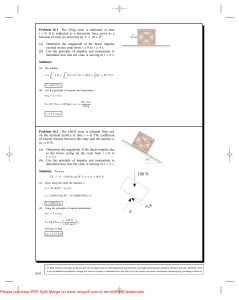
... Problem 16.6 A bioengineer models the force generated by the wings of the 0.2-kg snow petrel by an equation of the form F = F0 (1 + sin ωt), where F0 and ω are constants. From video measurements of a bird taking off, he estimates that ω = 18 and determines that the bird requires 1.42 s to take off ...
... Problem 16.6 A bioengineer models the force generated by the wings of the 0.2-kg snow petrel by an equation of the form F = F0 (1 + sin ωt), where F0 and ω are constants. From video measurements of a bird taking off, he estimates that ω = 18 and determines that the bird requires 1.42 s to take off ...
Problem 19.1 The moment of inertia of the rotor of the medical
... to any prohibited reproduction, storage in a retrieval system, or transmission in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording or likewise. ...
... to any prohibited reproduction, storage in a retrieval system, or transmission in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording or likewise. ...
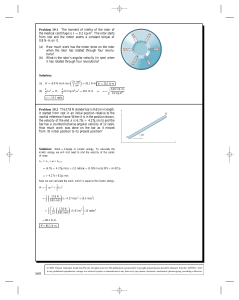
1 A 0.40 kg toy car moves at constant acceleration of 2.3 m/s2
... B object accelerates downward at a constant acceleration of 1.8 m/s2 ? What is the tension force in the rope when the object C accelerates upward at a constant acceleration of 1.8 m/s2 ? ...
... B object accelerates downward at a constant acceleration of 1.8 m/s2 ? What is the tension force in the rope when the object C accelerates upward at a constant acceleration of 1.8 m/s2 ? ...