Physics 1 - Peda.net
... Newton’s second law is giving a more precise definition to force as an action capable of accelerating an object. Force is needed to chance the direction of motion and to change the velocity of the body. Force is also needed to chance the shape of a body. For instance friction is slowing down the vel ...
... Newton’s second law is giving a more precise definition to force as an action capable of accelerating an object. Force is needed to chance the direction of motion and to change the velocity of the body. Force is also needed to chance the shape of a body. For instance friction is slowing down the vel ...
$doc.title
... now I’ve compressed it 5cm from it’s equilibrium point. Which way will the mass move if I let it go? ...
... now I’ve compressed it 5cm from it’s equilibrium point. Which way will the mass move if I let it go? ...
Lab #11: Simple Harmonic Motion of a Linear Oscillator
... Fspring kx In fact, it has been shown that a mass oscillating at the end of a spring (with no frictional forces) experiences pure simple harmonic motion. By combining the above two equations, an equation for the theoretical value of the angular frequency of the frictionless system is obtained: ...
... Fspring kx In fact, it has been shown that a mass oscillating at the end of a spring (with no frictional forces) experiences pure simple harmonic motion. By combining the above two equations, an equation for the theoretical value of the angular frequency of the frictionless system is obtained: ...
Physics 11 Assignment #2
... d. in the direction of motion A cable on an elevator exerts a 6 N upward force. The downward force of gravity on the elevator is 4 N. The elevator could be a. moving upward with constant speed. b. downward with a constant speed. c. moving upward with decreasing speed. d. moving upward with increasin ...
... d. in the direction of motion A cable on an elevator exerts a 6 N upward force. The downward force of gravity on the elevator is 4 N. The elevator could be a. moving upward with constant speed. b. downward with a constant speed. c. moving upward with decreasing speed. d. moving upward with increasin ...
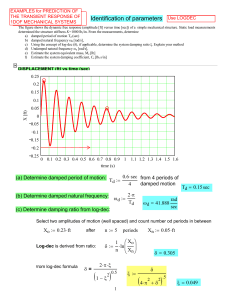
The Spring 2013 Qualifying Exam, Part 2
... instantaneously changes the nucleus into He3, which consists of two protons and one neutron. Calculate the probability that the electron remains in the ground state of the new atom. Problem 2: (a) Consider a circular cylinder of radius R and length L, rotating about its symmetry axis with angular ve ...
... instantaneously changes the nucleus into He3, which consists of two protons and one neutron. Calculate the probability that the electron remains in the ground state of the new atom. Problem 2: (a) Consider a circular cylinder of radius R and length L, rotating about its symmetry axis with angular ve ...