Activity 1 Where are the Volcanoes?
... down beneath the continents. Look at Figure 2 to see an example.The Nazca Plate, moving eastward from the East Pacific Ridge, slides down beneath the west coast of South America.The plate is heated as it sinks into the much hotter rocks of the deep Earth.The heat causes fluids, especially water, to ...
... down beneath the continents. Look at Figure 2 to see an example.The Nazca Plate, moving eastward from the East Pacific Ridge, slides down beneath the west coast of South America.The plate is heated as it sinks into the much hotter rocks of the deep Earth.The heat causes fluids, especially water, to ...
Mountain Building Processes in Four-Dimensions (4D-MB)
... & Gebrande 2006, Diehl et al. 2009). The newest Moho map of this area based on combined controlledsource and receiver-function information indicates a Moho gap beneath part of the Eastern Alps (white area in Fig. 4c, Spada et al. 2013), one of the targets in this SPP (section V). Given these discrep ...
... & Gebrande 2006, Diehl et al. 2009). The newest Moho map of this area based on combined controlledsource and receiver-function information indicates a Moho gap beneath part of the Eastern Alps (white area in Fig. 4c, Spada et al. 2013), one of the targets in this SPP (section V). Given these discrep ...
Tonalites from the Hospitais Massif (Ossa
... 2B) that are commonly parallel or slightly oblique to the foliation, although they also can be seen, rarely, cutting that structure. Within these discordant layers, it is possible to identify an internal fabric defined by the alignment of undeformed grains of mafic minerals and feldspars. At the two ...
... 2B) that are commonly parallel or slightly oblique to the foliation, although they also can be seen, rarely, cutting that structure. Within these discordant layers, it is possible to identify an internal fabric defined by the alignment of undeformed grains of mafic minerals and feldspars. At the two ...
Analysis of the spatial and temporal distribution of
... hazard and risk in the region, and historically have caused more deaths and damage than large earthquakes in the subduction zone (White and Harlow, 1993). During the twentieth century such earthquakes struck El Salvador on at least seven occasions, sometimes occurring in clusters of two or three sim ...
... hazard and risk in the region, and historically have caused more deaths and damage than large earthquakes in the subduction zone (White and Harlow, 1993). During the twentieth century such earthquakes struck El Salvador on at least seven occasions, sometimes occurring in clusters of two or three sim ...
Mechanisms for the Origin of Mid-Ocean Ridge Axial Topography: Implications
... Tm by 100øC then either vertical mantle flow or magma intrusion into the as suggestedfrom petrologic studies,this would increase the viscosity by approximatelytwo ordersof magnitude. While this effect has not been previously considered,it is potentially important and could result in the formation of ...
... Tm by 100øC then either vertical mantle flow or magma intrusion into the as suggestedfrom petrologic studies,this would increase the viscosity by approximatelytwo ordersof magnitude. While this effect has not been previously considered,it is potentially important and could result in the formation of ...
Fierce Volcanoes and Extreme Earthquakes
... We have seen that the plates of the Earth’s crust are constantly shifting, but the Earth’s crust underneath our feet is not as solid as we might think. There are many cracks and areas where the crust is weaker. These cracks between shifting rocks are called fault lines. These fault lines also occur ...
... We have seen that the plates of the Earth’s crust are constantly shifting, but the Earth’s crust underneath our feet is not as solid as we might think. There are many cracks and areas where the crust is weaker. These cracks between shifting rocks are called fault lines. These fault lines also occur ...
Essentials of Geology, 10e (Lutgens/Tarbuck/Tasa)
... 44) The doctrine of uniformitarianism implies that the current forces and processes shaping the Earth have been operating for a very long time. Answer: TRUE Diff: 1 ...
... 44) The doctrine of uniformitarianism implies that the current forces and processes shaping the Earth have been operating for a very long time. Answer: TRUE Diff: 1 ...
Numerical comparison of different convergent plate contacts
... overall dynamics. For the operation of plate tectonics a relatively low shear strength is a critical mechanical property of plate contacts (Tackley 2000). The effective friction at a subduction zone has a first order control on plate boundary topography and the plate-like motion (Zhong et al. 1998). ...
... overall dynamics. For the operation of plate tectonics a relatively low shear strength is a critical mechanical property of plate contacts (Tackley 2000). The effective friction at a subduction zone has a first order control on plate boundary topography and the plate-like motion (Zhong et al. 1998). ...
PDF
... and a stretched margin beneath Louisiana is also consistent with BAB behavior: igneous activity is most prolific nearest the arc and diminishes with distance from the trench. A possible objection to the GoM BAB hypothesis is that the spreading ridge was oriented at high angles to the Nazas arc trend ...
... and a stretched margin beneath Louisiana is also consistent with BAB behavior: igneous activity is most prolific nearest the arc and diminishes with distance from the trench. A possible objection to the GoM BAB hypothesis is that the spreading ridge was oriented at high angles to the Nazas arc trend ...
Available - UNLV Geoscience - University of Nevada, Las Vegas
... Extension, heating, anatexis, magmatism, and perhaps rock uplift were widespread during a restricted time interval in the Late Cretaceous (75–67 Ma) along the axis of maximum crustal thickening within the Mojave sector of the Sevier orogen, and to a lesser extent within the interior of the Idaho-Uta ...
... Extension, heating, anatexis, magmatism, and perhaps rock uplift were widespread during a restricted time interval in the Late Cretaceous (75–67 Ma) along the axis of maximum crustal thickening within the Mojave sector of the Sevier orogen, and to a lesser extent within the interior of the Idaho-Uta ...
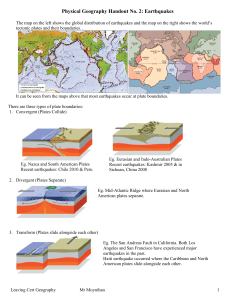
Earthquake handout
... the seventh strongest earthquake ever measured, five hundred times more forceful than the 7.0 Mw earthquake in Haiti in January of 2010. The Mercalli Scale is also used to describe the magnitude of earthquakes. The scale is based on the effects of an earthquake on the Earth's surface, humans, objec ...
... the seventh strongest earthquake ever measured, five hundred times more forceful than the 7.0 Mw earthquake in Haiti in January of 2010. The Mercalli Scale is also used to describe the magnitude of earthquakes. The scale is based on the effects of an earthquake on the Earth's surface, humans, objec ...
Stratigraphy Characteristic of Reservoar Zone in Hululais
... characterize the subsurface condition in Hululais. The process of identification, correlation, and zonation of each unit resulted in a subsurface model that showed the lithology types, alteration zones, and distribution of mineral assemblages. 3.1 Lithology Based on the depth, from the shallow to th ...
... characterize the subsurface condition in Hululais. The process of identification, correlation, and zonation of each unit resulted in a subsurface model that showed the lithology types, alteration zones, and distribution of mineral assemblages. 3.1 Lithology Based on the depth, from the shallow to th ...
Lesson 2 Volcanoes
... Use the vocabulary from the chapter to complete the sentences or answer the statements below. ...
... Use the vocabulary from the chapter to complete the sentences or answer the statements below. ...
Thickness of the lithosphere beneath Turkey and
... of the LAB topography below Anatolia and adjacent regions based on a combination of data from several different networks in the area. To achieve this, we have employed the S-receiver function technique, which is particularly suited to identify seismic discontinuities in the upper mantle, especially ...
... of the LAB topography below Anatolia and adjacent regions based on a combination of data from several different networks in the area. To achieve this, we have employed the S-receiver function technique, which is particularly suited to identify seismic discontinuities in the upper mantle, especially ...
Flat versus steep subduction: Contrasting modes for the formation
... subduction to collision. Slab inclination conditions for these two stages can be strongly dissimilar, which is taken into account by our models in a simplified manner: the initial slab dip angle corresponds to the early subduction stage and the final slab inclination characterizes the later collision ...
... subduction to collision. Slab inclination conditions for these two stages can be strongly dissimilar, which is taken into account by our models in a simplified manner: the initial slab dip angle corresponds to the early subduction stage and the final slab inclination characterizes the later collision ...
Geochemistry of continental subduction
... OH and molecular H2O with P-T changes in HP to UHP metamorphic rocks. With subduction of crustal rocks to mantle depths, the majority of water is released in the form of molecular water through breakdown of hydrous minerals. Significant amounts of structural hydroxyl and molecular water are also dis ...
... OH and molecular H2O with P-T changes in HP to UHP metamorphic rocks. With subduction of crustal rocks to mantle depths, the majority of water is released in the form of molecular water through breakdown of hydrous minerals. Significant amounts of structural hydroxyl and molecular water are also dis ...
Risks of future Earthquake- and extreme hydrological
... Southeast Asia’s risk of natural hazards is high, compounded by the rapid increas of the rate of urbanization, its proximity to seismically active faults and volcanic zones, its tsunamiprone coasts, and its susceptibility to the effects of extreme weather pattern and, not to the least to climate cha ...
... Southeast Asia’s risk of natural hazards is high, compounded by the rapid increas of the rate of urbanization, its proximity to seismically active faults and volcanic zones, its tsunamiprone coasts, and its susceptibility to the effects of extreme weather pattern and, not to the least to climate cha ...
Introductory Video Script Template
... http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/com mons/a/ab/US_Navy_110315-N-5503T311_An_aerial_view_of_damage_to_Wak ...
... http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/com mons/a/ab/US_Navy_110315-N-5503T311_An_aerial_view_of_damage_to_Wak ...
Chemical Geodynamics - Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution
... field of inquiry that has evolved from a marriage of mantle geochemistry and geophysics. By its very nature, geophysics can only characterize the present state of the Earth; geochemistry, on the other hand, supplies the necessary historical or time-averaging power but is inherently weak in terms of ...
... field of inquiry that has evolved from a marriage of mantle geochemistry and geophysics. By its very nature, geophysics can only characterize the present state of the Earth; geochemistry, on the other hand, supplies the necessary historical or time-averaging power but is inherently weak in terms of ...
Next Generation Sunshine State Standards Chapter 1
... understanding of Earth requires that we relate our planet to the larger universe. Because Earth is related to all of the other objects in space, the science of astronomy—the study of the universe—is very useful in probing the origins of our own environment. Because we are so closely acquainted with ...
... understanding of Earth requires that we relate our planet to the larger universe. Because Earth is related to all of the other objects in space, the science of astronomy—the study of the universe—is very useful in probing the origins of our own environment. Because we are so closely acquainted with ...
GeoNeutrino Analysis in KamLAND: Input and Desiderata
... 2004 – La Thuile, Aosta Valley, Italy (March 21-28, 2004) ...
... 2004 – La Thuile, Aosta Valley, Italy (March 21-28, 2004) ...
Diastrophism
... • Fold & Thrust Mountains - Large compressional stresses can be generated in the crust by tectonic forces that cause continental crustal areas to collide. When this occurs the rocks between the two continental blocks become folded and faulted under compressional stresses and are pushed upward to fo ...
... • Fold & Thrust Mountains - Large compressional stresses can be generated in the crust by tectonic forces that cause continental crustal areas to collide. When this occurs the rocks between the two continental blocks become folded and faulted under compressional stresses and are pushed upward to fo ...
Geology of the Eagle Spring Area, Eagle Mountain, Hudspeth
... one throughout most of its length. It is apparently a normal fault, although there is no definite evidence to prove this. The stratigraphic throw is approximately 2,500 feet. The fault extending southeast from Eagle Spring, which is located on the south side of the fault, has a smaller throw than th ...
... one throughout most of its length. It is apparently a normal fault, although there is no definite evidence to prove this. The stratigraphic throw is approximately 2,500 feet. The fault extending southeast from Eagle Spring, which is located on the south side of the fault, has a smaller throw than th ...
Large igneous province

A large igneous province (LIP) is an extremely large accumulation of igneous rocks, including liquid rock (intrusive) or volcanic rock formations (extrusive), when hot magma extrudes from inside the Earth and flows out. The source of many or all LIPs is variously attributed to mantle plumes or to processes associated with plate tectonics. Types of LIPs can include large volcanic provinces (LVP), created through flood basalt and large plutonic provinces (LPP). Eleven distinct flood basalt episodes occurred in the past 250 million years, creating volcanic provinces, which coincided with mass extinctions in prehistoric times. Formation depends on a range of factors, such as continental configuration, latitude, volume, rate, duration of eruption, style and setting (continental vs. oceanic), the preexisting climate state, and the biota resilience to change.