The Theory of Plate Tectonics
... What happens when the rock is sheared (or “cut”) from the Stress of Shearing? • A STRIKE-SLIP FAULT • Rocks on each side of the fault slip past each other as they break. ...
... What happens when the rock is sheared (or “cut”) from the Stress of Shearing? • A STRIKE-SLIP FAULT • Rocks on each side of the fault slip past each other as they break. ...
The evolution of shallow crustal structures in early rift
... BTF, is situated at its northern end, and is an active rift. The second structural domain is a large, NE-SW-trending anticlinorium 60 km wide to the southeast of the rift zone, towards the Tiburon basin. One possibility is that it represents a positive flower structure and thus indicates a transpres ...
... BTF, is situated at its northern end, and is an active rift. The second structural domain is a large, NE-SW-trending anticlinorium 60 km wide to the southeast of the rift zone, towards the Tiburon basin. One possibility is that it represents a positive flower structure and thus indicates a transpres ...
Objectives: Define rocks Describe the rock cycle and some changes
... Recognize magma and lava as the materials that cool to form igneous rocks. •Contrast the formation of intrusive and extrusive igneous rock. •Contrast granitic and basaltic igneous rocks. ...
... Recognize magma and lava as the materials that cool to form igneous rocks. •Contrast the formation of intrusive and extrusive igneous rock. •Contrast granitic and basaltic igneous rocks. ...
Magnetic Reversals
... surprising difference. In the ocean floor the magnetization was orderly, Mid-Atlantic Ridge arranged in long strips. The strips on the Atlantic ocean floor, in particular, all seemed parallel to the "mid-Atlantic ridge." That is a volcanic ridge running roughly north-to-south (with some zigs and zag ...
... surprising difference. In the ocean floor the magnetization was orderly, Mid-Atlantic Ridge arranged in long strips. The strips on the Atlantic ocean floor, in particular, all seemed parallel to the "mid-Atlantic ridge." That is a volcanic ridge running roughly north-to-south (with some zigs and zag ...
Plates on the Move
... • Everyone agreed that Wegener’s evidence was compelling. But wouldn’t we feel the movement? • Also, wouldn’t there be evidence to show that the continents were still moving today? • Wegener was a meteorologist and his theory was not well accepted. (He died on an expedition in Greenland collecting i ...
... • Everyone agreed that Wegener’s evidence was compelling. But wouldn’t we feel the movement? • Also, wouldn’t there be evidence to show that the continents were still moving today? • Wegener was a meteorologist and his theory was not well accepted. (He died on an expedition in Greenland collecting i ...
Department of Geology and Geological Engineering
... the greenstone belts were formed ca. 2720 Ma and were all previously broadly interpreted to be deposited in a rifted-arc to back-arc tectonic setting. While this interpreted tectonic setting should be prospective for synvolcanic Cu-Zn-Pb mineralization, the greenstone belts in this region show vastl ...
... the greenstone belts were formed ca. 2720 Ma and were all previously broadly interpreted to be deposited in a rifted-arc to back-arc tectonic setting. While this interpreted tectonic setting should be prospective for synvolcanic Cu-Zn-Pb mineralization, the greenstone belts in this region show vastl ...
Judgement Statement
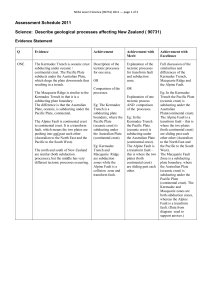
... Plate(continental crust). The Alpine Fault is a transform fault – this is where the two plates (both continental crust) are sliding past each other other (Australian to the North East and the Pacific to the South West). The Macquarie Fault Zone is a subducting plate boundary, where the Australian Pl ...
... Plate(continental crust). The Alpine Fault is a transform fault – this is where the two plates (both continental crust) are sliding past each other other (Australian to the North East and the Pacific to the South West). The Macquarie Fault Zone is a subducting plate boundary, where the Australian Pl ...
Metamorphic Rock Metamorphic rocks have been changed over
... surface, from the extreme heat caused by magma or by the intense collisions and friction of tectonic plates. Uplift and erosion help bring metamorphic rock to the Earth's surface. Examples of metamorphic rocks include anthracite, quartzite, marble, slate, gneiss and schist. Marble is a metamorphic r ...
... surface, from the extreme heat caused by magma or by the intense collisions and friction of tectonic plates. Uplift and erosion help bring metamorphic rock to the Earth's surface. Examples of metamorphic rocks include anthracite, quartzite, marble, slate, gneiss and schist. Marble is a metamorphic r ...
Landscape Development - Gouverneur Central School District
... Landscape – region of Earth’s surface where physical features are related by a common origin Stream Drainage Patterns – the shape of the streams as seen from the air Gradient (slope) – a way to describe the land because it is a measurable characteristic and useful because it shows the development of ...
... Landscape – region of Earth’s surface where physical features are related by a common origin Stream Drainage Patterns – the shape of the streams as seen from the air Gradient (slope) – a way to describe the land because it is a measurable characteristic and useful because it shows the development of ...
Schedule
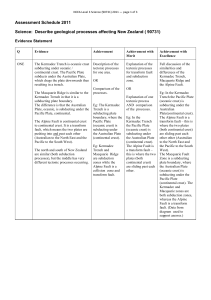
... Plate(continental crust). The Alpine Fault is a transform fault – this is where the two plates (both continental crust) are sliding past each other other (Australian to the North East and the Pacific to the South West). The Macquarie Fault Zone is a subducting plate boundary, where the Australian Pl ...
... Plate(continental crust). The Alpine Fault is a transform fault – this is where the two plates (both continental crust) are sliding past each other other (Australian to the North East and the Pacific to the South West). The Macquarie Fault Zone is a subducting plate boundary, where the Australian Pl ...
The Martian Dichotomy - Department of Earth and Space Sciences
... smooth topography, and virtually no vertical scarps. Slow spreading centers build up topography, and have a large number of high angle scarps. East Pacific Rise ...
... smooth topography, and virtually no vertical scarps. Slow spreading centers build up topography, and have a large number of high angle scarps. East Pacific Rise ...
Students should know the physical properties (e.g., hardness, color
... plates are moving relative to one another. The movement is never smooth; it may produce fractures or faults and may also generate heat. The sudden shift of one plate on another plate along faults causes earthquakes. Volcanic eruptions may occur along faults in which one plate slides under another an ...
... plates are moving relative to one another. The movement is never smooth; it may produce fractures or faults and may also generate heat. The sudden shift of one plate on another plate along faults causes earthquakes. Volcanic eruptions may occur along faults in which one plate slides under another an ...
File
... 5. Look at the chocolate chip cookie. This cookie represents continental crust! 6. DO NOT push the cookie down on the icing. 7. Gently move the chocolate chip cookie and the graham cracker toward each other until the edge of the chocolate chip cookie is ON TOP of the edge of the graham cracker. 8. T ...
... 5. Look at the chocolate chip cookie. This cookie represents continental crust! 6. DO NOT push the cookie down on the icing. 7. Gently move the chocolate chip cookie and the graham cracker toward each other until the edge of the chocolate chip cookie is ON TOP of the edge of the graham cracker. 8. T ...
Erosion and Plate tectonics part 2
... --Land on Earth is ______________________! Instead, it is several pieces of rock ____________ on an ocean of magma. --Plate Tectonics studies how these rock sections (called _________________) move and ___________________. Continental Drift -- of years ago, Earth was _____________________ called Pan ...
... --Land on Earth is ______________________! Instead, it is several pieces of rock ____________ on an ocean of magma. --Plate Tectonics studies how these rock sections (called _________________) move and ___________________. Continental Drift -- of years ago, Earth was _____________________ called Pan ...
Light: The Cosmic Messenger
... • Two types of plate material: thin, younger, more dense (~3gm/cm3) Ocean Plates; and thick, older, less dense (~2.5gm/cm3) Continental Plates. Density and isostatic ...
... • Two types of plate material: thin, younger, more dense (~3gm/cm3) Ocean Plates; and thick, older, less dense (~2.5gm/cm3) Continental Plates. Density and isostatic ...
Earthquake Notes
... Volcanoes are the result of hot spots within the crust or mantle of the earth. The hot, liquid rock will break through weak spots in the surface and form volcanoes or flood basalts. Many volcanoes do not release lava, instead they spit ash and small bits of lava called lapilli. Some eruptions are qu ...
... Volcanoes are the result of hot spots within the crust or mantle of the earth. The hot, liquid rock will break through weak spots in the surface and form volcanoes or flood basalts. Many volcanoes do not release lava, instead they spit ash and small bits of lava called lapilli. Some eruptions are qu ...
Seafloor spreading model
... debated in the scientific community. Some argue that it is driven by convection currents in the mantle. Others argue that the upwelling of magma and creation of new crust at mid-ocean ridges pushes the older crust out of the way (the “Ridge Push” theory). Others argue that the sinking of the old cru ...
... debated in the scientific community. Some argue that it is driven by convection currents in the mantle. Others argue that the upwelling of magma and creation of new crust at mid-ocean ridges pushes the older crust out of the way (the “Ridge Push” theory). Others argue that the sinking of the old cru ...
Convergent Boundaries
... • May form Mountain Ranges. These are Folded Mountains. Like the Himalayas or the Rockies. ...
... • May form Mountain Ranges. These are Folded Mountains. Like the Himalayas or the Rockies. ...
plate tectonics - School of Ocean and Earth Science and Technology
... process called convection. As rocks near Earth’s surface cool, they become more dense than the hot rocks that lie beneath them and eventually become dense enough that they begin to sink into the mantle’s interior, forming a downwelling of downward-moving mantle. At the base of the mantle, movement o ...
... process called convection. As rocks near Earth’s surface cool, they become more dense than the hot rocks that lie beneath them and eventually become dense enough that they begin to sink into the mantle’s interior, forming a downwelling of downward-moving mantle. At the base of the mantle, movement o ...
Our Changing Landforms
... Deep within the Earth's crust rocks can be put under huge pressures and temperatures are very high. These conditions can cause the minerals in the rock to change. This process is called metamorphism. All rocks can be metamorphosed, and there are many different types of metamorphic rock. Limestone ca ...
... Deep within the Earth's crust rocks can be put under huge pressures and temperatures are very high. These conditions can cause the minerals in the rock to change. This process is called metamorphism. All rocks can be metamorphosed, and there are many different types of metamorphic rock. Limestone ca ...
Powerpoint Presentation Physical Geology, 10/e
... composition of a magma body, can occur by differentiation, partial melting, assimilation, or magma mixing • differentiation involves the changing of magma composition by the removal of denser early-formed ferromagnesian minerals by ...
... composition of a magma body, can occur by differentiation, partial melting, assimilation, or magma mixing • differentiation involves the changing of magma composition by the removal of denser early-formed ferromagnesian minerals by ...
Plate Tec Online
... below. Use the arrows on the bottom of the web page to navigate through this section. 8. What is the Mid-Atlantic Ridge? __________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________ ...
... below. Use the arrows on the bottom of the web page to navigate through this section. 8. What is the Mid-Atlantic Ridge? __________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________ ...
Large igneous province

A large igneous province (LIP) is an extremely large accumulation of igneous rocks, including liquid rock (intrusive) or volcanic rock formations (extrusive), when hot magma extrudes from inside the Earth and flows out. The source of many or all LIPs is variously attributed to mantle plumes or to processes associated with plate tectonics. Types of LIPs can include large volcanic provinces (LVP), created through flood basalt and large plutonic provinces (LPP). Eleven distinct flood basalt episodes occurred in the past 250 million years, creating volcanic provinces, which coincided with mass extinctions in prehistoric times. Formation depends on a range of factors, such as continental configuration, latitude, volume, rate, duration of eruption, style and setting (continental vs. oceanic), the preexisting climate state, and the biota resilience to change.