Astronomy SOL Review
... - two types of planets in our solar system: terrestrial and gas giants - four inner terrestrial planets consist mostly of solid rock - four of outer planets (“gas giants”) consist of thick outer layers of gaseous materials, perhaps with small rocky cores - fifth outer planet is Pluto: has an unknown ...
... - two types of planets in our solar system: terrestrial and gas giants - four inner terrestrial planets consist mostly of solid rock - four of outer planets (“gas giants”) consist of thick outer layers of gaseous materials, perhaps with small rocky cores - fifth outer planet is Pluto: has an unknown ...
Plate Tectonics - NagelBeelmanScience
... underneath the westward moving North American plate. Seduction is when an oceanic plate is forced down into the mantle by a thicker but less dense continental-land-plate. Convergent boundaries can cause many hazards to our environment Some of these hazards are earthquakes, volcanoes and crustal defo ...
... underneath the westward moving North American plate. Seduction is when an oceanic plate is forced down into the mantle by a thicker but less dense continental-land-plate. Convergent boundaries can cause many hazards to our environment Some of these hazards are earthquakes, volcanoes and crustal defo ...
Geology and Nonrenewable Mineral Resources - Baxley
... plates cause them to grind into one another at convergent plate boundaries, move apart at divergent plate boundaries and slide past at transform plate boundaries. Figure 15-4 ...
... plates cause them to grind into one another at convergent plate boundaries, move apart at divergent plate boundaries and slide past at transform plate boundaries. Figure 15-4 ...
Earth Science SOL Must Knows
... - two types of planets in our solar system: terrestrial and gas giants - four inner terrestrial planets consist mostly of solid rock - four of outer planets (“gas giants”) consist of thick outer layers of gaseous materials, perhaps with small rocky cores - fifth outer planet is Pluto: has an unknown ...
... - two types of planets in our solar system: terrestrial and gas giants - four inner terrestrial planets consist mostly of solid rock - four of outer planets (“gas giants”) consist of thick outer layers of gaseous materials, perhaps with small rocky cores - fifth outer planet is Pluto: has an unknown ...
Science Q and A
... which causes a huge wave to come up over the land. On average about 500 mi. which is as fast as a commercial jet. ...
... which causes a huge wave to come up over the land. On average about 500 mi. which is as fast as a commercial jet. ...
SOL "Must
... - two types of planets in our solar system: terrestrial and gas giants - four inner terrestrial planets consist mostly of solid rock - four of outer planets (“gas giants”) consist of thick outer layers of gaseous materials, perhaps with small rocky cores - fifth outer planet is Pluto: has an unknown ...
... - two types of planets in our solar system: terrestrial and gas giants - four inner terrestrial planets consist mostly of solid rock - four of outer planets (“gas giants”) consist of thick outer layers of gaseous materials, perhaps with small rocky cores - fifth outer planet is Pluto: has an unknown ...
Astronomy SOL Review
... Weather and Climate - weather: describes day-to-day changes in atmospheric conditions energy transfer between the Earth’s surface and the atmosphere creates the weather convection in the atmosphere is a major cause of weather convection is the major mechanism of energy transfer in the oceans, ...
... Weather and Climate - weather: describes day-to-day changes in atmospheric conditions energy transfer between the Earth’s surface and the atmosphere creates the weather convection in the atmosphere is a major cause of weather convection is the major mechanism of energy transfer in the oceans, ...
The Era
... o most reptiles have a ______________ posture o ________________ many dinosaurs had an __________ posture o Mass extinction terrestrial dinosaurs, most marine ___________, plants, & many other organisms why? combo of: massive ____________ (stressed climate) large ______________ impact @ ...
... o most reptiles have a ______________ posture o ________________ many dinosaurs had an __________ posture o Mass extinction terrestrial dinosaurs, most marine ___________, plants, & many other organisms why? combo of: massive ____________ (stressed climate) large ______________ impact @ ...
Plate boundaries
... – Often forms volcanoes on the ocean floor – If the volcanoes emerge as islands, a volcanic island arc is formed (Japan, Aleutian islands, ...
... – Often forms volcanoes on the ocean floor – If the volcanoes emerge as islands, a volcanic island arc is formed (Japan, Aleutian islands, ...
Mantle plumes: Why the current skepticism?
... Nevertheless, dissenting voices were never entirely absent, and even included those of influential contributors to the development of plate tectonics. During the 1990s, skeptics were in the minority. Most papers published about plumes assumed the hypothesis to be correct, sought merely to validate i ...
... Nevertheless, dissenting voices were never entirely absent, and even included those of influential contributors to the development of plate tectonics. During the 1990s, skeptics were in the minority. Most papers published about plumes assumed the hypothesis to be correct, sought merely to validate i ...
Earth Science Questions and Answers for Teachers Teaching Grade 6
... (through computer modeling), the fossil and sedimentary evidence of ancient life distributions and climate becomes coherent, providing strong support for the existence of Pangaea. As plates move in relation to one another, landforms and topographic features, such as volcanoes, mountains, valleys, oc ...
... (through computer modeling), the fossil and sedimentary evidence of ancient life distributions and climate becomes coherent, providing strong support for the existence of Pangaea. As plates move in relation to one another, landforms and topographic features, such as volcanoes, mountains, valleys, oc ...
Unit 4 Chapter 13
... They contain basaltic lava with only few gases, smooth easily flowing lava They are found in spreading centers (division boundaries) Mid Atlantic Ridge ...
... They contain basaltic lava with only few gases, smooth easily flowing lava They are found in spreading centers (division boundaries) Mid Atlantic Ridge ...
Unit 3 Lesson 3 Rock Cycle Activity
... Liquid (molten) rock material solidifies either at or below the surface of the earth to form igneous rocks. Uplifting occurs forming mountains made of rock. The exposure of rocks to weathering and erosion at the earth's surface breaks them down into smaller grains producing soil. The grains (soil) a ...
... Liquid (molten) rock material solidifies either at or below the surface of the earth to form igneous rocks. Uplifting occurs forming mountains made of rock. The exposure of rocks to weathering and erosion at the earth's surface breaks them down into smaller grains producing soil. The grains (soil) a ...
the COMPLETED version of "Slip... Slide... Collide"
... 3. During the Cambrian Period, the largest landmass was known as GONDWANA 4. During the Triassic Period, this LARGE landmass existed on Earth. a. Laurentia b. Godwana c. Pangaea 5. The _________________ Mountains formed when India collided with the Asian Plate a. Appalachian b. Himalayas c. Andes 6 ...
... 3. During the Cambrian Period, the largest landmass was known as GONDWANA 4. During the Triassic Period, this LARGE landmass existed on Earth. a. Laurentia b. Godwana c. Pangaea 5. The _________________ Mountains formed when India collided with the Asian Plate a. Appalachian b. Himalayas c. Andes 6 ...
Honors Earth and Space Final Exam Jeopardy
... support his theory of continental drift. Why was his theory not widely accepted at that time? He couldn’t explain how or why the continents moved. The technology needed to discover seafloor spreading and convection currents didn’t exist at that time. ...
... support his theory of continental drift. Why was his theory not widely accepted at that time? He couldn’t explain how or why the continents moved. The technology needed to discover seafloor spreading and convection currents didn’t exist at that time. ...
Deeply buried continental crust under Iceland
... (2015) suggest that a continental sliver, representing a south-western extension of the Jan Mayen Microcontinent, is deeply buried under a thick pile of volcanic rocks. Iceland and the surrounding plateau, straddling the Mid-Atlantic ridge, are lifted above sea level by a light and hot column of roc ...
... (2015) suggest that a continental sliver, representing a south-western extension of the Jan Mayen Microcontinent, is deeply buried under a thick pile of volcanic rocks. Iceland and the surrounding plateau, straddling the Mid-Atlantic ridge, are lifted above sea level by a light and hot column of roc ...
M S P S T U D Y G U I D E 2014 MSP STUDY GUIDE 2014
... Compression Wave- P WAVE --like sound waves they compress and expand the material they travel through energy travel parallel to direction the wave is moving Transverse Wave-S WAVE- energy (wave) travels perpendicular to direction of wave. Liquefaction- solids behaving like a liquid by vibrations. EQ ...
... Compression Wave- P WAVE --like sound waves they compress and expand the material they travel through energy travel parallel to direction the wave is moving Transverse Wave-S WAVE- energy (wave) travels perpendicular to direction of wave. Liquefaction- solids behaving like a liquid by vibrations. EQ ...
Plate Tectonics
... These boundaries are created when plates move apart and new material is added to the Earth’s crust. An example is the Mid-Atlantic Ridge. ...
... These boundaries are created when plates move apart and new material is added to the Earth’s crust. An example is the Mid-Atlantic Ridge. ...
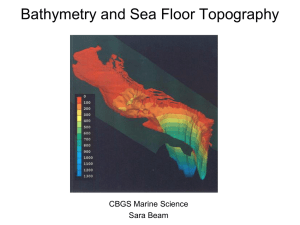
Bathymetry
... • How do organisms spread there colonists over thousands of miles in the deep ocean ?????? ...
... • How do organisms spread there colonists over thousands of miles in the deep ocean ?????? ...
First Hour Exam, Fall, 2016
... d. from Cape Cod north to the Gulf of Maine b. the Oregon-Washington coast e. the eastern Florida coast c. the Texas-Louisiana coast f. from New Jersey to Georgia 17. Typical island-arc systems include all of the following island groups except a. the Kuril Islands c. the Hawaiian Islands b. the Japa ...
... d. from Cape Cod north to the Gulf of Maine b. the Oregon-Washington coast e. the eastern Florida coast c. the Texas-Louisiana coast f. from New Jersey to Georgia 17. Typical island-arc systems include all of the following island groups except a. the Kuril Islands c. the Hawaiian Islands b. the Japa ...
How are metamorphic rocks classified?
... Rocks may be flattened or bent or atoms may be exchanged to form new minerals. ...
... Rocks may be flattened or bent or atoms may be exchanged to form new minerals. ...
Puerto-Rico Trench
... “earthquake zones” and most of these zones form bands or lines. • Scientists came to realize that these bands represent divisions in the lithosphere and separate it into pieces (plates). ...
... “earthquake zones” and most of these zones form bands or lines. • Scientists came to realize that these bands represent divisions in the lithosphere and separate it into pieces (plates). ...
Rocks
... Intrusive igneous rock has been left as weaker rock (like sedimentary) has worn away due to weathering & erosion. ...
... Intrusive igneous rock has been left as weaker rock (like sedimentary) has worn away due to weathering & erosion. ...
Large igneous province

A large igneous province (LIP) is an extremely large accumulation of igneous rocks, including liquid rock (intrusive) or volcanic rock formations (extrusive), when hot magma extrudes from inside the Earth and flows out. The source of many or all LIPs is variously attributed to mantle plumes or to processes associated with plate tectonics. Types of LIPs can include large volcanic provinces (LVP), created through flood basalt and large plutonic provinces (LPP). Eleven distinct flood basalt episodes occurred in the past 250 million years, creating volcanic provinces, which coincided with mass extinctions in prehistoric times. Formation depends on a range of factors, such as continental configuration, latitude, volume, rate, duration of eruption, style and setting (continental vs. oceanic), the preexisting climate state, and the biota resilience to change.