2-1 Directed Reading
... a. the solid, outer layer of Earth that consists of the crust and the rigid upper part of the mantle b. the central part of Earth below the mantle c. the strong, lower part of the mantle between the asthenosphere and the outer core d. the thin, solid, outermost layer of Earth above the mantle e. the ...
... a. the solid, outer layer of Earth that consists of the crust and the rigid upper part of the mantle b. the central part of Earth below the mantle c. the strong, lower part of the mantle between the asthenosphere and the outer core d. the thin, solid, outermost layer of Earth above the mantle e. the ...
Chapter 3 Plate Tectonics
... are the deepest parts of the oceans close to continents or near strings of islands such as Alaska’s Aleutian Islands . • Why is the location of these trenches significant? • The trenches create the Ring of Fire. ...
... are the deepest parts of the oceans close to continents or near strings of islands such as Alaska’s Aleutian Islands . • Why is the location of these trenches significant? • The trenches create the Ring of Fire. ...
Final Exam Practice Quiz 1. What is the chief source of energy for
... 11. What sedimentary rock is composed of rounded gravel-sized particles? a) Sandstone b) Shale c) Limestone d) Conglomerate 12. Volcanic rocks such as pumice that have small cavities left by escaping gas bubbles are described as 'coarse-grained' in texture. a) True b) False 13. Salt and gypsum are c ...
... 11. What sedimentary rock is composed of rounded gravel-sized particles? a) Sandstone b) Shale c) Limestone d) Conglomerate 12. Volcanic rocks such as pumice that have small cavities left by escaping gas bubbles are described as 'coarse-grained' in texture. a) True b) False 13. Salt and gypsum are c ...
Ch 8 Earth Resources Content
... • Improved stream quality • Better habitat for grassland birds and other wildlife ...
... • Improved stream quality • Better habitat for grassland birds and other wildlife ...
1 GS104 Lab 5 Answer Key - Study of Common Rocks Pre
... 1. What are the three main classes of rocks and how do each of them form? Igenous - cooling of magma / lava Sedimentary - formed from lithification of sediment at earth surface Metamorphic - formed by alteration of pre-existing rock 2. Draw and label a diagram of the rock cycle. Be sure to show the ...
... 1. What are the three main classes of rocks and how do each of them form? Igenous - cooling of magma / lava Sedimentary - formed from lithification of sediment at earth surface Metamorphic - formed by alteration of pre-existing rock 2. Draw and label a diagram of the rock cycle. Be sure to show the ...
Molnar, P. (2011), Jack Oliver (1923-2011), Nature, 470, 176.
... waves, at their seismographs. These waves travel through the interior of Earth. Longperiod waves that ripple over the surface of the planet offered a ‘place’ where few had gone before. Oliver was the first to recognize many of the peculiarities of the waveforms that computers now analyse and simulat ...
... waves, at their seismographs. These waves travel through the interior of Earth. Longperiod waves that ripple over the surface of the planet offered a ‘place’ where few had gone before. Oliver was the first to recognize many of the peculiarities of the waveforms that computers now analyse and simulat ...
Geohazards Name: Period: Date: _____
... destruction and the dimension of the disaster are parts of the definition of extreme. That, combined with their physical features that normally are several orders higher or more powerful than the average geohazard. So, when we talk about extreme geohazards we not only refer to the physical character ...
... destruction and the dimension of the disaster are parts of the definition of extreme. That, combined with their physical features that normally are several orders higher or more powerful than the average geohazard. So, when we talk about extreme geohazards we not only refer to the physical character ...
here
... rock and hot gas, fluidized in one body like a giant cloud, and it devastated an area larger than 22 sq miles from Grand Riviere to Schooelcher. The ash from pyroclastic flows can get as hot as 100-800 degrees Celsius, past boiling point and when blasted out from the volcano it can be a deadly combi ...
... rock and hot gas, fluidized in one body like a giant cloud, and it devastated an area larger than 22 sq miles from Grand Riviere to Schooelcher. The ash from pyroclastic flows can get as hot as 100-800 degrees Celsius, past boiling point and when blasted out from the volcano it can be a deadly combi ...
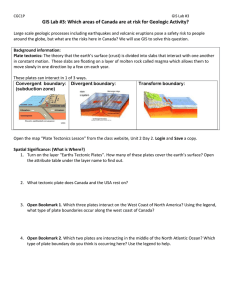
GIS lab #3 Plate Tectonics 20171p
... GIS Lab #3: Which areas of Canada are at risk for Geologic Activity? Large scale geologic processes including earthquakes and volcanic eruptions pose a safety risk to people around the globe, but what are the risks here in Canada? We will use GIS to solve this question. Background information: Plate ...
... GIS Lab #3: Which areas of Canada are at risk for Geologic Activity? Large scale geologic processes including earthquakes and volcanic eruptions pose a safety risk to people around the globe, but what are the risks here in Canada? We will use GIS to solve this question. Background information: Plate ...
Section 1
... 6. a. Plate tectonics is the theory that Earth's outer shell is divided into several plates that glide over the mantle, the rocky inner layer above the core. The plates act like a hard and rigid shell compared to Earth's mantle. b. A : Lithosphere B : Asthenosphere c. The plates along the surface of ...
... 6. a. Plate tectonics is the theory that Earth's outer shell is divided into several plates that glide over the mantle, the rocky inner layer above the core. The plates act like a hard and rigid shell compared to Earth's mantle. b. A : Lithosphere B : Asthenosphere c. The plates along the surface of ...
Data Collection: Recording Metamorphism and Lithology at the
... Parry Sound to Killarney, Ontario. Samples chosen for data collection were part of the exposed bedrock and maintained the alignment of the source bedrock. Each specimen was recorded with north facing alignment, angle of dip, and elevation. Specimens were separated from the bedrock by utilizing pre-e ...
... Parry Sound to Killarney, Ontario. Samples chosen for data collection were part of the exposed bedrock and maintained the alignment of the source bedrock. Each specimen was recorded with north facing alignment, angle of dip, and elevation. Specimens were separated from the bedrock by utilizing pre-e ...
Antiquity of the Oceans and Continents
... inherent feature of this crustal dichotomy would have been linear crustal accretion and collisional orogeny at convergent plate boundaries (de Wit 1998), although the architecture of these systems may have differed from that at modern plate boundaries. However, it is increasingly apparent that an ar ...
... inherent feature of this crustal dichotomy would have been linear crustal accretion and collisional orogeny at convergent plate boundaries (de Wit 1998), although the architecture of these systems may have differed from that at modern plate boundaries. However, it is increasingly apparent that an ar ...
Supporting Content Web Sites
... This book provides a good picture of the dynamic forces that constantly change our Earth. It is a good resource to teach the structure of the Earth. Indicators: 8-3.6 , 8-3.7 Johnson, Rebecca L. (2005) Plate Tectonics. Twenty-First Century Books/Lerner Publishing ...
... This book provides a good picture of the dynamic forces that constantly change our Earth. It is a good resource to teach the structure of the Earth. Indicators: 8-3.6 , 8-3.7 Johnson, Rebecca L. (2005) Plate Tectonics. Twenty-First Century Books/Lerner Publishing ...
Chapter 11
... Key Idea: Mountains can be classified by features that result from forces involved in plate interactions. The process by which each type of mountain is created: 1. Folded Mountains Two continental plates move toward ...
... Key Idea: Mountains can be classified by features that result from forces involved in plate interactions. The process by which each type of mountain is created: 1. Folded Mountains Two continental plates move toward ...
Why does Venus lack a magnetic field?
... • for Venus, Fc is in the range of 11-30 mW/m^2 • thermal convection will cease if the heat being extracted from the core is less than Fc • rate at which the core loses heat depends on the temperature difference between the mantle and the core ...
... • for Venus, Fc is in the range of 11-30 mW/m^2 • thermal convection will cease if the heat being extracted from the core is less than Fc • rate at which the core loses heat depends on the temperature difference between the mantle and the core ...
printer-friendly version of benchmark
... Students understand the concept of plate tectonics including the evidence that supports it (structural, geophysical and paleontological evidence). E/S Common misconceptions associate with this benchmark 1. Students incorrectly believe that the continents randomly drift about the Earth or that the co ...
... Students understand the concept of plate tectonics including the evidence that supports it (structural, geophysical and paleontological evidence). E/S Common misconceptions associate with this benchmark 1. Students incorrectly believe that the continents randomly drift about the Earth or that the co ...
10-5 Stations.notebook
... d. Carribbean Plate e. Juan de Fuca Plate f. Scotia Plate g. Arabian Plate h. Indian Plate ...
... d. Carribbean Plate e. Juan de Fuca Plate f. Scotia Plate g. Arabian Plate h. Indian Plate ...
Inferring Plate Boundary Deformation Mechanisms from Lithospheric
... in northern Taiwan as well as subduction of the Eurasian plate underneath the island. It has long been recognized that one model for this flipping of subduction polarity beneath Taiwan is the progressive tearing of the Eurasian plate along the continental margin. Global tomography combined with loca ...
... in northern Taiwan as well as subduction of the Eurasian plate underneath the island. It has long been recognized that one model for this flipping of subduction polarity beneath Taiwan is the progressive tearing of the Eurasian plate along the continental margin. Global tomography combined with loca ...
Document
... The theory of plate tectonics states that the crust of the Earth is composed of moving plates. These plates move along the lithosphere (Earth’s crust and upper mantle) and the asthenosphere (the plastic-like layer beneath the lithosphere). This theory also says that these plates are always in motion ...
... The theory of plate tectonics states that the crust of the Earth is composed of moving plates. These plates move along the lithosphere (Earth’s crust and upper mantle) and the asthenosphere (the plastic-like layer beneath the lithosphere). This theory also says that these plates are always in motion ...
Lithological Processes, Hazards and Management (1)
... Linear scars, offset stream channels, elongated ponds Eg. San Andreas fault ...
... Linear scars, offset stream channels, elongated ponds Eg. San Andreas fault ...
Lecture 23 - Igneous Rocks
... (volcaniclastic) fabric. High-T disordered fsp is common (e.g. sanadine). Also see leucite, tridymite, and cristobalite. ...
... (volcaniclastic) fabric. High-T disordered fsp is common (e.g. sanadine). Also see leucite, tridymite, and cristobalite. ...
Large igneous province

A large igneous province (LIP) is an extremely large accumulation of igneous rocks, including liquid rock (intrusive) or volcanic rock formations (extrusive), when hot magma extrudes from inside the Earth and flows out. The source of many or all LIPs is variously attributed to mantle plumes or to processes associated with plate tectonics. Types of LIPs can include large volcanic provinces (LVP), created through flood basalt and large plutonic provinces (LPP). Eleven distinct flood basalt episodes occurred in the past 250 million years, creating volcanic provinces, which coincided with mass extinctions in prehistoric times. Formation depends on a range of factors, such as continental configuration, latitude, volume, rate, duration of eruption, style and setting (continental vs. oceanic), the preexisting climate state, and the biota resilience to change.