volcanoes - Math/Science Nucleus
... Mt. Lassen is in northern California. The last eruption was in the early 1900's. The volcano is dormant and the type of rock is andesite. 4. The students should conclude that volcanoes produce different types of rocks. The samples that the students have are insufficient to conclude if there are diff ...
... Mt. Lassen is in northern California. The last eruption was in the early 1900's. The volcano is dormant and the type of rock is andesite. 4. The students should conclude that volcanoes produce different types of rocks. The samples that the students have are insufficient to conclude if there are diff ...
Seafloor Spreading
... •! Alfred Wegener had a hypothesis that the continents drifted to their presentday locations. But, it was rejected by scientists because they couldn’t think of a force strong enough to move the continents. Seafloor spreading was a hypothesis created by Harry Hess; this was the theory that the seaflo ...
... •! Alfred Wegener had a hypothesis that the continents drifted to their presentday locations. But, it was rejected by scientists because they couldn’t think of a force strong enough to move the continents. Seafloor spreading was a hypothesis created by Harry Hess; this was the theory that the seaflo ...
Sample exam 1
... equally dangerous (or not dangerous), you should state that clearly. 14. On the map of the Aegean Sea below, I’ve marked four volcanoes (the triangles). In order from west to east they are: Methana (2258 years ago), Milos (1860 years ago), Santorini (59 years ago), and Nisyros (121 years ago). Are t ...
... equally dangerous (or not dangerous), you should state that clearly. 14. On the map of the Aegean Sea below, I’ve marked four volcanoes (the triangles). In order from west to east they are: Methana (2258 years ago), Milos (1860 years ago), Santorini (59 years ago), and Nisyros (121 years ago). Are t ...
Chap02 2 TECTONICS OF TAIWAN
... along the decollement. Figure 2.4 shows an image of faulting. The initial break which started around the hypocenter propagated upward along the Chelungpu fault, and downward along the decollement. The rupture within the prism should be slow already. If not, severe damages would have occurred around ...
... along the decollement. Figure 2.4 shows an image of faulting. The initial break which started around the hypocenter propagated upward along the Chelungpu fault, and downward along the decollement. The rupture within the prism should be slow already. If not, severe damages would have occurred around ...
LECTURE 13
... – The accreting plate boundary zone (mid-ocean ridge) at which new oceanic crust is created – The passive crust, which after creation at the ridge axis has moved away. Basalt was first dredged from the ocean floor at the turn of the century and since then extensive sampling programs have shown that ...
... – The accreting plate boundary zone (mid-ocean ridge) at which new oceanic crust is created – The passive crust, which after creation at the ridge axis has moved away. Basalt was first dredged from the ocean floor at the turn of the century and since then extensive sampling programs have shown that ...
Types of Rock
... • Extrusive Rocks: forms when magma erupts onto the Earth’s surface (lava), cools quickly with very small or no crystals formed http://www.windows.ucar.edu/tour/link=/earth/geology/ig_intrusive.html&edu=high&fr=t ...
... • Extrusive Rocks: forms when magma erupts onto the Earth’s surface (lava), cools quickly with very small or no crystals formed http://www.windows.ucar.edu/tour/link=/earth/geology/ig_intrusive.html&edu=high&fr=t ...
rock - Images
... Water, wind, ice, and gravity can erode and move sediments and cause them to collect. • Sediment is another name for small pieces of rock, dirt, or dust. ...
... Water, wind, ice, and gravity can erode and move sediments and cause them to collect. • Sediment is another name for small pieces of rock, dirt, or dust. ...
perception of first-year geology students on the tectonic plates theory
... school knowledge as well as a wider social reality without any connection to the theory of tectonic plates. One of the most interesting insights from this research is the fact that significant difference in the distribution of responses is observed between two similar questions about the convergent ...
... school knowledge as well as a wider social reality without any connection to the theory of tectonic plates. One of the most interesting insights from this research is the fact that significant difference in the distribution of responses is observed between two similar questions about the convergent ...
mantle plumes and hot spots - The Centre for Earth Evolution and
... and age data indicate that these form during short time-spans with much higher eruption rates than are found at present-day hotspots. Examples of continental flood basalts (CFBs) include the Deccan Traps (associated with the Reunion hotspot) and the Parana basalts (associated with the Tristan hotspo ...
... and age data indicate that these form during short time-spans with much higher eruption rates than are found at present-day hotspots. Examples of continental flood basalts (CFBs) include the Deccan Traps (associated with the Reunion hotspot) and the Parana basalts (associated with the Tristan hotspo ...
Geologic History of Chapel Hill
... folded sediments and volcanics. This molten magma cooled to form solidified intrusive igneous rocks consisting of some gabbro, and much more diorite and granite, with smaller dikes of aplite (feldspar and quartz) and mineral veins of epidote and quartz. Much of the gold-bearing rocks in NC are assoc ...
... folded sediments and volcanics. This molten magma cooled to form solidified intrusive igneous rocks consisting of some gabbro, and much more diorite and granite, with smaller dikes of aplite (feldspar and quartz) and mineral veins of epidote and quartz. Much of the gold-bearing rocks in NC are assoc ...
Continental Drift - sciencewithskinner
... • Paleomagnetism of the ocean floor (1960’s) – Magma cools and iron-bearing ...
... • Paleomagnetism of the ocean floor (1960’s) – Magma cools and iron-bearing ...
Drive from UW to Snoqualmie Pass
... occurred late in the ice-age period (Pleistocene). In addition, these stops give a look at the Yakima fold belts, which are caused by a strong north-south compression in the Columbia Basin. These folds shape the topography and control the course of the Bretz flood here at the western margin of the b ...
... occurred late in the ice-age period (Pleistocene). In addition, these stops give a look at the Yakima fold belts, which are caused by a strong north-south compression in the Columbia Basin. These folds shape the topography and control the course of the Bretz flood here at the western margin of the b ...
Flashcard Friday List #6 - Science with Mrs. Barton
... 2 Subscript: A number written slightly below and to the right of a chemical symbol that shows how many atoms of an element are in a compound. Example: 2H2 + O2 2H2O 3 Divergent Boundary: A plate boundary where two plates are moving away from each other and a new crust is forming from magma that ...
... 2 Subscript: A number written slightly below and to the right of a chemical symbol that shows how many atoms of an element are in a compound. Example: 2H2 + O2 2H2O 3 Divergent Boundary: A plate boundary where two plates are moving away from each other and a new crust is forming from magma that ...
platetectonics
... Looking at the world map, what do you notice about the shape of the continents? ...
... Looking at the world map, what do you notice about the shape of the continents? ...
INTRODUCCIÓN: LOS ANDES
... All units described so far, with exception of tha lavas, such as these in the above mentioned paragraphs, are more likely semiconsolidated volcaniclastic accumulations rather than real rock strata. All units with same rock and stability characteristics appear below the platform area of the planned n ...
... All units described so far, with exception of tha lavas, such as these in the above mentioned paragraphs, are more likely semiconsolidated volcaniclastic accumulations rather than real rock strata. All units with same rock and stability characteristics appear below the platform area of the planned n ...
FREE Sample Here
... 3. Demonstrate the relationship between hot spots and surface volcanic chains with a piece of paper and a lighted match. As you move the paper over the match a burn trace is left with the oldest burn at the farthest distance from the match. Be careful! 4. Use this idea to explain mid ocean ridge spr ...
... 3. Demonstrate the relationship between hot spots and surface volcanic chains with a piece of paper and a lighted match. As you move the paper over the match a burn trace is left with the oldest burn at the farthest distance from the match. Be careful! 4. Use this idea to explain mid ocean ridge spr ...
Historical Geology
... • Lithosphere – solid upper mantle and crust – broken into plates that move over the asthenosphere ...
... • Lithosphere – solid upper mantle and crust – broken into plates that move over the asthenosphere ...
KS3 Russia
... the mechanisms by which they have changed position over time (its origins lie with Wegener’s theory of Continental Drift from 1912). Seven major crustal plates and twelve smaller plates have been recognised, each of which extends down into the earth’s upper mantle. These plates are thought to be mov ...
... the mechanisms by which they have changed position over time (its origins lie with Wegener’s theory of Continental Drift from 1912). Seven major crustal plates and twelve smaller plates have been recognised, each of which extends down into the earth’s upper mantle. These plates are thought to be mov ...
spirit 2 - CEENBoT / TekBot Site
... Plate tectonics is the motion of the outer part of the earth called the lithosphere. The lithosphere is comprised of the earth’s crust and upper part of the mantel. Currently, it is thought that there are 8 major plates and many minor plates that are moving across the surface of the earth. The cause ...
... Plate tectonics is the motion of the outer part of the earth called the lithosphere. The lithosphere is comprised of the earth’s crust and upper part of the mantel. Currently, it is thought that there are 8 major plates and many minor plates that are moving across the surface of the earth. The cause ...
Article
... to overturn the long held belief in active volcanism - and substantially reduce the calculated risk for the region. The authors found that the spontaneous combustion of buried peat layers, not magma, caused the subsurface fires. In his original survey of the Lac Faguibine region, about 50 miles west ...
... to overturn the long held belief in active volcanism - and substantially reduce the calculated risk for the region. The authors found that the spontaneous combustion of buried peat layers, not magma, caused the subsurface fires. In his original survey of the Lac Faguibine region, about 50 miles west ...
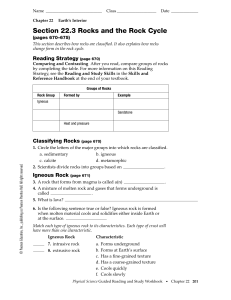
Section 22.3 Rocks and the Rock Cycle
... 10. When sediment is squeezed and cemented together, rocks are formed. 11. Circle the groups into which geologists classify sedimentary rocks. a. clastic rocks b. foliated rocks c. organic rocks d. chemical rocks 12. Sedimentary rocks formed from broken fragments of other rocks are called rocks. 13. ...
... 10. When sediment is squeezed and cemented together, rocks are formed. 11. Circle the groups into which geologists classify sedimentary rocks. a. clastic rocks b. foliated rocks c. organic rocks d. chemical rocks 12. Sedimentary rocks formed from broken fragments of other rocks are called rocks. 13. ...
msword - rgs.org
... the mechanisms by which they have changed position over time (its origins lie with Wegener’s theory of Continental Drift from 1912). Seven major crustal plates and twelve smaller plates have been recognised, each of which extends down into the earth’s upper mantle. These plates are thought to be mov ...
... the mechanisms by which they have changed position over time (its origins lie with Wegener’s theory of Continental Drift from 1912). Seven major crustal plates and twelve smaller plates have been recognised, each of which extends down into the earth’s upper mantle. These plates are thought to be mov ...
A Little Geology Lesson - Department of Earth Sciences
... Igneous rock (derived from the Latin word igneus meaning of fire, from ignis meaning fire) forms through the cooling and solidification of magma or lava. This magma can be derived from partial melts of pre-existing rocks in either a planet's mantle or crust. Typically, the melting of rocks is caused ...
... Igneous rock (derived from the Latin word igneus meaning of fire, from ignis meaning fire) forms through the cooling and solidification of magma or lava. This magma can be derived from partial melts of pre-existing rocks in either a planet's mantle or crust. Typically, the melting of rocks is caused ...
The Earth
... Heat generated by radioactive decay in the Earth creates movement of rock This movement of material is called convection Convection occurs because hotter material will be less dense than its cooler surroundings and consequently will rise while cooler material sinks ...
... Heat generated by radioactive decay in the Earth creates movement of rock This movement of material is called convection Convection occurs because hotter material will be less dense than its cooler surroundings and consequently will rise while cooler material sinks ...
1 - TeacherWeb
... 12. The scientist who proposed the Theory of Continental Drift was a. James Hutton. c. Charles Lyell. b. Alfred Wegener. d. Charles Darwin. 13. A plate boundary at which two plates slide past each other horizontally is a a. divergent boundary. c. convergent boundary. b. transform boundary. d. subdu ...
... 12. The scientist who proposed the Theory of Continental Drift was a. James Hutton. c. Charles Lyell. b. Alfred Wegener. d. Charles Darwin. 13. A plate boundary at which two plates slide past each other horizontally is a a. divergent boundary. c. convergent boundary. b. transform boundary. d. subdu ...
Large igneous province

A large igneous province (LIP) is an extremely large accumulation of igneous rocks, including liquid rock (intrusive) or volcanic rock formations (extrusive), when hot magma extrudes from inside the Earth and flows out. The source of many or all LIPs is variously attributed to mantle plumes or to processes associated with plate tectonics. Types of LIPs can include large volcanic provinces (LVP), created through flood basalt and large plutonic provinces (LPP). Eleven distinct flood basalt episodes occurred in the past 250 million years, creating volcanic provinces, which coincided with mass extinctions in prehistoric times. Formation depends on a range of factors, such as continental configuration, latitude, volume, rate, duration of eruption, style and setting (continental vs. oceanic), the preexisting climate state, and the biota resilience to change.