Ppt_Optl_Garnierite
... • GARNIERITE COMPOSITION 1. Ni-BEARING TALC – WILLEMSEITE ( UP TO 25 WT % Ni) 2. Ni-LIZARDITE – NEPOUITE (UP TO 34 WT% Ni) 3. NI-SEPIOLITE – FALCONDIOTE (UP TO 24 WT% NiZ) LATERIZATION OF ULTRAMAFIC ROCKS • DISSOLUTION & REMOVAL OF Ni & SiO2 TO RESIDUAL CONCENTRATION OF Ni & Fe IN GOETHITE-RICH S ...
... • GARNIERITE COMPOSITION 1. Ni-BEARING TALC – WILLEMSEITE ( UP TO 25 WT % Ni) 2. Ni-LIZARDITE – NEPOUITE (UP TO 34 WT% Ni) 3. NI-SEPIOLITE – FALCONDIOTE (UP TO 24 WT% NiZ) LATERIZATION OF ULTRAMAFIC ROCKS • DISSOLUTION & REMOVAL OF Ni & SiO2 TO RESIDUAL CONCENTRATION OF Ni & Fe IN GOETHITE-RICH S ...
Chapter 8: Geologic Time
... Vast Duration Sediments were buried under a Mountain Range, metamorphosed, half the crust was uplifted & eroded, glaciers carried it, lake storms removed all but the biggest rocks. ...
... Vast Duration Sediments were buried under a Mountain Range, metamorphosed, half the crust was uplifted & eroded, glaciers carried it, lake storms removed all but the biggest rocks. ...
The viability and style of the modern plate
... subduction below an 5-cm/yr overriding plate is followed by a sudden drop in vconv and vrms , as a result of the removed overriding plate motion. Subduction then slowly develops until the slab reaches 400 km depth, and the subduction is reinforced by the extra phase buoyancy of the exothermic olivin ...
... subduction below an 5-cm/yr overriding plate is followed by a sudden drop in vconv and vrms , as a result of the removed overriding plate motion. Subduction then slowly develops until the slab reaches 400 km depth, and the subduction is reinforced by the extra phase buoyancy of the exothermic olivin ...
Can Ocean Tides Drive the Continents?
... bia moving faster than the African plate. The fastest-moving plates are those in which a large part of the plate boundary is a subduction zone, and the slower-moving plates are those that lack subducting boundaries or that have large continental blocks embedded in them. This relation has been interp ...
... bia moving faster than the African plate. The fastest-moving plates are those in which a large part of the plate boundary is a subduction zone, and the slower-moving plates are those that lack subducting boundaries or that have large continental blocks embedded in them. This relation has been interp ...
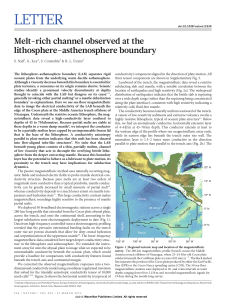
Melt-rich channel observed at the lithosphere
... to coincide with our observed high-conductivity layer. This intersection may culminate in a freezing front where melt solidifies owing to the colder temperatures above. We infer that this freezing front forms a permeability barrier that traps buoyant melt beneath, rather than allowing it to percolat ...
... to coincide with our observed high-conductivity layer. This intersection may culminate in a freezing front where melt solidifies owing to the colder temperatures above. We infer that this freezing front forms a permeability barrier that traps buoyant melt beneath, rather than allowing it to percolat ...
Slide 1 - Linn-Benton Community College
... and tons of sediment annually “sediment gorged” – huge deltas on margins • Only 200 million years old • Average depth – 2.2 mi • “Limestone ocean” due to warm sea temperatures • Significantly fewer islands, seamounts &guyots than Pacific ...
... and tons of sediment annually “sediment gorged” – huge deltas on margins • Only 200 million years old • Average depth – 2.2 mi • “Limestone ocean” due to warm sea temperatures • Significantly fewer islands, seamounts &guyots than Pacific ...
What Causes EARTHQUAKES?
... caused by a catastrophic event resulting from plate movements and design possible devices or solutions to minimize the effects of that event on Earth’s surface and/or human structures. WHAT IS AN EARTHQUAKE? ______________________ are vibrations produced when rocks break along a _______________. The ...
... caused by a catastrophic event resulting from plate movements and design possible devices or solutions to minimize the effects of that event on Earth’s surface and/or human structures. WHAT IS AN EARTHQUAKE? ______________________ are vibrations produced when rocks break along a _______________. The ...
Discussion Answers
... Yes. Divergent boundaries produce new crust and are red on the map. Convergent boundaries occur when plates collide and colors are very different. See the collision of Philippine ...
... Yes. Divergent boundaries produce new crust and are red on the map. Convergent boundaries occur when plates collide and colors are very different. See the collision of Philippine ...
Unit 3 Rocks and Minerals
... Glossary for Rocks and Minerals Mineral – is a naturally occurring solid crystalline substance with a distinct chemical composition and is usually inorganic. Rock – is an assemblage of minerals usually cemented together. It may contain only one type of mineral or many. Rock Type Classification – thi ...
... Glossary for Rocks and Minerals Mineral – is a naturally occurring solid crystalline substance with a distinct chemical composition and is usually inorganic. Rock – is an assemblage of minerals usually cemented together. It may contain only one type of mineral or many. Rock Type Classification – thi ...
Earth / Environmental Science Ch. 8 – EARTHQUAKES AND
... z A seismogram shows all three types of seismic waves – surface waves, P waves and S waves. z P waves arrive at the recording station first, followed by S waves, followed by the surface waves. z These waves travel at different speeds. z Generally, P waves travel 1.7 times faster than S waves. z Surf ...
... z A seismogram shows all three types of seismic waves – surface waves, P waves and S waves. z P waves arrive at the recording station first, followed by S waves, followed by the surface waves. z These waves travel at different speeds. z Generally, P waves travel 1.7 times faster than S waves. z Surf ...
5th Grade Discovery Lab - Summit Hill Elementary PTO
... Discussion: We need to explain the main layers of the earth; the core, mantle and crust. Explain you have two eggs: one hard boiled and one raw. Take the hard boiled egg, which is one solid mass and spin it. Stop it. Have the children visualize how since everything is solid, everything stops at the ...
... Discussion: We need to explain the main layers of the earth; the core, mantle and crust. Explain you have two eggs: one hard boiled and one raw. Take the hard boiled egg, which is one solid mass and spin it. Stop it. Have the children visualize how since everything is solid, everything stops at the ...
Expedition Worksheet, if you do not have course workbook
... point to cause the material to fracture, thereby sending seismic waves through the Earth…..and strong rock only is found in the rigid lithosphere…deeper in the Earth the temperatures are too high allowing the rocks to flow rather than fracture. 3. Undersea Earthquakes and Plate Boundaries You now se ...
... point to cause the material to fracture, thereby sending seismic waves through the Earth…..and strong rock only is found in the rigid lithosphere…deeper in the Earth the temperatures are too high allowing the rocks to flow rather than fracture. 3. Undersea Earthquakes and Plate Boundaries You now se ...
Professor`s Notes: The black and blue text are those of
... preexisting faults. Motions along faults are explained by plate tectonics theory. These mobile plates interact with neighboring plates, straining and deforming the rocks at their margins. It is along faults associated with plate boundaries that most earthquakes occur. ...
... preexisting faults. Motions along faults are explained by plate tectonics theory. These mobile plates interact with neighboring plates, straining and deforming the rocks at their margins. It is along faults associated with plate boundaries that most earthquakes occur. ...
What type of volcano?
... What conditions would the laboratory need to duplicate to create synthetic gems? 2. Metamorphic rocks are formed at various depths in the Earth. Why would the depth at which a rock forms determine its type? 3. Explain why metamorphic rock will form neither synthetically nor naturally if the temperat ...
... What conditions would the laboratory need to duplicate to create synthetic gems? 2. Metamorphic rocks are formed at various depths in the Earth. Why would the depth at which a rock forms determine its type? 3. Explain why metamorphic rock will form neither synthetically nor naturally if the temperat ...
Hard Rocks Questions
... 2. Different gems are different colors because they a. have different lights shining on them. b. take on the color of the background they are placed on. c. are dyed to increase their sparkle. d. are formed from different minerals. 3. In the sentence, “Diamonds are born hundreds of miles below Earth' ...
... 2. Different gems are different colors because they a. have different lights shining on them. b. take on the color of the background they are placed on. c. are dyed to increase their sparkle. d. are formed from different minerals. 3. In the sentence, “Diamonds are born hundreds of miles below Earth' ...
Some reflections on the charts of the ocean floor: Do they hide more
... subduction by logically considering that the centered position of the “mid”ocean ridge of the Pacific was spoiled by differing rates of subduction along its borders. The impression is that along North America not only the eastern half of the ocean disappeared by subduction but also the ridge itself ...
... subduction by logically considering that the centered position of the “mid”ocean ridge of the Pacific was spoiled by differing rates of subduction along its borders. The impression is that along North America not only the eastern half of the ocean disappeared by subduction but also the ridge itself ...
Why Africa is being torn apart
... • 8. crust. The pressure is forcing the African continent to • 3. break and separate. This Great Rift Valley is a constructive plate • 10. margin where the plates are • 6. slowly moving • 1. away from each other. The molten • 11. rock continues to push the crust • 2. apart creating new crust as it d ...
... • 8. crust. The pressure is forcing the African continent to • 3. break and separate. This Great Rift Valley is a constructive plate • 10. margin where the plates are • 6. slowly moving • 1. away from each other. The molten • 11. rock continues to push the crust • 2. apart creating new crust as it d ...
Lecture Outlines Natural Disasters, 6th edition
... Plate-Tectonic Setting of Volcanoes • No volcanism associated with transform faults or continentcontinent collisions • Oceanic volcanoes are peaceful • Subduction-zone volcanoes are explosive and dangerous – Subduction zones last tens of millions of years – Volcanoes may be active any time, with ce ...
... Plate-Tectonic Setting of Volcanoes • No volcanism associated with transform faults or continentcontinent collisions • Oceanic volcanoes are peaceful • Subduction-zone volcanoes are explosive and dangerous – Subduction zones last tens of millions of years – Volcanoes may be active any time, with ce ...
snack tectonics - kmstorres
... 1. Use the spoon to spread the frosting into a layer about 0.5 cm thick. In this model, the frosting represents the______________________________________, the layer on which Earth’s plates ride. The ___________in this model are represented by the fruit roll ups (oceanic crust which is thin and dense ...
... 1. Use the spoon to spread the frosting into a layer about 0.5 cm thick. In this model, the frosting represents the______________________________________, the layer on which Earth’s plates ride. The ___________in this model are represented by the fruit roll ups (oceanic crust which is thin and dense ...
lesson 24 effects of ash fall
... Magma is buoyont, and lighter than the solid rock that surrounds it, which is why it rises. ...
... Magma is buoyont, and lighter than the solid rock that surrounds it, which is why it rises. ...
Sea Floor Spreading - Sterlingmontessoriscience
... He conjectured that hot material rose at the oceanic ridges, thus explaining the high heat flow and basaltic volcanic activity, and why the ocean floor is bulged up at the ridges. He further thought that where continent and ocean meet, at the trenches, ocean crust is being returned to the mantle at ...
... He conjectured that hot material rose at the oceanic ridges, thus explaining the high heat flow and basaltic volcanic activity, and why the ocean floor is bulged up at the ridges. He further thought that where continent and ocean meet, at the trenches, ocean crust is being returned to the mantle at ...
Large igneous province

A large igneous province (LIP) is an extremely large accumulation of igneous rocks, including liquid rock (intrusive) or volcanic rock formations (extrusive), when hot magma extrudes from inside the Earth and flows out. The source of many or all LIPs is variously attributed to mantle plumes or to processes associated with plate tectonics. Types of LIPs can include large volcanic provinces (LVP), created through flood basalt and large plutonic provinces (LPP). Eleven distinct flood basalt episodes occurred in the past 250 million years, creating volcanic provinces, which coincided with mass extinctions in prehistoric times. Formation depends on a range of factors, such as continental configuration, latitude, volume, rate, duration of eruption, style and setting (continental vs. oceanic), the preexisting climate state, and the biota resilience to change.