Simple Harmonic Motion ILAP
... Energy, the total amount of energy (kinetic and potential) is the same at all times in this system, ignoring air friction. We will show that a sinusoidal position function is the solution to the associated differential equation. [If you would like to add any comments about what you hope to achieve f ...
... Energy, the total amount of energy (kinetic and potential) is the same at all times in this system, ignoring air friction. We will show that a sinusoidal position function is the solution to the associated differential equation. [If you would like to add any comments about what you hope to achieve f ...
Work - TeacherWeb
... When net work due to all forces acting upon an object is positive, the kinetic energy of the object will increase. When net work due to all forces acting upon an object is negative, the kinetic energy of the object will decrease. When there is no net work acting upon an object, the kinetic energy of ...
... When net work due to all forces acting upon an object is positive, the kinetic energy of the object will increase. When net work due to all forces acting upon an object is negative, the kinetic energy of the object will decrease. When there is no net work acting upon an object, the kinetic energy of ...
lecture23
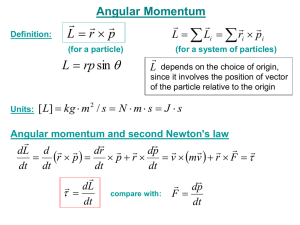
... speed is v2. What is the angular speed ω of the stick after the collision? External forces: weight of the stick and force on the stick by the pivoting axle produce no torque. Weight of the bullet is negligible. ...
... speed is v2. What is the angular speed ω of the stick after the collision? External forces: weight of the stick and force on the stick by the pivoting axle produce no torque. Weight of the bullet is negligible. ...
Unit 5 Notes
... Momentum in an isolated system is conserved. That is, it is not lost or gained when a process occurs. An isolated system is one in which there are no outside forces. The most common application of this is in collisions. There are two main types of collisions, elastic, and inelastic. This has nothing ...
... Momentum in an isolated system is conserved. That is, it is not lost or gained when a process occurs. An isolated system is one in which there are no outside forces. The most common application of this is in collisions. There are two main types of collisions, elastic, and inelastic. This has nothing ...
Orbital Motion
... A playful astronaut releases a bowling ball, of mass = 7.20 kg, into circular orbit about Earth at an altitude of 350 km. (a) What is the mechanical energy of the ball in its orbit? (b) What is the mechanical energy of the ball on the launch pad at Cape Canaveral? (c) What is the change in the ball’ ...
... A playful astronaut releases a bowling ball, of mass = 7.20 kg, into circular orbit about Earth at an altitude of 350 km. (a) What is the mechanical energy of the ball in its orbit? (b) What is the mechanical energy of the ball on the launch pad at Cape Canaveral? (c) What is the change in the ball’ ...
Unit 1
... • Each element has a number of electrons equal to the number of protons • The electron orbitals are different for each element, and the energy differences between the orbitals are unique as well. • This means that if we can detect the energy emitted or absorbed by an atom during an electronic transi ...
... • Each element has a number of electrons equal to the number of protons • The electron orbitals are different for each element, and the energy differences between the orbitals are unique as well. • This means that if we can detect the energy emitted or absorbed by an atom during an electronic transi ...
VI. Conservation of Energy and Momentum C. Momentum 12. The
... The Titanic hit an iceberg estimated to be half of her mass. Before hitting the iceberg, the Titanic was estimated to be going 22 knots (11.3 m/s). After hitting the iceberg, the Titanic was estimated to be going about 6.0 knots (3.1 m/s). How fast was the iceberg going after the collision? ...
... The Titanic hit an iceberg estimated to be half of her mass. Before hitting the iceberg, the Titanic was estimated to be going 22 knots (11.3 m/s). After hitting the iceberg, the Titanic was estimated to be going about 6.0 knots (3.1 m/s). How fast was the iceberg going after the collision? ...
DES601-Module13
... equation, such as Manning’s equation, Chezy equation, Darcy-Weisbach equation or HazenWilliams (water only!) ...
... equation, such as Manning’s equation, Chezy equation, Darcy-Weisbach equation or HazenWilliams (water only!) ...
Date ______ Period _____ CP Physics PRACTICE Quiz Work
... DEGREE MODE, and include proper units with your answer. In order to clear his driveway of 18+ inches of snow from a recent storm, disgruntled Mr. Bradshaw pushed down on his shovel with a force of 400 N at an angle of 35 degrees. Assume the snow in question has a mass of 20 kg. If he pushed the snow ...
... DEGREE MODE, and include proper units with your answer. In order to clear his driveway of 18+ inches of snow from a recent storm, disgruntled Mr. Bradshaw pushed down on his shovel with a force of 400 N at an angle of 35 degrees. Assume the snow in question has a mass of 20 kg. If he pushed the snow ...