Sect. 5.2 (IA)
... Line Distribution: (one d; M = ∫ρ(r)ds) Φ = - G ∫[ρ(r)ds/r] Integral over line Γ ...
... Line Distribution: (one d; M = ∫ρ(r)ds) Φ = - G ∫[ρ(r)ds/r] Integral over line Γ ...
Ch6Lecture1
... Energy = ability to change the condition of matter 1) When you add energy to a system, something must change 2) Heat is a form of Energy a) Heat a beaker of water b) Motion of the water as it boils c) Vaporization of the water into steam 3) Push down a spring—the spring changes shape then snaps back ...
... Energy = ability to change the condition of matter 1) When you add energy to a system, something must change 2) Heat is a form of Energy a) Heat a beaker of water b) Motion of the water as it boils c) Vaporization of the water into steam 3) Push down a spring—the spring changes shape then snaps back ...
Test Review - Ms. Gamm
... 8. The two blocks of masses M shown above initially travel at the same speed v but in opposite directions. Momentum is conserved as they collide and stick together. How much mechanical energy is lost to other forms of energy during the collision? a. zero b. ½Mv2 c.Mv2 d. 34 Mv2 e. 23 Mv2 9. A 5kg ba ...
... 8. The two blocks of masses M shown above initially travel at the same speed v but in opposite directions. Momentum is conserved as they collide and stick together. How much mechanical energy is lost to other forms of energy during the collision? a. zero b. ½Mv2 c.Mv2 d. 34 Mv2 e. 23 Mv2 9. A 5kg ba ...
The Atwood Machine
... Newton's first law of motion states that objects at rest remain at rest unless an unbalanced force is applied. The second law of motion describes what happens if the resultant force is different from zero. If the acceleration is constant, the body is said to be moving with uniformly accelerated moti ...
... Newton's first law of motion states that objects at rest remain at rest unless an unbalanced force is applied. The second law of motion describes what happens if the resultant force is different from zero. If the acceleration is constant, the body is said to be moving with uniformly accelerated moti ...
Midterm 1 PHOTO ID SIT IN YOUR REQUIRED!
... smaller is its acceleration? And similar questions involving the other equations.. ...
... smaller is its acceleration? And similar questions involving the other equations.. ...
Document
... you can find the work by finding • A) The area under a curve of Force as a function of time • B) The area under a curve of Force as a function of displacement • C) The slope curve of Force as a function of time • D) The slope of a curve of Force as a function of displacement ...
... you can find the work by finding • A) The area under a curve of Force as a function of time • B) The area under a curve of Force as a function of displacement • C) The slope curve of Force as a function of time • D) The slope of a curve of Force as a function of displacement ...
Impulse, momentum, and center of mass
... Because force and velocity are vectors, impulse and momentum are also vectors, quantities often analyzed in two dimensions. If the net external force acting on a system is zero, the total momentum of the system remains constant. Symbolically, if ΣFexternal = 0 For the center of mass, Rcm = ...
... Because force and velocity are vectors, impulse and momentum are also vectors, quantities often analyzed in two dimensions. If the net external force acting on a system is zero, the total momentum of the system remains constant. Symbolically, if ΣFexternal = 0 For the center of mass, Rcm = ...
First Semester Final Practice
... person stands against the wall, and after the cylinder is rotating at a certain rate the floor drops away. The person remains ‘stuck’ in position against the wall - like a fly. ...
... person stands against the wall, and after the cylinder is rotating at a certain rate the floor drops away. The person remains ‘stuck’ in position against the wall - like a fly. ...
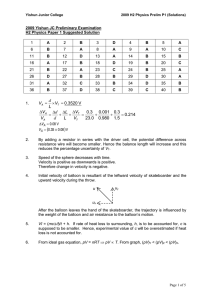
(8%) Write (a) the mass-balance expression and (b) the charge-balance equation
... wavefunction for Hz in a excited state with Sz= 0. 4s= (hint: express it in tenns of a(l),a(2),P(1) and P(2). YT = y$s= (1~ ~ ( 1 ) ls~(2)- 1S A ( ~1)s~(1))+s. You may ignore the normalization factor). c. Give the coefficient k- for the sp2 hybrid orbital ~ h =y (2s+h2pz) in BH3 pointing to the HI a ...
... wavefunction for Hz in a excited state with Sz= 0. 4s= (hint: express it in tenns of a(l),a(2),P(1) and P(2). YT = y$s= (1~ ~ ( 1 ) ls~(2)- 1S A ( ~1)s~(1))+s. You may ignore the normalization factor). c. Give the coefficient k- for the sp2 hybrid orbital ~ h =y (2s+h2pz) in BH3 pointing to the HI a ...
inertial fictitious forces - Tennessee State University
... Note. Kinetic energy is used to describe the motion of an object. When an object is approximated by a particle, the kinetic energy defined above is called the translational kinetic energy of the object. ...
... Note. Kinetic energy is used to describe the motion of an object. When an object is approximated by a particle, the kinetic energy defined above is called the translational kinetic energy of the object. ...
Conservation of Energy
... List the points in order from the point where the car would have the greatest potential energy to the point where it would have the least potential energy. ...
... List the points in order from the point where the car would have the greatest potential energy to the point where it would have the least potential energy. ...
Transparancies for Dynamics - University of Manchester
... Conservative & Dissipative Forces • For a system conserving K.E. + P.E., then – Conservative forces ...
... Conservative & Dissipative Forces • For a system conserving K.E. + P.E., then – Conservative forces ...
PHYSICAL SCIENCE WORKSHEET CONSERVATION OF ENERGY #2 Name:________________________________________________ Date:___________________ Class:_____________
... List the points in order from the point where the car would have the greatest potential energy to the point where it would have the least potential energy. ...
... List the points in order from the point where the car would have the greatest potential energy to the point where it would have the least potential energy. ...