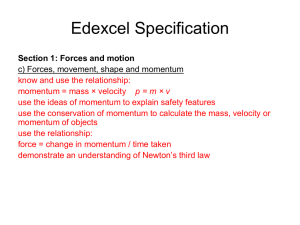
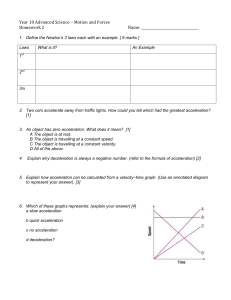
Forces - SCHOOLinSITES
... Newton’s 2nd Law of Motion – states that the unbalanced force acting on an object equals the object’s mass times its acceleration. It connects force, mass, and acceleration in the equation a = f / m, acceleration = net force / mass, ...
... Newton’s 2nd Law of Motion – states that the unbalanced force acting on an object equals the object’s mass times its acceleration. It connects force, mass, and acceleration in the equation a = f / m, acceleration = net force / mass, ...
Assignment of Laws of Motion
... Q4. what is the inertial frame of reference? Q5. A 50gm bullet is fired from 10kg gun with velocity of 500m/s what is the speed of recoil of gun? Q6. A force of 98 N just required to move a mass of 45 kg on a rough surface find the coefficient of friction and angle of friction? Q7.For the next sever ...
... Q4. what is the inertial frame of reference? Q5. A 50gm bullet is fired from 10kg gun with velocity of 500m/s what is the speed of recoil of gun? Q6. A force of 98 N just required to move a mass of 45 kg on a rough surface find the coefficient of friction and angle of friction? Q7.For the next sever ...
Ball 1 of mass m moving right with speed v bounces off ball 2 with
... Answer: This one is tricky. The hoop goes faster at the top. Both hoop and puck have the same KEtrans = (1/2)mv2, but , in addition, the hoop has some KErot. In going up the hill, both hoop and puck lose the same amount of KE (KE = –mgh). But for the puck, all of its lost KE was translational KE. W ...
... Answer: This one is tricky. The hoop goes faster at the top. Both hoop and puck have the same KEtrans = (1/2)mv2, but , in addition, the hoop has some KErot. In going up the hill, both hoop and puck lose the same amount of KE (KE = –mgh). But for the puck, all of its lost KE was translational KE. W ...
Cuestionario Capítulo 1
... E) The force the particle experiences is a negative restoring force. 31. A body moving in simple harmonic motion has maximum acceleration when it has A) maximum velocity. D) minimum kinetic energy. B) maximum kinetic energy. E) zero displacement. C) minimum potential energy. 32. The displacement in ...
... E) The force the particle experiences is a negative restoring force. 31. A body moving in simple harmonic motion has maximum acceleration when it has A) maximum velocity. D) minimum kinetic energy. B) maximum kinetic energy. E) zero displacement. C) minimum potential energy. 32. The displacement in ...
IGCSE-14-Momentum
... velocity to fall to zero. The time taken for their passenger’s ________ momentum to fall to ______zero is also increased. Therefore the _______ exertedforce on the driver or passenger is __________ decreased injury and so is the potential ________ caused. WORD SELECTION: time velocity zero momentum ...
... velocity to fall to zero. The time taken for their passenger’s ________ momentum to fall to ______zero is also increased. Therefore the _______ exertedforce on the driver or passenger is __________ decreased injury and so is the potential ________ caused. WORD SELECTION: time velocity zero momentum ...
Interm Exam Summer 2014 Solution Set
... our efforts to advance understanding in the education of mathematics. We believe this constitutes a ’fair use’ of any such copyrighted material as provided by the TRNC or EU Copyright Law. This document is distributed without profit to those who have expressed a prior interest in receiving the inclu ...
... our efforts to advance understanding in the education of mathematics. We believe this constitutes a ’fair use’ of any such copyrighted material as provided by the TRNC or EU Copyright Law. This document is distributed without profit to those who have expressed a prior interest in receiving the inclu ...
F = force, m = mass, a = acceleration
... Now imagine we make the ball twice as big (double the mass) but keep the acceleration constant. F = ma says that this new ball has twice the force of the old ball. Now imagine the original ball moving at twice the original acceleration. F = ma says that the ball will again have twice the force of th ...
... Now imagine we make the ball twice as big (double the mass) but keep the acceleration constant. F = ma says that this new ball has twice the force of the old ball. Now imagine the original ball moving at twice the original acceleration. F = ma says that the ball will again have twice the force of th ...
Work, Energy, Power, Momentum
... friends to pull them back (the same distance from the bottom of the swing) and let them go. When they collide in the center, which way do they swing (as a heap), if any? What if Fred was pulled higher than George before release? • A 100 kg ogre clobbers a dainty 50 kg figure skater while trying to l ...
... friends to pull them back (the same distance from the bottom of the swing) and let them go. When they collide in the center, which way do they swing (as a heap), if any? What if Fred was pulled higher than George before release? • A 100 kg ogre clobbers a dainty 50 kg figure skater while trying to l ...
Work, Energy, Power, Momentum - ICP
... friends to pull them back (the same distance from the bottom of the swing) and let them go. When they collide in the center, which way do they swing (as a heap), if any? What if Fred was pulled higher than George before release? • A 100 kg ogre clobbers a dainty 50 kg figure skater while trying to l ...
... friends to pull them back (the same distance from the bottom of the swing) and let them go. When they collide in the center, which way do they swing (as a heap), if any? What if Fred was pulled higher than George before release? • A 100 kg ogre clobbers a dainty 50 kg figure skater while trying to l ...
98ST_Q
... (b) (1) Calculate the value of the gravitational field strength in the orbit. (2) Calculate the speed and period of the shuttle in the orbit. (c) (1) Show that the total mechanical energy of the shuttle is proportional to –1/r, where r is the radius of its orbit. (2) In order to overtake the telesco ...
... (b) (1) Calculate the value of the gravitational field strength in the orbit. (2) Calculate the speed and period of the shuttle in the orbit. (c) (1) Show that the total mechanical energy of the shuttle is proportional to –1/r, where r is the radius of its orbit. (2) In order to overtake the telesco ...
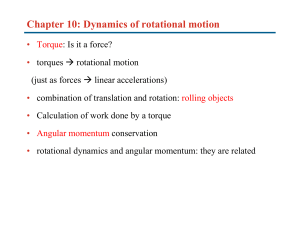
Chapter 10: Dynamics of rotational motion
... • Torque: Is it a force? • torques rotational motion (just as forces linear accelerations) • combination of translation and rotation: rolling objects • Calculation of work done by a torque • Angular momentum conservation • rotational dynamics and angular momentum: they are related ...
... • Torque: Is it a force? • torques rotational motion (just as forces linear accelerations) • combination of translation and rotation: rolling objects • Calculation of work done by a torque • Angular momentum conservation • rotational dynamics and angular momentum: they are related ...