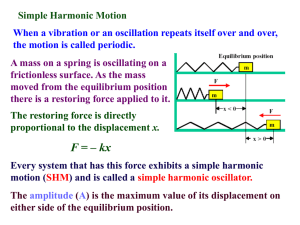
energy - Humble ISD
... able to trace the circuit from the positive end of the battery all the way around to the negative end without a break. Ohm’s Law relates current to voltage and resistance. ...
... able to trace the circuit from the positive end of the battery all the way around to the negative end without a break. Ohm’s Law relates current to voltage and resistance. ...
Name
... a rope to the pumpkin on which you pull upward at an angle of 40.0 degrees with a force of 650.0 N. If the coefficient of friction between the pumpkin and the ground is 0.25 (a) what is the net force acting on the pumpkin? (b) What will the acceleration of the pumpkin be? (c) How far will the pumpki ...
... a rope to the pumpkin on which you pull upward at an angle of 40.0 degrees with a force of 650.0 N. If the coefficient of friction between the pumpkin and the ground is 0.25 (a) what is the net force acting on the pumpkin? (b) What will the acceleration of the pumpkin be? (c) How far will the pumpki ...
here
... For the following problems, solve for any unknowns. Show all work and box all answers. Unclear work will not be graded. Use g=10m/s2. Write the conservation of energy equations for any mathematical problem. 1. Describe the law of conservation of energy in your own terms. 2. What are the units for: a ...
... For the following problems, solve for any unknowns. Show all work and box all answers. Unclear work will not be graded. Use g=10m/s2. Write the conservation of energy equations for any mathematical problem. 1. Describe the law of conservation of energy in your own terms. 2. What are the units for: a ...
IV. Force & Acceleration - Lamar County School District
... • Recall that when an object slows down it is accelerating. • By Newton’s second law, if the skateboard is accelerating, there must be a net force acting on it. • The force that slows the skateboard and brings it to a stop is friction. ...
... • Recall that when an object slows down it is accelerating. • By Newton’s second law, if the skateboard is accelerating, there must be a net force acting on it. • The force that slows the skateboard and brings it to a stop is friction. ...
Physics Review
... what would be the frequency of the sound you hear if the source is producing a frequency of 410 Hz? Assume that the temperature is 25oC. 12. What is the threshold of hearing? What is the threshold of pain? How many decibels is normal conversation? At what point is damage being done to your ear? 13. ...
... what would be the frequency of the sound you hear if the source is producing a frequency of 410 Hz? Assume that the temperature is 25oC. 12. What is the threshold of hearing? What is the threshold of pain? How many decibels is normal conversation? At what point is damage being done to your ear? 13. ...
PHYSICS
... website and Moodle to keep up if you are out. You are expected to be aware of what was missed during an absence prior to returning to class. Notebook suggestions: Your notebook should be a three-ring binder of about 1.5-inch width. The notebook is not graded, however, the course is cumulative in nat ...
... website and Moodle to keep up if you are out. You are expected to be aware of what was missed during an absence prior to returning to class. Notebook suggestions: Your notebook should be a three-ring binder of about 1.5-inch width. The notebook is not graded, however, the course is cumulative in nat ...
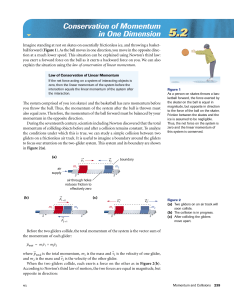
Student Text, pp. 239-245
... of the person, Earth’s change in velocity when the person lands is, of course, too small to measure. The person–Earth system is isolated, but the person–deck system is not. Experiments can be performed to determine if momentum is conserved in a variety of collisions. However, much more can be learne ...
... of the person, Earth’s change in velocity when the person lands is, of course, too small to measure. The person–Earth system is isolated, but the person–deck system is not. Experiments can be performed to determine if momentum is conserved in a variety of collisions. However, much more can be learne ...