Describing Motion - Science
... First we need to define the word FORCE: • The cause of motion (what causes objects to move) • Two types of forces – Pushes – Pulls ...
... First we need to define the word FORCE: • The cause of motion (what causes objects to move) • Two types of forces – Pushes – Pulls ...
Chapter9
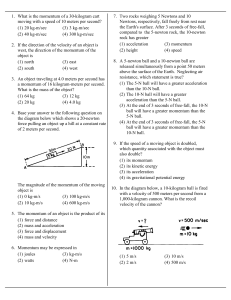
... Assume the ultimate strength of legos is 4.0x104 Pa. If the density of legos is 150 kg/m3, what is the maximum possible height for a lego tower? ...
... Assume the ultimate strength of legos is 4.0x104 Pa. If the density of legos is 150 kg/m3, what is the maximum possible height for a lego tower? ...
worksheet 4
... 1. When one object exerts a force on a second object, the second object exerts a force that is equal in size and opposite in direction. 2. The backward "kick" of a rifle that is fired is an example of a(n) __ force. 3. The total amount of momentum of a group of objects does not change unless outside ...
... 1. When one object exerts a force on a second object, the second object exerts a force that is equal in size and opposite in direction. 2. The backward "kick" of a rifle that is fired is an example of a(n) __ force. 3. The total amount of momentum of a group of objects does not change unless outside ...
Review - Flipped Physics
... 3. An object travels for 8.00 seconds with an average speed of 160 meters per second. The distance traveled by the object is a) 20.0 m b) 200 m c) 1280 m d) 2560 m 4. A car is accelerated at 4.0 meters per second 2 from rest. The car will reach a speed of 28 meters per second at the end of a) 3.5 m ...
... 3. An object travels for 8.00 seconds with an average speed of 160 meters per second. The distance traveled by the object is a) 20.0 m b) 200 m c) 1280 m d) 2560 m 4. A car is accelerated at 4.0 meters per second 2 from rest. The car will reach a speed of 28 meters per second at the end of a) 3.5 m ...
Force (or free-body) diagrams
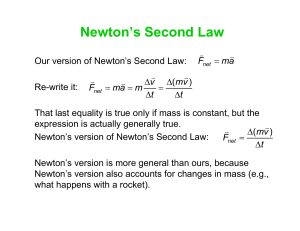
... • Investigate the relationship between mass, force, and acceleration. • State Newton’s second law and give examples to illustrate the law. • Draw an accurate free body diagram locating each of the forces acting on an object or a system of objects. • Use free body diagrams and Newton's laws of motion ...
... • Investigate the relationship between mass, force, and acceleration. • State Newton’s second law and give examples to illustrate the law. • Draw an accurate free body diagram locating each of the forces acting on an object or a system of objects. • Use free body diagrams and Newton's laws of motion ...
Slide 1
... 6) At the strike of midnight, a new-year’s reveler shoots his .357 Remington, aimed upwards at a 45° angle. How far away does the bullet land? vmuzzle = 46 m/s R=(v2/g)sin2θ = [(46 m/s)2/9.8 m/s] × (sin90°) R=216 m At what time does the bullet go through your living room window? (Magic: vhorizontal ...
... 6) At the strike of midnight, a new-year’s reveler shoots his .357 Remington, aimed upwards at a 45° angle. How far away does the bullet land? vmuzzle = 46 m/s R=(v2/g)sin2θ = [(46 m/s)2/9.8 m/s] × (sin90°) R=216 m At what time does the bullet go through your living room window? (Magic: vhorizontal ...
I. Force, Mass, and Acceleration
... º Thrown objects tend to curve downward. º Anything thrown or shot through the air is a projectile. º Projectiles curve because of inertia and gravity. º They have a horizontal (the throw) and vertical (gravity) velocities. Horizontal and Vertical Motion º When you throw a ball you give it horizonta ...
... º Thrown objects tend to curve downward. º Anything thrown or shot through the air is a projectile. º Projectiles curve because of inertia and gravity. º They have a horizontal (the throw) and vertical (gravity) velocities. Horizontal and Vertical Motion º When you throw a ball you give it horizonta ...
12. Work Power & Energy
... Total work done by all the forces acting on a body is equal to the change in its kinetic energy. ...
... Total work done by all the forces acting on a body is equal to the change in its kinetic energy. ...
Work, Energy and Power - Thomas Tallis Science
... The law of conservation of energy states that: Energy cannot be created, or destroyed; it can only be changed into another form. In other words, the total energy of a system is constant. A bungee jumper’s gravitational potential energy is changed into kinetic energy as they jump, and then stored as ...
... The law of conservation of energy states that: Energy cannot be created, or destroyed; it can only be changed into another form. In other words, the total energy of a system is constant. A bungee jumper’s gravitational potential energy is changed into kinetic energy as they jump, and then stored as ...
Forces and Motion
... and opposite force on the first object • Momentum – Product of an object’s mass and its velocity – Objects momentum at rest is zero – Unit kg m/s ...
... and opposite force on the first object • Momentum – Product of an object’s mass and its velocity – Objects momentum at rest is zero – Unit kg m/s ...
Experiment 13 The Motion of a Beach Ball in the Air
... In this experiment we attempt to minimize the effects of the drag force, so we can accurately measure the buoyant force and the added mass. Our experiment consists of throwing a ball up in the air and observing its motion with an ultrasonic motion sensor (see Fig. 1). The position versus time data n ...
... In this experiment we attempt to minimize the effects of the drag force, so we can accurately measure the buoyant force and the added mass. Our experiment consists of throwing a ball up in the air and observing its motion with an ultrasonic motion sensor (see Fig. 1). The position versus time data n ...