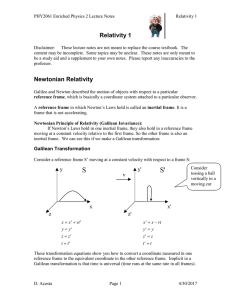
Relativity1
... although nobody knew what this ether was. It was supposed that this ether might be at rest with respect to the solar system, or maybe the galaxy. In any case, the Earth would move through this ether, and we should observe light traveling at a speed different than c. The issue was settled experimenta ...
... although nobody knew what this ether was. It was supposed that this ether might be at rest with respect to the solar system, or maybe the galaxy. In any case, the Earth would move through this ether, and we should observe light traveling at a speed different than c. The issue was settled experimenta ...
Reading Graphs and Interpreting slope: A math/Science
... PS3.B: Conservation of Energy /Energy Transfer What is meant by conservation of energy? How is energy transferred between objects or systems? PS3.C: Relationship Between Energy and Forces How are forces related to energy? ...
... PS3.B: Conservation of Energy /Energy Transfer What is meant by conservation of energy? How is energy transferred between objects or systems? PS3.C: Relationship Between Energy and Forces How are forces related to energy? ...
to full article
... your side stick shakes. The First Flight Officer wakes up to the situation and he pushes his side control forward to unstall the wings. You are now pulling and he is pushing and the autopilot goes “wazimu” and does not know what is happening. The Airbus does not know very well what to do either and ...
... your side stick shakes. The First Flight Officer wakes up to the situation and he pushes his side control forward to unstall the wings. You are now pulling and he is pushing and the autopilot goes “wazimu” and does not know what is happening. The Airbus does not know very well what to do either and ...
AP Physics - Circular Motion Lab
... Discussion: We have been studying circular motion and have talked about what causes circular motion. Our discussion led us to the conclusion that centripetal forces (forces that redirect an object so that it will turn continuously and end up in circular motion) are really other forces such as normal ...
... Discussion: We have been studying circular motion and have talked about what causes circular motion. Our discussion led us to the conclusion that centripetal forces (forces that redirect an object so that it will turn continuously and end up in circular motion) are really other forces such as normal ...
Transfer Functions
... The transfer function defined above was expressed in terms of the displacement. Other response quantities such as the velocity and acceleration of the mass can also be used to define a transfer function for various applications. The names associated with each of these transfer or frequency response ...
... The transfer function defined above was expressed in terms of the displacement. Other response quantities such as the velocity and acceleration of the mass can also be used to define a transfer function for various applications. The names associated with each of these transfer or frequency response ...
Lectures 15 and 16 - NUS Physics Department
... An isolated system is one for which there are no energy transfers across the boundary. The energy in such a system is conserved , i.e., at anytime the sum is a constant but its form can change in part or in whole. E.g., a block sliding across a frictionless table is moving in an isolated system. If ...
... An isolated system is one for which there are no energy transfers across the boundary. The energy in such a system is conserved , i.e., at anytime the sum is a constant but its form can change in part or in whole. E.g., a block sliding across a frictionless table is moving in an isolated system. If ...
momentum class notes
... A 15-kg medicine ball is thrown at a velocity of 20 km/hr to a 60-kg person who is at rest on ice. The person catches the ball and subsequently slides with the ball across the ice. Determine the velocity of the person and the ball after the collision. Such a motion can be considered as a collision ...
... A 15-kg medicine ball is thrown at a velocity of 20 km/hr to a 60-kg person who is at rest on ice. The person catches the ball and subsequently slides with the ball across the ice. Determine the velocity of the person and the ball after the collision. Such a motion can be considered as a collision ...
The Force Be With You
... Imagine that different forces are acting on a hockey puck. Draw arrows to show the forces acting on each hockey puck, and then answer the questions. ...
... Imagine that different forces are acting on a hockey puck. Draw arrows to show the forces acting on each hockey puck, and then answer the questions. ...
Word document
... 2. Know that power is the rate at which work is done (or the rate at which energy is delivered or used). Find the power delivered or used in moving an object through some displacement in some time. 3. Find the kinetic energy of an object. 4. Use the Work-Energy Theorem to find the final speed of an ...
... 2. Know that power is the rate at which work is done (or the rate at which energy is delivered or used). Find the power delivered or used in moving an object through some displacement in some time. 3. Find the kinetic energy of an object. 4. Use the Work-Energy Theorem to find the final speed of an ...
Chapter 10 (Read Please)
... Angular Position, final We can associate the angle q with the entire rigid object as well as with an individual particle. Remember every particle on the object rotates through the same angle. The angular position of the rigid object is the angle q between the reference line on the object and the ...
... Angular Position, final We can associate the angle q with the entire rigid object as well as with an individual particle. Remember every particle on the object rotates through the same angle. The angular position of the rigid object is the angle q between the reference line on the object and the ...