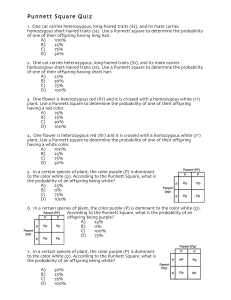
Test of a population
... RULE 7 If two events A and B are independent, the probability of both events A and B occurring is equal to the product of their individual probabilities. Two events are independent if the occurrence of one event in no way affects the probability of the second event. RULE 8 If two events A and B are ...
... RULE 7 If two events A and B are independent, the probability of both events A and B occurring is equal to the product of their individual probabilities. Two events are independent if the occurrence of one event in no way affects the probability of the second event. RULE 8 If two events A and B are ...
Quantifying Uncertainty
... Pr(A): Probability A is true Pr(AB): Prob. both A & B are true Pr(~A): Prob. of not A: 1-Pr(A) Pr(A|B): Prob. of A given B Pr(AB)/Pr(B) Pr(A+B): Probability A or B is true Pr(A) + Pr(B) – Pr(AB) ...
... Pr(A): Probability A is true Pr(AB): Prob. both A & B are true Pr(~A): Prob. of not A: 1-Pr(A) Pr(A|B): Prob. of A given B Pr(AB)/Pr(B) Pr(A+B): Probability A or B is true Pr(A) + Pr(B) – Pr(AB) ...
HP 30S Powers and Roots
... A convenient way of computing x y is as e y ln x since x y = e ln x = e y ln x The HP-35, the world’s first scientific electronic pocket calculator, used this method to save valuable space in ROM. Therefore, ...
... A convenient way of computing x y is as e y ln x since x y = e ln x = e y ln x The HP-35, the world’s first scientific electronic pocket calculator, used this method to save valuable space in ROM. Therefore, ...
Discrete Finite Probability Probability 1
... An outcome that is impossible (e.g., drawing a green ball in our experiment) is assigned the probability 0 (or 0%). An outcome that is inevitable (e.g., getting "heads" when flipping a twoheaded coin) is assigned the probability 1 (or 100%). Of course, most interesting outcomes are neither impossibl ...
... An outcome that is impossible (e.g., drawing a green ball in our experiment) is assigned the probability 0 (or 0%). An outcome that is inevitable (e.g., getting "heads" when flipping a twoheaded coin) is assigned the probability 1 (or 100%). Of course, most interesting outcomes are neither impossibl ...
Probability of an event - UH
... probability assignments are made for the simple events in a sample space S. 1. Theoretical. We use assumptions and analytical reasoning (the die is fair so the outcomes have equal probability; the coin is biased in a certain way), and impose the two conditions that the probability assignment must sa ...
... probability assignments are made for the simple events in a sample space S. 1. Theoretical. We use assumptions and analytical reasoning (the die is fair so the outcomes have equal probability; the coin is biased in a certain way), and impose the two conditions that the probability assignment must sa ...
Lecture 13
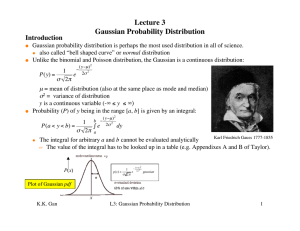
... And as we increase x this event accumulates more and more values of y to the left of x. In fact, it should be clear that as x , the event [ X x] S X . Hence, from the above property (P3), Pr[ X x] Pr( S X ) 1. Now, let’s graph this accumulating probability corresponding to Figure 3.1. ...
... And as we increase x this event accumulates more and more values of y to the left of x. In fact, it should be clear that as x , the event [ X x] S X . Hence, from the above property (P3), Pr[ X x] Pr( S X ) 1. Now, let’s graph this accumulating probability corresponding to Figure 3.1. ...
Conditional probability and Bayes` rule
... Events are said to be dependent when the occurrence of one event has an effect on the other. As an example, consider the experiment of drawing two cards from a pack, when the first card is not replaced before drawing the second. If the probability of getting two Aces is required, then let A = an Ace ...
... Events are said to be dependent when the occurrence of one event has an effect on the other. As an example, consider the experiment of drawing two cards from a pack, when the first card is not replaced before drawing the second. If the probability of getting two Aces is required, then let A = an Ace ...