11 Test Review - The Planet Earth
... 2. frequency – how often, duration – how long, extent(area) – how much space it takes up, speed of onset – the rapidness of the storm, spatial dispersion – the most likely area to be affected, temporal spacing – how it occurs in time 3. Lithosphere – earth’s crust (soil, rocks, and minerals) Hydrosp ...
... 2. frequency – how often, duration – how long, extent(area) – how much space it takes up, speed of onset – the rapidness of the storm, spatial dispersion – the most likely area to be affected, temporal spacing – how it occurs in time 3. Lithosphere – earth’s crust (soil, rocks, and minerals) Hydrosp ...
How old is the Earth really? THE AGE OF THE EARTH- 1850
... that radioactive decay produced heat. This discovery proved that the calculations of GeorgeLouis Leclerc and Lord Kelvin could not be accurate because these scientist had assumed that heat was always being lost; they did not know that heat could also be created. During the first few years of the 20t ...
... that radioactive decay produced heat. This discovery proved that the calculations of GeorgeLouis Leclerc and Lord Kelvin could not be accurate because these scientist had assumed that heat was always being lost; they did not know that heat could also be created. During the first few years of the 20t ...
The Earth’s movement - Thomas Tallis Science Department
... There may also have been water vapour and small proportions of methane and ammonia. Plants and algae produced the oxygen that is now in the atmosphere ...
... There may also have been water vapour and small proportions of methane and ammonia. Plants and algae produced the oxygen that is now in the atmosphere ...
Movement of tectonic plates (N12)
... Forces that alter the Earth's surface; Rocks: their formation, characteristics, and uses; Soil, its changes and uses; Natural resources used by humankind; and Forces within the Earth (not in grade 4). ...
... Forces that alter the Earth's surface; Rocks: their formation, characteristics, and uses; Soil, its changes and uses; Natural resources used by humankind; and Forces within the Earth (not in grade 4). ...
Spheres glossary quiz - HSIE Teachers
... The in situ physical and chemical disintegration of rocks and minerals at or near the earth’s surface by atmospheric or biological agents ...
... The in situ physical and chemical disintegration of rocks and minerals at or near the earth’s surface by atmospheric or biological agents ...
Primary Standards for Processes that Change the Earth
... 7th Grade Standards for Processes that Change the Earth SC-7-EU-U-4 Students will understand that models of the interior of the Earth have been constructed primarily from inferences based on limited data obtained during earthquakes and volcanic eruptions. These models are useful, but are open to rev ...
... 7th Grade Standards for Processes that Change the Earth SC-7-EU-U-4 Students will understand that models of the interior of the Earth have been constructed primarily from inferences based on limited data obtained during earthquakes and volcanic eruptions. These models are useful, but are open to rev ...
“Physical Geography: A Living Planet”
... d. the plants and animals that live on earth? ___________________________________ 3. Describe the process of continental drift. ...
... d. the plants and animals that live on earth? ___________________________________ 3. Describe the process of continental drift. ...
Question you are trying to answer. Ex
... j. Crater – PIT AT THE TOP OF A VOLCANIC CONE 3. Is Earth’s surface covered more by land or water? WATER 4. What are the two main gases in our atmosphere? NITROGEN & OXYGEN 5. The movement of tectonic plates is caused by CONVECTION CURRENTS in the Earth’s MANTLE. 6. The idea that Earth’s crust is ma ...
... j. Crater – PIT AT THE TOP OF A VOLCANIC CONE 3. Is Earth’s surface covered more by land or water? WATER 4. What are the two main gases in our atmosphere? NITROGEN & OXYGEN 5. The movement of tectonic plates is caused by CONVECTION CURRENTS in the Earth’s MANTLE. 6. The idea that Earth’s crust is ma ...
Unit 7 Earth`s Resources
... Overarching Concept: 9.7 - Elements on Earth move among reservoirs in the solid earth, oceans, atmosphere and organisms as part of biogeochemical cycles. Elements on Earth exist in essentially fixed amounts and are located in various chemical reservoirs. The cyclical movement of matter between r ...
... Overarching Concept: 9.7 - Elements on Earth move among reservoirs in the solid earth, oceans, atmosphere and organisms as part of biogeochemical cycles. Elements on Earth exist in essentially fixed amounts and are located in various chemical reservoirs. The cyclical movement of matter between r ...
Appendix F - Mineralogical Society
... The legendary pugilist Muhammed Ali said ‘The man who views the world at fifty the same as he did at twenty has wasted thirty years of his life’. Our scientific understanding of the Earth shows no such failing, amply demonstrated by the recent “New Views of the Earth’s Interior” meeting held in the ...
... The legendary pugilist Muhammed Ali said ‘The man who views the world at fifty the same as he did at twenty has wasted thirty years of his life’. Our scientific understanding of the Earth shows no such failing, amply demonstrated by the recent “New Views of the Earth’s Interior” meeting held in the ...
Global Systems - Vocabulary Worksheet File
... We can consider that materials are moved or recycled through the Earth through several interconnected natural systems by natural processes. For example, an atom of oxygen will move through the biosphere through the processes of photosynthesis and respiration but will also enter the hydrosphere throu ...
... We can consider that materials are moved or recycled through the Earth through several interconnected natural systems by natural processes. For example, an atom of oxygen will move through the biosphere through the processes of photosynthesis and respiration but will also enter the hydrosphere throu ...
Time - Research School of Earth Sciences
... books on similar subject, the research and lectures of my colleagues from various universities around the world, my own research, and finally, numerous web sites. I am grateful for some figures I used in this lecture to E. Garnero and L. Breger. I am thankful to many others who make their research a ...
... books on similar subject, the research and lectures of my colleagues from various universities around the world, my own research, and finally, numerous web sites. I am grateful for some figures I used in this lecture to E. Garnero and L. Breger. I am thankful to many others who make their research a ...
study guide for mid term 6th grade
... 23. Transform plate boundary the plates slide past each other. 24. The Independent variable is changed by the Investigator. The Dependent variable depends on the independent variable. 25. Scientific Law is true and states that an event will happen, Scientific theory explains why things happen or is ...
... 23. Transform plate boundary the plates slide past each other. 24. The Independent variable is changed by the Investigator. The Dependent variable depends on the independent variable. 25. Scientific Law is true and states that an event will happen, Scientific theory explains why things happen or is ...
ch01 (1)
... are about 4.2 billion years. It is unlikely that older rocks will be found because Earth’s earliest history has been destroyed by the recycling of plate tectonics and the processes of rock weathering. 7. There is strong evidence, as presented in this chapter that the Mediterranean Sea evaporated and ...
... are about 4.2 billion years. It is unlikely that older rocks will be found because Earth’s earliest history has been destroyed by the recycling of plate tectonics and the processes of rock weathering. 7. There is strong evidence, as presented in this chapter that the Mediterranean Sea evaporated and ...
Science Vocabulary Constructive and Destructive Forces Lava
... Lava: Molten rock that flows from a volcano onto the earth’s surface. Sand Dune: A hill of sand made and shaped by the wind. Topography: Surface landforms of an area. Erosion: The process of moving sediment by wind, moving water, or ice. Delta: An area of new land at the mouth of a river formed from ...
... Lava: Molten rock that flows from a volcano onto the earth’s surface. Sand Dune: A hill of sand made and shaped by the wind. Topography: Surface landforms of an area. Erosion: The process of moving sediment by wind, moving water, or ice. Delta: An area of new land at the mouth of a river formed from ...
RESTLESS EARTH Chapter 3: Uniformitarianism~ A principle that
... processes shaping the Earth today have been at work throughout Earth’s history. These changes remain uniform or do not change over time. “The present is the key to the past” Catastrophism ~ A principle that states that all geologic change occurs suddenly. Mountains, canyons, and seas can be expl ...
... processes shaping the Earth today have been at work throughout Earth’s history. These changes remain uniform or do not change over time. “The present is the key to the past” Catastrophism ~ A principle that states that all geologic change occurs suddenly. Mountains, canyons, and seas can be expl ...
Page 751 - ClassZone
... mineral A naturally occurring inorganic solid with a distinct chemical composition and crystalline structure. (p. 96) mineral deposit A deposit that is left behind when groundwater that contains minerals cools or evaporates. (p. 309) mineralogy The study of minerals and their properties. (p. 104) mi ...
... mineral A naturally occurring inorganic solid with a distinct chemical composition and crystalline structure. (p. 96) mineral deposit A deposit that is left behind when groundwater that contains minerals cools or evaporates. (p. 309) mineralogy The study of minerals and their properties. (p. 104) mi ...
Earth Space Science
... Earth’s crust consists of major and minor tectonic plates that move relative to each other. A combination of constructive and destructive geologic processes formed Earth’s surface. Evidence of the dynamic changes of Earth’s surface through time is found in the geologic record. ...
... Earth’s crust consists of major and minor tectonic plates that move relative to each other. A combination of constructive and destructive geologic processes formed Earth’s surface. Evidence of the dynamic changes of Earth’s surface through time is found in the geologic record. ...
Unpacking the Standards
... d. Describe processes that change rocks and the surface of the earth. e. Recognize that lithospheric plates constantly move and cause major geological events on the earth’s surface. f. Explain the effects of physical processes (plate tectonics, erosion, deposition, volcanic eruption, gravity) on geo ...
... d. Describe processes that change rocks and the surface of the earth. e. Recognize that lithospheric plates constantly move and cause major geological events on the earth’s surface. f. Explain the effects of physical processes (plate tectonics, erosion, deposition, volcanic eruption, gravity) on geo ...
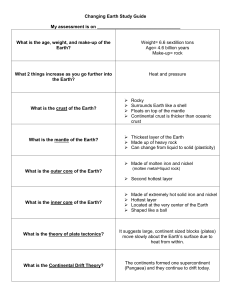
Changing Earth Study Guide My assessment is on What is the age
... What 2 things increase as you go further into the Earth? ...
... What 2 things increase as you go further into the Earth? ...
Earth Science Vocab
... Mantle- Earth’s thickest layer; made of hot rock; less dense than the metallic core ...
... Mantle- Earth’s thickest layer; made of hot rock; less dense than the metallic core ...
Spheres of the Earth
... air, which we call the atmosphere. • It reaches over 560 kilometers (348 miles) from the surface of the Earth. • Life on Earth is supported by the atmosphere, solar energy, and our planet's magnetic fields. ...
... air, which we call the atmosphere. • It reaches over 560 kilometers (348 miles) from the surface of the Earth. • Life on Earth is supported by the atmosphere, solar energy, and our planet's magnetic fields. ...
Earth Science
... Blanket of gases that surrounds our planet. It is Needed for respiration, protection from UV radiation (Ozone layer), Regulate temperature. Composition of atmosphere: 78% Nitrogen 21% Oxygen 1% (H2O vapor, argon, CO2, other trace gases) ...
... Blanket of gases that surrounds our planet. It is Needed for respiration, protection from UV radiation (Ozone layer), Regulate temperature. Composition of atmosphere: 78% Nitrogen 21% Oxygen 1% (H2O vapor, argon, CO2, other trace gases) ...
How Earth`s Broken Surface Keeps Us Alive
... More than a quarter of Earth is made up of this chemical, for example, sand is made of silicon. But looking at Janet’s star, the planet probably contains much more silicon than Earth. If Janet does contain more silicon than Earth, it would make it less likely to have what we call 'plate tectonics'. ...
... More than a quarter of Earth is made up of this chemical, for example, sand is made of silicon. But looking at Janet’s star, the planet probably contains much more silicon than Earth. If Janet does contain more silicon than Earth, it would make it less likely to have what we call 'plate tectonics'. ...
iscience earth science unit 1 chapter 2 study guide
... dug? Have we even been able to dig our way to the Mantle? Why not? ...
... dug? Have we even been able to dig our way to the Mantle? Why not? ...