Linear Transformations and Matrix Algebra
... chapter 6 where we find that by using the inner-product on vectors from R we will define the notion of angle and from that distance. Using these definitions and Schwarz’s inequality will then give us a triangle-inequality for arbitrary finite-dimensional vectors. This is to say that the algebra of v ...
... chapter 6 where we find that by using the inner-product on vectors from R we will define the notion of angle and from that distance. Using these definitions and Schwarz’s inequality will then give us a triangle-inequality for arbitrary finite-dimensional vectors. This is to say that the algebra of v ...
Q 19: Quantum Optics III - DPG
... Quantum interference of two independent particles in pure quantum states is fully described by the particles’ distinguishability: the closer the particles are to being identical, the higher the degree of quantum interference. When more than two particles are involved, the situation becomes more comp ...
... Quantum interference of two independent particles in pure quantum states is fully described by the particles’ distinguishability: the closer the particles are to being identical, the higher the degree of quantum interference. When more than two particles are involved, the situation becomes more comp ...
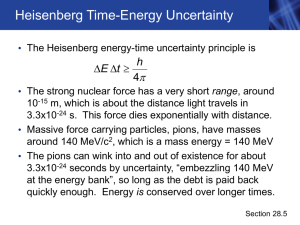
Chapter 28 - Purdue Physics
... theory): a cat, a flask of poison, and a radioactive source are placed in a sealed box. If an internal monitor detects radioactivity (i.e. a single atom decaying), the flask is shattered, releasing the poison that kills the cat. The Copenhagen interpretation of quantum mechanics implies that after a ...
... theory): a cat, a flask of poison, and a radioactive source are placed in a sealed box. If an internal monitor detects radioactivity (i.e. a single atom decaying), the flask is shattered, releasing the poison that kills the cat. The Copenhagen interpretation of quantum mechanics implies that after a ...
Entanglement and Quantum Teleportation
... Alice has managed to communicate two bits of information to Bob by sending only one qubit, provided they shared a Bell state to start To create and share a Bell state, they must have (at some point) transmitted a qubit, although this transmission could be in either direction The important point: the ...
... Alice has managed to communicate two bits of information to Bob by sending only one qubit, provided they shared a Bell state to start To create and share a Bell state, they must have (at some point) transmitted a qubit, although this transmission could be in either direction The important point: the ...
quantum - Academia Sinica
... (1) One of the founders of the quantum concept (2) A first, thought there must be something wrong with the quantum theory. (3) After much debate with Bohr, he finally was convinced that QM gives correct results, but it could not be the final theory. It is incomplete! ...
... (1) One of the founders of the quantum concept (2) A first, thought there must be something wrong with the quantum theory. (3) After much debate with Bohr, he finally was convinced that QM gives correct results, but it could not be the final theory. It is incomplete! ...
subatomic-particles
... reflect that quantum-scale "particles" behave like both particles and waves (also known as wavicles). Another new concept, the uncertainty principle, states that some of their properties taken together, such as their simultaneous position and momentum, cannot be measured exactly. In more recent time ...
... reflect that quantum-scale "particles" behave like both particles and waves (also known as wavicles). Another new concept, the uncertainty principle, states that some of their properties taken together, such as their simultaneous position and momentum, cannot be measured exactly. In more recent time ...
The Learnability of Quantum States
... Problem In Experimental Physics (!) (well, actually the starting point was whether BQP/qpoly QMA/poly … but let’s say it was experimental physics) ...
... Problem In Experimental Physics (!) (well, actually the starting point was whether BQP/qpoly QMA/poly … but let’s say it was experimental physics) ...
Entanglement Entropy
... Let’s consider a quantum system: we usually identify it through its state, i.e. its wave function. In this way, we assume it is possible to define the system completely and build the function which represents it. However, this is not always feasible. For instance, in an electron-target scattering ex ...
... Let’s consider a quantum system: we usually identify it through its state, i.e. its wave function. In this way, we assume it is possible to define the system completely and build the function which represents it. However, this is not always feasible. For instance, in an electron-target scattering ex ...
Mixed states and pure states
... These are brief notes on the abstract formalism of quantum mechanics. They will introduce the concepts of pure and mixed quantum states. Some statements are indicated by a P. You should try and prove these statements. If you understand the formalism, then these statements should not be hard to prove ...
... These are brief notes on the abstract formalism of quantum mechanics. They will introduce the concepts of pure and mixed quantum states. Some statements are indicated by a P. You should try and prove these statements. If you understand the formalism, then these statements should not be hard to prove ...
Heisenberg, Matrix Mechanics, and the Uncertainty Principle Genesis
... scales of length, mass and time, however, this intuition is as likely as not to be misleading or even wrong. This is indeed the main message of the revolutionary advances in the physical sciences in the 20th century. The discovery of quantum mechanics is the centre-piece of that revolution. By the e ...
... scales of length, mass and time, however, this intuition is as likely as not to be misleading or even wrong. This is indeed the main message of the revolutionary advances in the physical sciences in the 20th century. The discovery of quantum mechanics is the centre-piece of that revolution. By the e ...
Slide 1
... Data transmission is synchronous. Data are sent in weak pulses of photons. The physical behavior of the particles themselves gives the receiver the encryption key. If a third party interrupts the data stream, the encryption key is rendered useless and both parties are alerted. The encrypti ...
... Data transmission is synchronous. Data are sent in weak pulses of photons. The physical behavior of the particles themselves gives the receiver the encryption key. If a third party interrupts the data stream, the encryption key is rendered useless and both parties are alerted. The encrypti ...