The Kimberley Volcano
... (“pillows”), vesicles, breccias, and other structures in these dark green to black rocks indicate eruption into shallow seas, and this same environment is indicated by well-preserved ripple marks and mud cracks in overlying sandstones. The flows cover some 250,000 square kilometres, and at an averag ...
... (“pillows”), vesicles, breccias, and other structures in these dark green to black rocks indicate eruption into shallow seas, and this same environment is indicated by well-preserved ripple marks and mud cracks in overlying sandstones. The flows cover some 250,000 square kilometres, and at an averag ...
Visio-Sub-idea A 11x17.vsd
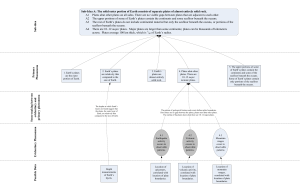
... The fact that the locations rock results in earthquakes. on different plates can Thus, the occurrence of move closer together or We know that the continents earthquakes at plate farther away from each are the top parts of plates. boundaries provides New rock is forming at the other indicates that pl ...
... The fact that the locations rock results in earthquakes. on different plates can Thus, the occurrence of move closer together or We know that the continents earthquakes at plate farther away from each are the top parts of plates. boundaries provides New rock is forming at the other indicates that pl ...
Igneous Rocks: Born of Fire
... • Partial melting and magma formation • Incomplete melting of rocks is known as partial melting • Formation of basaltic magmas – Most originate from partial melting of ultramafic rock in the mantle at oceanic ridges – Large outpourings of basaltic magma are common at Earth’s surface – These mafic ma ...
... • Partial melting and magma formation • Incomplete melting of rocks is known as partial melting • Formation of basaltic magmas – Most originate from partial melting of ultramafic rock in the mantle at oceanic ridges – Large outpourings of basaltic magma are common at Earth’s surface – These mafic ma ...
Homework of 9/19
... that erupt basaltic magma also occur on both oceanic and continental crust. —The source of basaltic magma, therefore, must be the mantle. —Everywhere along the midocean ridges, volcanoes erupt basaltic magma. —Some large basaltic volcanoes are not located along midocean ridges. The Hawaiian volcanic ...
... that erupt basaltic magma also occur on both oceanic and continental crust. —The source of basaltic magma, therefore, must be the mantle. —Everywhere along the midocean ridges, volcanoes erupt basaltic magma. —Some large basaltic volcanoes are not located along midocean ridges. The Hawaiian volcanic ...
Geologica: Earth`s Dynamic Forces by Robert Coenraads and John I
... each year. The West Coast is most at risk of having an earthquake in the United States, but earthquakes can happen in the Midwest and along the East Coast. Earthquakes can be felt over large areas although they usually last less than one minute. Earthquakes cannot be predicted although scientists ar ...
... each year. The West Coast is most at risk of having an earthquake in the United States, but earthquakes can happen in the Midwest and along the East Coast. Earthquakes can be felt over large areas although they usually last less than one minute. Earthquakes cannot be predicted although scientists ar ...
GEOTHERMAL SYSTEMS IN GLOBAL PERSPECTIVE
... Hotspot volcanism is off, sometimes far off, from spreading centres. Two examples will be mentioned, one located on oceanic crust the other on continental crust. Both have a hot spot track associated with them. 3.2.1 Hawaii and Yellowstone At Hawaii basaltic shield volcanoes begin on top of the plum ...
... Hotspot volcanism is off, sometimes far off, from spreading centres. Two examples will be mentioned, one located on oceanic crust the other on continental crust. Both have a hot spot track associated with them. 3.2.1 Hawaii and Yellowstone At Hawaii basaltic shield volcanoes begin on top of the plum ...
Igneous Rock
... more than 2 km thick in some places. Mathematicians calculate that if the lava from the eruptions in western India were spread evenly over the entire Earth, it would cover the Earth with a layer more than 2 m thick! ...
... more than 2 km thick in some places. Mathematicians calculate that if the lava from the eruptions in western India were spread evenly over the entire Earth, it would cover the Earth with a layer more than 2 m thick! ...
Student Edition Sample Chapter (3MB PDF)
... 3. Alfred Wegener thought that all continents were once connected. Explain one observation that led to this belief. 4. Why did scientists reject Wegener’s idea of continental drift? 5. In this section, you read that the development of the theory of plate tectonics is a good example of the scientific ...
... 3. Alfred Wegener thought that all continents were once connected. Explain one observation that led to this belief. 4. Why did scientists reject Wegener’s idea of continental drift? 5. In this section, you read that the development of the theory of plate tectonics is a good example of the scientific ...
The Origin of the Land Under the Sea
... constitutes a nearly continuous band of rock 500 kilometers long and up to 100 kilometers wide. Like all ophiolites, the mantle part of the Oman ophiolite is generally weathered to a rusty brown color and conspicuously laced with thousands of veins of tan-colored rock. Geologists had long ago identi ...
... constitutes a nearly continuous band of rock 500 kilometers long and up to 100 kilometers wide. Like all ophiolites, the mantle part of the Oman ophiolite is generally weathered to a rusty brown color and conspicuously laced with thousands of veins of tan-colored rock. Geologists had long ago identi ...
Chapter 4: Igneous Rocks: Product of Earth`s Internal Fire
... that erupt basaltic magma also occur on both oceanic and continental crust. —The source of basaltic magma, therefore, must be the mantle. —Everywhere along the midocean ridges, volcanoes erupt basaltic magma. —Some large basaltic volcanoes are not located along midocean ridges. The Hawaiian volcanic ...
... that erupt basaltic magma also occur on both oceanic and continental crust. —The source of basaltic magma, therefore, must be the mantle. —Everywhere along the midocean ridges, volcanoes erupt basaltic magma. —Some large basaltic volcanoes are not located along midocean ridges. The Hawaiian volcanic ...
A mantle plume below the Eifel volcanic ¢elds, Germany
... imply that the maximum temperature anomaly might be slightly lower for the Eifel than it is for other plumes. The main implication of our result is that even small intra-continental volcanic ¢elds can draw their magma supply from much more voluminous up£ows, rising from greater depth in the mantle. ...
... imply that the maximum temperature anomaly might be slightly lower for the Eifel than it is for other plumes. The main implication of our result is that even small intra-continental volcanic ¢elds can draw their magma supply from much more voluminous up£ows, rising from greater depth in the mantle. ...
Volcanism of the Palaeoproterozoic Bushveld Large Igneous Province: the Rooiberg
... geochronologic data, the temporal span of the Rooiberg Group is poorly understood. The Rooiberg Group consists of basaltic to rhyolitic lava erupted from fissural volcanism with estimated eruption temperatures of the rhyolitic lavas exceeding 1000°C. Minor explosive eruptions are represented by pyro ...
... geochronologic data, the temporal span of the Rooiberg Group is poorly understood. The Rooiberg Group consists of basaltic to rhyolitic lava erupted from fissural volcanism with estimated eruption temperatures of the rhyolitic lavas exceeding 1000°C. Minor explosive eruptions are represented by pyro ...
The Almeria-Nijar Basin
... magmatic chambers. In such a situation the magmas may partly crystallize, assimilate the country rock and suffer other modifications, the final result of which is a series of derived magmas of different compositions. This process is known as magmatic differentiation. Magmas are generally less dense ...
... magmatic chambers. In such a situation the magmas may partly crystallize, assimilate the country rock and suffer other modifications, the final result of which is a series of derived magmas of different compositions. This process is known as magmatic differentiation. Magmas are generally less dense ...
East Java: Cenozoic Basins, Volcanoes and Ancient Basement
... rocks. The Semilir and Nglanggran Formations form part of this sequence and are exposed over a large area. The Semilir Formation is a thick accumulation of dacitic air-fall, pyroclastic surge and flow deposits produced by an explosive eruption, and the Nglanggran Formation is a series of andesitic ...
... rocks. The Semilir and Nglanggran Formations form part of this sequence and are exposed over a large area. The Semilir Formation is a thick accumulation of dacitic air-fall, pyroclastic surge and flow deposits produced by an explosive eruption, and the Nglanggran Formation is a series of andesitic ...
Practice Exam #5 - El Camino College
... 11. Why does water come out of hydrothermal vents? ● Convection Cell: Ocean water sinks down into cracks in the ocean floor near hydrothermal vents. The water comes into contact with Hot Rock / Magma beneath the ocean floor, so it gets warmer and its density gets Higher / Lower, causing the water to ...
... 11. Why does water come out of hydrothermal vents? ● Convection Cell: Ocean water sinks down into cracks in the ocean floor near hydrothermal vents. The water comes into contact with Hot Rock / Magma beneath the ocean floor, so it gets warmer and its density gets Higher / Lower, causing the water to ...
ABSTRAeT RESUMEN
... Between the Pliocene and the Present the volcanic belt from 33-34°S, at the northern end of the Southern Volcanic Zone (SVZ) of the Andes, narrowed into a single chain 01 volcanos as the volcanic lront migrated 35 km to the east and the boundary separating the volcanically quiescent zone to the nort ...
... Between the Pliocene and the Present the volcanic belt from 33-34°S, at the northern end of the Southern Volcanic Zone (SVZ) of the Andes, narrowed into a single chain 01 volcanos as the volcanic lront migrated 35 km to the east and the boundary separating the volcanically quiescent zone to the nort ...
Contbined Volunte Containing Units: 16
... relatively dense, thin crust, lying beneath the ocean floors a wide belt of underwater mountains on some ocean floors a great early super-continent, from which all present continents have broken offby sea-floor spreading a rigid section ofthe Earth's lithosphere also referred to as margins and bound ...
... relatively dense, thin crust, lying beneath the ocean floors a wide belt of underwater mountains on some ocean floors a great early super-continent, from which all present continents have broken offby sea-floor spreading a rigid section ofthe Earth's lithosphere also referred to as margins and bound ...
Magmas and Igneous Rocks
... magma takes place much more rapidly. This is the extrusive or volcanic environment and results in extrusive or volcanic igneous rocks. Extrusive Environments When magmas reach the surface of the Earth they erupt from a vent called a volcano. They may erupt explosively or non-explosively. z ...
... magma takes place much more rapidly. This is the extrusive or volcanic environment and results in extrusive or volcanic igneous rocks. Extrusive Environments When magmas reach the surface of the Earth they erupt from a vent called a volcano. They may erupt explosively or non-explosively. z ...
Volcano

A volcano is a rupture on the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface.Earth's volcanoes occur because its crust is broken into 17 major, rigid tectonic plates that float on a hotter, softer layer in its mantle. Therefore, on Earth, volcanoes are generally found where tectonic plates are diverging or converging. For example, a mid-oceanic ridge, such as the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, has volcanoes caused by divergent tectonic plates pulling apart; the Pacific Ring of Fire has volcanoes caused by convergent tectonic plates coming together. Volcanoes can also form where there is stretching and thinning of the crust's interior plates, e.g., in the East African Rift and the Wells Gray-Clearwater volcanic field and Rio Grande Rift in North America. This type of volcanism falls under the umbrella of ""plate hypothesis"" volcanism. Volcanism away from plate boundaries has also been explained as mantle plumes. These so-called ""hotspots"", for example Hawaii, are postulated to arise from upwelling diapirs with magma from the core–mantle boundary, 3,000 km deep in the Earth. Volcanoes are usually not created where two tectonic plates slide past one another.Erupting volcanoes can pose many hazards, not only in the immediate vicinity of the eruption. One such hazard is that volcanic ash can be a threat to aircraft, in particular those with jet engines where ash particles can be melted by the high operating temperature; the melted particles then adhere to the turbine blades and alter their shape, disrupting the operation of the turbine. Large eruptions can affect temperature as ash and droplets of sulfuric acid obscure the sun and cool the Earth's lower atmosphere (or troposphere); however, they also absorb heat radiated up from the Earth, thereby warming the upper atmosphere (or stratosphere). Historically, so-called volcanic winters have caused catastrophic famines.