Shield Volcano
... allowing trapped gasses to expand and propel the magma through openings in the Earth’s surface causing an eruption. • Erupted magma is called lava. ...
... allowing trapped gasses to expand and propel the magma through openings in the Earth’s surface causing an eruption. • Erupted magma is called lava. ...
volcanoes - TeacherXin
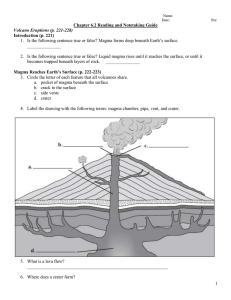
... – Magma chamber: magma is collected there – Pipe: long tube in the ground that connects the magma chamber to Earth's surface. – Vent: opening where molten rock and gas leave the volcano. – Lava flow: area covered by lava as it pours out of a vent – Crater: bowl-shaped area that may form at the top a ...
... – Magma chamber: magma is collected there – Pipe: long tube in the ground that connects the magma chamber to Earth's surface. – Vent: opening where molten rock and gas leave the volcano. – Lava flow: area covered by lava as it pours out of a vent – Crater: bowl-shaped area that may form at the top a ...
What is like living near a volcano?
... broken down before they form rich soils. • When they do become soils though, they form some of the richest ones on the planet. • The Naples area, which includes Mount Vesuvius, has such rich soils thanks to two large eruptions 35,000 and 12000 years ago. Both eruptions produced very thick deposits o ...
... broken down before they form rich soils. • When they do become soils though, they form some of the richest ones on the planet. • The Naples area, which includes Mount Vesuvius, has such rich soils thanks to two large eruptions 35,000 and 12000 years ago. Both eruptions produced very thick deposits o ...
Earth Science - Mr.E Science
... An enormous eruption may empty a volcano's main vent and magma chamber. With nothing to support it, the top of the mountain collapses ...
... An enormous eruption may empty a volcano's main vent and magma chamber. With nothing to support it, the top of the mountain collapses ...
Birth of the Universe
... Molten material rising from deep within the Earth. Mafic magma chemistry. Can form shield volcanoes – broad and gently sloping sides, non-violent eruptions, built by repeated layers of lava ...
... Molten material rising from deep within the Earth. Mafic magma chemistry. Can form shield volcanoes – broad and gently sloping sides, non-violent eruptions, built by repeated layers of lava ...
Unit 4 Chapter
... therefore very, very explosive with a lot of tephra (pyroclastic) form steep sided volcanoes with a lot of activity Most famous volcanoes Mt St Helen's & Mt Vesuvius The Aleutian Islands, island arcs, by the North Pacific Ocean, ...
... therefore very, very explosive with a lot of tephra (pyroclastic) form steep sided volcanoes with a lot of activity Most famous volcanoes Mt St Helen's & Mt Vesuvius The Aleutian Islands, island arcs, by the North Pacific Ocean, ...
Developing a Clincher Sentence
... quietly, or it may spew forth in a violent explosion. Clincher sentence: _____ 3. Geologists are not the only scientists who study volcanoes. Biologists and meteorologists are concerned with what happens on the earth’s surface after volcanic events. Biologists may be interested in how life adapts to ...
... quietly, or it may spew forth in a violent explosion. Clincher sentence: _____ 3. Geologists are not the only scientists who study volcanoes. Biologists and meteorologists are concerned with what happens on the earth’s surface after volcanic events. Biologists may be interested in how life adapts to ...
Hawaii Volcanoes National Park
... flows, they continue to destroy whatever is remaining in the path of the lava. Many plants may become extinct because there are not as many as there used to be and the animals continue to eat whatever is remaining for food. Once the plants stop growing or become extinct, animals that eat the plants ...
... flows, they continue to destroy whatever is remaining in the path of the lava. Many plants may become extinct because there are not as many as there used to be and the animals continue to eat whatever is remaining for food. Once the plants stop growing or become extinct, animals that eat the plants ...
Ch. 7.2 Volcanic Eruptions
... Only a few hundred meters high at most; very steep sides. Result from explosive eruptions of solid fragments. ...
... Only a few hundred meters high at most; very steep sides. Result from explosive eruptions of solid fragments. ...
Earth Study Guide
... moves up and over the oceanic plate. • Folded Mountains – Form when two continental plates collide and their edges crumble. • Dome Mountains – Form when the surface is lifted up by ...
... moves up and over the oceanic plate. • Folded Mountains – Form when two continental plates collide and their edges crumble. • Dome Mountains – Form when the surface is lifted up by ...
VOLCANOES – Study Guide
... fireplace or furnace * We could not build a fire because there was a bird’s nest in our chimney. moves with a quick shaking motion * The tiny dog trembles in the cold. violent shaking or shifting motion of the ground caused by the sudden movement of rock far beneath Earth’s surface * My cousin lives ...
... fireplace or furnace * We could not build a fire because there was a bird’s nest in our chimney. moves with a quick shaking motion * The tiny dog trembles in the cold. violent shaking or shifting motion of the ground caused by the sudden movement of rock far beneath Earth’s surface * My cousin lives ...
Volcanoes
... • C) Volcanoes were formed when the earth was formed and haven’t changed much since then. • D) Both A and B ...
... • C) Volcanoes were formed when the earth was formed and haven’t changed much since then. • D) Both A and B ...
Volcanoes
... • C) Volcanoes were formed when the earth was formed and haven’t changed much since then. • D) Both A and B ...
... • C) Volcanoes were formed when the earth was formed and haven’t changed much since then. • D) Both A and B ...
1 Fig. 1 shows concentration of volcanoes within th
... Volcanoes are formed along boundaries where an oceanic plate meets a continental plate These volcanoes are formed where the denser oceanic plate is subducted beneath the less dense continental plate ...
... Volcanoes are formed along boundaries where an oceanic plate meets a continental plate These volcanoes are formed where the denser oceanic plate is subducted beneath the less dense continental plate ...
Monitoring Methods
... Chemistry — As the molten material (magma) rises to shallow levels, gases are released and they rise to the surface. Gas — When molten material (magma) moves into a volcano it gives off volcanic gas emissions, sulphur dioxide (SO2), carbon dioxide (CO2) and hydrogen sulphide (H2S) which are measured ...
... Chemistry — As the molten material (magma) rises to shallow levels, gases are released and they rise to the surface. Gas — When molten material (magma) moves into a volcano it gives off volcanic gas emissions, sulphur dioxide (SO2), carbon dioxide (CO2) and hydrogen sulphide (H2S) which are measured ...
EarthquakesandVolcan..
... granitic and basaltic lava flows (quieter than granitic but more violent than basaltic). Gas filled lava – This lava cools to form hole filled rock that has the appearance of a sponge or loaf of bread. This rock type is typically light in weight. Pumice and scoria are examples of this type of igneou ...
... granitic and basaltic lava flows (quieter than granitic but more violent than basaltic). Gas filled lava – This lava cools to form hole filled rock that has the appearance of a sponge or loaf of bread. This rock type is typically light in weight. Pumice and scoria are examples of this type of igneou ...
Name_________________________________
... c. Which islands are made out of extinct volcanoes? __________________ d. Which island volcanoes are still active?__________________ e. Which islands still has the hotspot under it?____________________ ...
... c. Which islands are made out of extinct volcanoes? __________________ d. Which island volcanoes are still active?__________________ e. Which islands still has the hotspot under it?____________________ ...
Chapter 5 Fast Changes on Earth: Volcanoes
... 1. A volcano is a mountain that builds up around an opening in the Earth’s crust. 2. An eruption occurs when the melted rock, gases, and pieces of rock are forced out of a volcano 3. Trapped gasses build up pressure which can lead to an explopsive eruption 4. Magma rises through the opening (vent) i ...
... 1. A volcano is a mountain that builds up around an opening in the Earth’s crust. 2. An eruption occurs when the melted rock, gases, and pieces of rock are forced out of a volcano 3. Trapped gasses build up pressure which can lead to an explopsive eruption 4. Magma rises through the opening (vent) i ...
Volcanoes
... 1. If rock temperature rises above its melting point then it will melt into magma 2. Rock can melt when too much pressure is removed from rock that is above its melting point 3. The addition of fluids, such as water, may lower the melting point of some rock and cause it to melt ...
... 1. If rock temperature rises above its melting point then it will melt into magma 2. Rock can melt when too much pressure is removed from rock that is above its melting point 3. The addition of fluids, such as water, may lower the melting point of some rock and cause it to melt ...
Volcano

A volcano is a rupture on the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface.Earth's volcanoes occur because its crust is broken into 17 major, rigid tectonic plates that float on a hotter, softer layer in its mantle. Therefore, on Earth, volcanoes are generally found where tectonic plates are diverging or converging. For example, a mid-oceanic ridge, such as the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, has volcanoes caused by divergent tectonic plates pulling apart; the Pacific Ring of Fire has volcanoes caused by convergent tectonic plates coming together. Volcanoes can also form where there is stretching and thinning of the crust's interior plates, e.g., in the East African Rift and the Wells Gray-Clearwater volcanic field and Rio Grande Rift in North America. This type of volcanism falls under the umbrella of ""plate hypothesis"" volcanism. Volcanism away from plate boundaries has also been explained as mantle plumes. These so-called ""hotspots"", for example Hawaii, are postulated to arise from upwelling diapirs with magma from the core–mantle boundary, 3,000 km deep in the Earth. Volcanoes are usually not created where two tectonic plates slide past one another.Erupting volcanoes can pose many hazards, not only in the immediate vicinity of the eruption. One such hazard is that volcanic ash can be a threat to aircraft, in particular those with jet engines where ash particles can be melted by the high operating temperature; the melted particles then adhere to the turbine blades and alter their shape, disrupting the operation of the turbine. Large eruptions can affect temperature as ash and droplets of sulfuric acid obscure the sun and cool the Earth's lower atmosphere (or troposphere); however, they also absorb heat radiated up from the Earth, thereby warming the upper atmosphere (or stratosphere). Historically, so-called volcanic winters have caused catastrophic famines.