Slide 1 - Henrico
... What would be a clue that a volcano might erupt? Small earthquakes near the volcano A bulge or tilt in the ground near the volcano ...
... What would be a clue that a volcano might erupt? Small earthquakes near the volcano A bulge or tilt in the ground near the volcano ...
Volcano - watertown.k12.wi.us
... The Cinder Cone tends to erode quickly and may bleed from the bottom or sides- called a "________________ eruption". These volcanoes ______________________often cause damage in that they are small, intermittent explosions of Felsic lava. Examples are _____________________________ (Crater Lake) and P ...
... The Cinder Cone tends to erode quickly and may bleed from the bottom or sides- called a "________________ eruption". These volcanoes ______________________often cause damage in that they are small, intermittent explosions of Felsic lava. Examples are _____________________________ (Crater Lake) and P ...
Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics
... V. Hot Spot Volcano A. A hot spot is an area where magma deep from within the mantle melts throught the crust like a blow torch. 1. Hot spots often lie in the middle of continental or ocean plates far from any plate boundaries. 2. Volcanoes at a hot spot do not result from subduction. B. A hot spot ...
... V. Hot Spot Volcano A. A hot spot is an area where magma deep from within the mantle melts throught the crust like a blow torch. 1. Hot spots often lie in the middle of continental or ocean plates far from any plate boundaries. 2. Volcanoes at a hot spot do not result from subduction. B. A hot spot ...
Volcanoes - Geog
... Usually most violent. Massive amounts of lava, gas and pyroclastic material emitted. Part of the volcano may be removed. ...
... Usually most violent. Massive amounts of lava, gas and pyroclastic material emitted. Part of the volcano may be removed. ...
Our dynamic earth
... • Both types of crust is 60 miles deep. • The inner core can reach to the level of heat , 5000 degrees twice as hot as the sun. ...
... • Both types of crust is 60 miles deep. • The inner core can reach to the level of heat , 5000 degrees twice as hot as the sun. ...
Volcanoes
... • Magma- molten mixture of rockforming substances, gases & water from the mantle • Lava- Magma that reaches the surface ...
... • Magma- molten mixture of rockforming substances, gases & water from the mantle • Lava- Magma that reaches the surface ...
Volcanoes
... escapes through these breaks. The magma is under great pressure. The pressure shoots melted rock and ashes high into the air. As the magma escapes, it cools. When it cools, it hardens. More lava-7 ...
... escapes through these breaks. The magma is under great pressure. The pressure shoots melted rock and ashes high into the air. As the magma escapes, it cools. When it cools, it hardens. More lava-7 ...
Volcano Fact Sheet Tarawera Volcano and the Okataina Volcanic
... •• The eruptions which formed the Okataina Caldera began around 400,000 years ago. •• The rhyolite lava flows which form the summit domes of Tarawera’s three peaks were formed about 800 years ago. •• The time between eruptions in the Okataina Volcanic Centre is long (700 to 3000 years) but eruptions ...
... •• The eruptions which formed the Okataina Caldera began around 400,000 years ago. •• The rhyolite lava flows which form the summit domes of Tarawera’s three peaks were formed about 800 years ago. •• The time between eruptions in the Okataina Volcanic Centre is long (700 to 3000 years) but eruptions ...
Chapter 5 - Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity
... – Produces basaltic magma sources in oceanic crust (e.g., Hawaii and Iceland) – Produces granitic magma sources in continental crust (e.g., Yellowstone Park) ...
... – Produces basaltic magma sources in oceanic crust (e.g., Hawaii and Iceland) – Produces granitic magma sources in continental crust (e.g., Yellowstone Park) ...
Volcano ppt that goes with notes
... The Ring of Fire is found where the oceanic crust of the Pacific Plate is subducting under nearby plates. Most volcanoes are located along plate boundaries. ...
... The Ring of Fire is found where the oceanic crust of the Pacific Plate is subducting under nearby plates. Most volcanoes are located along plate boundaries. ...
Chapter 12: Volcanoes Study Guide
... 1. _____________________ melted rock formed by heat and pressure deep inside Earth 2. _____________________ area between mantle and core where hot rock is forced into the crust 3. _____________________ places where most volcanoes occur 4. _____________________ opening in Earth’s surface through whic ...
... 1. _____________________ melted rock formed by heat and pressure deep inside Earth 2. _____________________ area between mantle and core where hot rock is forced into the crust 3. _____________________ places where most volcanoes occur 4. _____________________ opening in Earth’s surface through whic ...
ESVolcanoes - Cole Camp R-1
... ▸When a plate with oceanic crust meets a plate with continental crust, the oceanic crust, which is more dense, moves beneath the continental crust. ▸A _________________________________ forms on the ocean floor along the edge of the continent where the plate is being subducted. ▸The plate with the co ...
... ▸When a plate with oceanic crust meets a plate with continental crust, the oceanic crust, which is more dense, moves beneath the continental crust. ▸A _________________________________ forms on the ocean floor along the edge of the continent where the plate is being subducted. ▸The plate with the co ...
No Slide Title
... What is for heating homes as hot water and for creating electricity by using steam to power turbines? (Accept reasonable answers) E 300 ...
... What is for heating homes as hot water and for creating electricity by using steam to power turbines? (Accept reasonable answers) E 300 ...
Chapter 7 Review
... What is for heating homes as hot water and for creating electricity by using steam to power turbines? (Accept reasonable answers) E 300 ...
... What is for heating homes as hot water and for creating electricity by using steam to power turbines? (Accept reasonable answers) E 300 ...
3A8 Week 01 Lecture 02-Rocks and minerals 01
... fluids, or are blown out as volcanic ash by violent explosions – Black volcanoes (effusive, mostly basaltic) – Red volcanoes (explosive, mostly felsic) This classification is based on composition. Formation of phenocrysts on cooling increases the viscosity ...
... fluids, or are blown out as volcanic ash by violent explosions – Black volcanoes (effusive, mostly basaltic) – Red volcanoes (explosive, mostly felsic) This classification is based on composition. Formation of phenocrysts on cooling increases the viscosity ...
Day-29
... sign of geologic activity. The movement of the tectonic plates generates a lot of thermal energy from friction. This energy combines with heat from convection cells in the mantle to heat portions of the lower crust and upper mantle as magma. ...
... sign of geologic activity. The movement of the tectonic plates generates a lot of thermal energy from friction. This energy combines with heat from convection cells in the mantle to heat portions of the lower crust and upper mantle as magma. ...
Volcanoesbackground_format
... by the downward-moving (subducting) plate as it becomes dehydrated during heating, this lowers the melting temperature of the overlying mantle, and magma is created. This magma slowly moves towards the surface, and where it reaches the surface it forms a volcano. Areas where two tectonic plates slid ...
... by the downward-moving (subducting) plate as it becomes dehydrated during heating, this lowers the melting temperature of the overlying mantle, and magma is created. This magma slowly moves towards the surface, and where it reaches the surface it forms a volcano. Areas where two tectonic plates slid ...
Earthquakes and Volcanoes Study Guide Pages 44 – 57 and 82
... 9. When an earthquake occurs, seismic waves travel from point ______ in all directions. 10. At point R, seismic waves from an earthquake would be ____________________ ___________________________________________________________________. 11. Volcanoes found where two oceanic plates collide form a ____ ...
... 9. When an earthquake occurs, seismic waves travel from point ______ in all directions. 10. At point R, seismic waves from an earthquake would be ____________________ ___________________________________________________________________. 11. Volcanoes found where two oceanic plates collide form a ____ ...
Chapter 10.1
... structures - most will form islands, like Hawaii. They are formed by fluid basaltic lava. ...
... structures - most will form islands, like Hawaii. They are formed by fluid basaltic lava. ...
Volcano

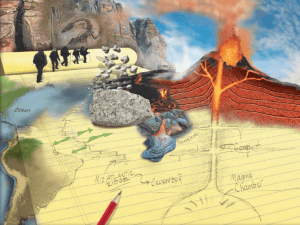
A volcano is a rupture on the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface.Earth's volcanoes occur because its crust is broken into 17 major, rigid tectonic plates that float on a hotter, softer layer in its mantle. Therefore, on Earth, volcanoes are generally found where tectonic plates are diverging or converging. For example, a mid-oceanic ridge, such as the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, has volcanoes caused by divergent tectonic plates pulling apart; the Pacific Ring of Fire has volcanoes caused by convergent tectonic plates coming together. Volcanoes can also form where there is stretching and thinning of the crust's interior plates, e.g., in the East African Rift and the Wells Gray-Clearwater volcanic field and Rio Grande Rift in North America. This type of volcanism falls under the umbrella of ""plate hypothesis"" volcanism. Volcanism away from plate boundaries has also been explained as mantle plumes. These so-called ""hotspots"", for example Hawaii, are postulated to arise from upwelling diapirs with magma from the core–mantle boundary, 3,000 km deep in the Earth. Volcanoes are usually not created where two tectonic plates slide past one another.Erupting volcanoes can pose many hazards, not only in the immediate vicinity of the eruption. One such hazard is that volcanic ash can be a threat to aircraft, in particular those with jet engines where ash particles can be melted by the high operating temperature; the melted particles then adhere to the turbine blades and alter their shape, disrupting the operation of the turbine. Large eruptions can affect temperature as ash and droplets of sulfuric acid obscure the sun and cool the Earth's lower atmosphere (or troposphere); however, they also absorb heat radiated up from the Earth, thereby warming the upper atmosphere (or stratosphere). Historically, so-called volcanic winters have caused catastrophic famines.