Quantum dynamics study of fulvene double bond photoisomerization: The
... have been several quantum dynamics studies on two- and three-dimensional surfaces with the goal of separating nuclear spin isomers.25–27 In one of these studies, it was found that the occurrence of the isomerization depended on the shape of the excitation laser pulse.26 The control of the photoisome ...
... have been several quantum dynamics studies on two- and three-dimensional surfaces with the goal of separating nuclear spin isomers.25–27 In one of these studies, it was found that the occurrence of the isomerization depended on the shape of the excitation laser pulse.26 The control of the photoisome ...
Polynomial-time degenerate ground state approximation of gapped
... subspace – guaranteed to contain low-energy states – on which this program can be efficiently solved. Our algorithm constructs such a space in the form of an n-viable set. ...
... subspace – guaranteed to contain low-energy states – on which this program can be efficiently solved. Our algorithm constructs such a space in the form of an n-viable set. ...
Atomic Electron Configurations and Chapter 8 Chemical Periodicity
... of four quantum numbers n, l, ml, and ms. ¾ Two electrons (max) per orbital ¾ Maximize parallel spins when filling a subshell ¾ If more than one orbital in a subshell is available, electrons will fill empty orbitals in the subshell first. (Hund’s Rule) ...
... of four quantum numbers n, l, ml, and ms. ¾ Two electrons (max) per orbital ¾ Maximize parallel spins when filling a subshell ¾ If more than one orbital in a subshell is available, electrons will fill empty orbitals in the subshell first. (Hund’s Rule) ...
Transition probabilities and dynamic structure factor in the ASEP
... much simpler system than the original one, namely to a system of non-interacting fermions. This fact suggests to use field theoretic free fermion techniques to compute time-dependent correlations in this particular large deviation limit of the classical stochastic dynamics of the conditioned ASEP. I ...
... much simpler system than the original one, namely to a system of non-interacting fermions. This fact suggests to use field theoretic free fermion techniques to compute time-dependent correlations in this particular large deviation limit of the classical stochastic dynamics of the conditioned ASEP. I ...
PASCOS - CERN Indico
... any massive flow including perturbations by relevant operators. The coupling of the dilaton to the trace of the energy momentum tensor is linear and the general statement is that the trace obeys an exact sum rule : ...
... any massive flow including perturbations by relevant operators. The coupling of the dilaton to the trace of the energy momentum tensor is linear and the general statement is that the trace obeys an exact sum rule : ...
Aspects of quantum work - Physik Uni-Augsburg
... those measurements that have to be performed in order to determine the work. It is this inherently quantum-mechanical requirement that renders the two classically equivalent definitions (1) and (2) inequivalent [4,10]. Based on the energy difference definition (1) work can be determined by the two e ...
... those measurements that have to be performed in order to determine the work. It is this inherently quantum-mechanical requirement that renders the two classically equivalent definitions (1) and (2) inequivalent [4,10]. Based on the energy difference definition (1) work can be determined by the two e ...
Atomic Orbitals - Stephen Berry
... of an electron and not by a moving point-charge, simply because the classical electron would go through many orbits during the event. Phenomena requiring less than lo-" see, say, are not well described by average distributions of charge in atoms. By the same ...
... of an electron and not by a moving point-charge, simply because the classical electron would go through many orbits during the event. Phenomena requiring less than lo-" see, say, are not well described by average distributions of charge in atoms. By the same ...
Lindblad driving for nonequilibrium steady
... The standard tool for describing nonequilibrium steady-state transport through a quantum system coupled to two leads with different chemical potentials is the Keldysh formalism [1]. However, when the quantum system is interacting, the treatment of interactions within the Keldysh formalism is difficu ...
... The standard tool for describing nonequilibrium steady-state transport through a quantum system coupled to two leads with different chemical potentials is the Keldysh formalism [1]. However, when the quantum system is interacting, the treatment of interactions within the Keldysh formalism is difficu ...
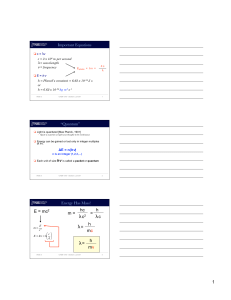
E = mc2 m = hc λc2 = h λc h λ= mv h λ= mc
... l is related to the shape of the orbital l = 0 is called an s orbital l = 1 is called a p orbital ψ(n, l = 2 is called a d orbital l = 3 is called an f orbital l = 4 is called a g orbital ...
... l is related to the shape of the orbital l = 0 is called an s orbital l = 1 is called a p orbital ψ(n, l = 2 is called a d orbital l = 3 is called an f orbital l = 4 is called a g orbital ...
2013 us national chemistry olympiad
... Part II of this test requires that student answers be written in a response booklet with blank pages. Only this "Blue Book" is graded for a score on Part II. Testing materials, scratch paper, and the "Blue Book" should be made available to the student only during the examination period. All testing ...
... Part II of this test requires that student answers be written in a response booklet with blank pages. Only this "Blue Book" is graded for a score on Part II. Testing materials, scratch paper, and the "Blue Book" should be made available to the student only during the examination period. All testing ...
Chapter 10 Pauli Spin Matrices
... this is not a definite state for x spin. That’s good, because the state is clearly not the same as |+xi when you write out that state in terms of |+zi and |−zi. It’s between those two. However, from just looking at the state, while you can fairly quickly see that |−zi has more amplitude than |+zi, a ...
... this is not a definite state for x spin. That’s good, because the state is clearly not the same as |+xi when you write out that state in terms of |+zi and |−zi. It’s between those two. However, from just looking at the state, while you can fairly quickly see that |−zi has more amplitude than |+zi, a ...
Background Material
... that this total energy can be represented as the sum of nine separate energies, one for each electron, the Hamiltonian allows a separation of variables H j=1,9 H(j) in which each H(j) describes the kinetic and potential energy of an individual electron. Of course, the full Hamiltonian contains el ...
... that this total energy can be represented as the sum of nine separate energies, one for each electron, the Hamiltonian allows a separation of variables H j=1,9 H(j) in which each H(j) describes the kinetic and potential energy of an individual electron. Of course, the full Hamiltonian contains el ...
The Quantum Hall Effect
... There is a clue in the experimental data about the origin of the plateaux. Experimental systems are typically dirty, filled with impurities. The technical name for this is disorder. Usually one wants to remove this dirt to get at the underlying physics. Yet, in the quantum Hall e↵ect, as you increas ...
... There is a clue in the experimental data about the origin of the plateaux. Experimental systems are typically dirty, filled with impurities. The technical name for this is disorder. Usually one wants to remove this dirt to get at the underlying physics. Yet, in the quantum Hall e↵ect, as you increas ...
Statistical Physics (PHY831), Part 2-Exact results and solvable models
... The most basic problem in statistical mechanics of quantum systems is where we have a system with a known set of single particle energy levels. Given this set of energy levels, we would like to know the behavior of the system. There are many possible cases, including non-relativistic and relativisti ...
... The most basic problem in statistical mechanics of quantum systems is where we have a system with a known set of single particle energy levels. Given this set of energy levels, we would like to know the behavior of the system. There are many possible cases, including non-relativistic and relativisti ...
Long-Range Correlations in the Nonequilibrium Quantum Relaxation of a Spin... V 85, N 15
... with g共x兲 ~ x 2 for x ø 1. The scaling parameter r兾t appearing in the scaling function g共x兲 is reminiscent of the fact that space and time scales are connected linearly at the critical point in the transverse Ising chain since the dynamical exponent is z 苷 1. Away from the critical point we have to ...
... with g共x兲 ~ x 2 for x ø 1. The scaling parameter r兾t appearing in the scaling function g共x兲 is reminiscent of the fact that space and time scales are connected linearly at the critical point in the transverse Ising chain since the dynamical exponent is z 苷 1. Away from the critical point we have to ...
The Noble Gases
... fractional spin. Electrons are fermions with a spin = ½. Protons and neutrons are also fermions with spin ½. Composite particles, like atoms, are also either fermions or bosons. Fermions can, and prefer to, pair in such a way that their spins cancel (+½ + –½ = 0). Thus, a particle composed of an eve ...
... fractional spin. Electrons are fermions with a spin = ½. Protons and neutrons are also fermions with spin ½. Composite particles, like atoms, are also either fermions or bosons. Fermions can, and prefer to, pair in such a way that their spins cancel (+½ + –½ = 0). Thus, a particle composed of an eve ...