pdf
... decouples the classical and quantum parts of the dynamics and only recognizes the classical part as a Hamiltonian system, whereas Faou and Lubich [10] show that the whole system is Hamiltonian. 1.2. Main Results and Outline. The main contribution of the present paper is to provide a symplectic and H ...
... decouples the classical and quantum parts of the dynamics and only recognizes the classical part as a Hamiltonian system, whereas Faou and Lubich [10] show that the whole system is Hamiltonian. 1.2. Main Results and Outline. The main contribution of the present paper is to provide a symplectic and H ...
Evidence of Correlation in Spin Excitations of Few
... According to Hund’s rules, a triplet ground state occurs only when two electrons are in a partially populated shell, as is the case of QDs with four electrons. This is confirmed by the calculations described below. In this interpretation, the narrow width is simply explained as due to the absence of ...
... According to Hund’s rules, a triplet ground state occurs only when two electrons are in a partially populated shell, as is the case of QDs with four electrons. This is confirmed by the calculations described below. In this interpretation, the narrow width is simply explained as due to the absence of ...
114, 125301 (2015)
... a stable effective modulation; for very small ω, the SOC strength barely changes and the system is also stable. In the intermediate regime, we use Floquet theory to describe the strong instability of the modulated BEC [17]. Figure 4(c) shows the Floquet band structure of a minimal model spanned by t ...
... a stable effective modulation; for very small ω, the SOC strength barely changes and the system is also stable. In the intermediate regime, we use Floquet theory to describe the strong instability of the modulated BEC [17]. Figure 4(c) shows the Floquet band structure of a minimal model spanned by t ...
Worksheet 3A on Molecules
... Of the species listed, only O3 and CO are polar. CO is polar due to the difference in electronegativity between O and C; O3 is polar because it has 3 RHED and one lone pair on the central atom. This lone pair is an area where negative charge is concentrated, so this results in the molecule having an ...
... Of the species listed, only O3 and CO are polar. CO is polar due to the difference in electronegativity between O and C; O3 is polar because it has 3 RHED and one lone pair on the central atom. This lone pair is an area where negative charge is concentrated, so this results in the molecule having an ...
Physics 243 Lecture Notes
... Electrons are emitted from a heated cathode, then are accelerated by the anode-cathode potential difference VAC , and eventually collide with the anode. Energy Balance kinetic energy of electrons = energy of emitted light+energy losses in the anode T. Stantcheva ...
... Electrons are emitted from a heated cathode, then are accelerated by the anode-cathode potential difference VAC , and eventually collide with the anode. Energy Balance kinetic energy of electrons = energy of emitted light+energy losses in the anode T. Stantcheva ...
Homework No. 09 (Spring 2016) PHYS 530A: Quantum Mechanics II
... 4. (20 points.) Construct the total angular momentum state |3, 3i for the composite system built out of two angular momenta j1 = 3, j2 = 1. 5. (20 points.) (Schwinger’s QM book, Prob. 3-4a.) Iso(topic) spin T : The nucleon is a particle of isospin T = 12 ; the state with T3 = 21 is the proton (p), t ...
... 4. (20 points.) Construct the total angular momentum state |3, 3i for the composite system built out of two angular momenta j1 = 3, j2 = 1. 5. (20 points.) (Schwinger’s QM book, Prob. 3-4a.) Iso(topic) spin T : The nucleon is a particle of isospin T = 12 ; the state with T3 = 21 is the proton (p), t ...
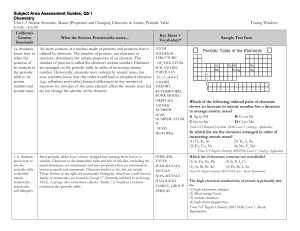
Subject Area Assessment Guides
... element from Group 2 will most often combine with two atoms of an element from Group 17 (e.g., MgCl2) because Group 2 elements have two electrons available for bonding, and Group 17 elements have only one electron position open in the outermost energy level. (Note that some periodic tables indicate ...
... element from Group 2 will most often combine with two atoms of an element from Group 17 (e.g., MgCl2) because Group 2 elements have two electrons available for bonding, and Group 17 elements have only one electron position open in the outermost energy level. (Note that some periodic tables indicate ...
CHAPTER 16: Quantum Mechanics and the Hydrogen Atom
... • For a given l, increasing n increases the average distance of electrons from the nucleus (& the size of the orbital). 3s larger than 2s. • Ψnlm has l angular nodes and n-l-1 radial nodes (total of n-1 nodes) • Only for s orbitals does Ψnlm remain nonzero as r→0. Only s orbitals “penetrate to the n ...
... • For a given l, increasing n increases the average distance of electrons from the nucleus (& the size of the orbital). 3s larger than 2s. • Ψnlm has l angular nodes and n-l-1 radial nodes (total of n-1 nodes) • Only for s orbitals does Ψnlm remain nonzero as r→0. Only s orbitals “penetrate to the n ...
here
... • Due to thermal fluctuations TRS is restored for T > 0 • For mass order parameter Ny is disordered + TR is preserved with a gap ...
... • Due to thermal fluctuations TRS is restored for T > 0 • For mass order parameter Ny is disordered + TR is preserved with a gap ...
Pdf - Text of NPTEL IIT Video Lectures
... kinetic energy of these two parts. So, you have this original nucleus X and then it emits this alpha particle so alpha particle goes this, this X is converted into Y A minus 4 and then this goes in one direction, this goes in other direction. So, the kinetic energy is distributed between these two a ...
... kinetic energy of these two parts. So, you have this original nucleus X and then it emits this alpha particle so alpha particle goes this, this X is converted into Y A minus 4 and then this goes in one direction, this goes in other direction. So, the kinetic energy is distributed between these two a ...
Quantum rings for beginners: energy spectra and persistent currents
... We then attempt to review the theory of quantum rings in a logical and pedagogical way, starting with the simplest case of noninteracting spinless fermions (Sections 3 and 4) and classical interacting electrons (Section 5), then introducing the e7ect of magnetic 8ux (Section 6) and spin (Section 7). ...
... We then attempt to review the theory of quantum rings in a logical and pedagogical way, starting with the simplest case of noninteracting spinless fermions (Sections 3 and 4) and classical interacting electrons (Section 5), then introducing the e7ect of magnetic 8ux (Section 6) and spin (Section 7). ...
Elementary Introduction to Quantum Field Theory in Curved Spacetime
... From now on, we shall only use the time-independent operators â± . Using Eqs. (3) and (6), it is easy to show that [â− , â+ ] = 1. Using the relations (6), the operator Ĥ can be expressed through the creation and annihilation operators â± as ...
... From now on, we shall only use the time-independent operators â± . Using Eqs. (3) and (6), it is easy to show that [â− , â+ ] = 1. Using the relations (6), the operator Ĥ can be expressed through the creation and annihilation operators â± as ...
Chapter 3 Statistical thermodynamics
... 3.4.1.2 Partition function of electrons Because in the chemical reaction, nucleus is always in the ground state, otherwise the energy level interval between the ground and the first excited state is very large,so commonly all the items after the second one in the bracket are ignored, so: ...
... 3.4.1.2 Partition function of electrons Because in the chemical reaction, nucleus is always in the ground state, otherwise the energy level interval between the ground and the first excited state is very large,so commonly all the items after the second one in the bracket are ignored, so: ...
Phases in noncommutative quantum mechanics on (pseudo) sphere
... exotic Let us remind [12], that for non-constant B the Jacobi identities failed in the “conventional” model, while in the “exotic” model the Jacobi identities hold for any B = A[1,2] , by definition. This reflects the different origin of magnetic fields B appearing in these two models. In the “conve ...
... exotic Let us remind [12], that for non-constant B the Jacobi identities failed in the “conventional” model, while in the “exotic” model the Jacobi identities hold for any B = A[1,2] , by definition. This reflects the different origin of magnetic fields B appearing in these two models. In the “conve ...