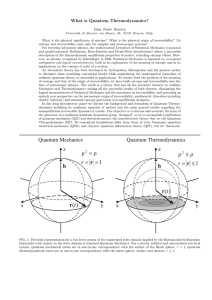
What is Quantum Thermodynamics?
... The state of a system may change with time either spontaneously due to its internal dynamics or as a result of interactions with other systems, or both. Systems that cannot induce any effects on each other’s state are called isolated. Systems that are not isolated can influence each other in a number ...
... The state of a system may change with time either spontaneously due to its internal dynamics or as a result of interactions with other systems, or both. Systems that cannot induce any effects on each other’s state are called isolated. Systems that are not isolated can influence each other in a number ...
Superconducting phase qubit coupled to a nanomechanical resonator:
... For a qubit with energy level spacing ⌬⑀ coupled with strength g to a resonator with angular frequency 0 and quality factor Q, the RWA is valid when both 兩0 − ⌬⑀ / ប兩 Ⰶ 0 / Q and g Ⰶ ⌬⑀. However, the resonant Rabi frequency, which is proportional to g, is then much smaller than the qubit frequenc ...
... For a qubit with energy level spacing ⌬⑀ coupled with strength g to a resonator with angular frequency 0 and quality factor Q, the RWA is valid when both 兩0 − ⌬⑀ / ប兩 Ⰶ 0 / Q and g Ⰶ ⌬⑀. However, the resonant Rabi frequency, which is proportional to g, is then much smaller than the qubit frequenc ...
Chapter 6 | Thermochemistry
... We are given the work functions for each of the elements (Ti = 6.94 10–19 J, Si = 7.24 10–19 J). Knowing the wavelength of the incident radiation (2.50 10–7 m), we can calculate the frequency of the incident radiation using = c/. Knowing , we can then calculate the kinetic energy of the ...
... We are given the work functions for each of the elements (Ti = 6.94 10–19 J, Si = 7.24 10–19 J). Knowing the wavelength of the incident radiation (2.50 10–7 m), we can calculate the frequency of the incident radiation using = c/. Knowing , we can then calculate the kinetic energy of the ...
Dynamical Symmetries of Planar Field Configurations
... of the model parameter. In fact, the constraint χ plays the role of Hamiltonian for the spin variables in the model (2.4), and the operator D is its quantum analog on the physical subspace [8]. Exactly this observation allows one to link our pseudoclassical model to the field system in question. Dyna ...
... of the model parameter. In fact, the constraint χ plays the role of Hamiltonian for the spin variables in the model (2.4), and the operator D is its quantum analog on the physical subspace [8]. Exactly this observation allows one to link our pseudoclassical model to the field system in question. Dyna ...
Vortex states of a disordered quantum Hall bilayer P. R. Eastham,
... Since dd is fixed by the sample, we expect the vortex density to vary with the magnetic length. In the limit of very strong disorder12 lc becomes of the order of the magnetic length l0 ⬇ 20 nm while d p remains of the order of dd. The vortex energy in this regime is Es ⬃ 2s共lc / dd兲, with the fact ...
... Since dd is fixed by the sample, we expect the vortex density to vary with the magnetic length. In the limit of very strong disorder12 lc becomes of the order of the magnetic length l0 ⬇ 20 nm while d p remains of the order of dd. The vortex energy in this regime is Es ⬃ 2s共lc / dd兲, with the fact ...
Morse Theory is a part pf differential geometry, concerned with
... forms. We will also define the Hodge operator, which will be used in the proof of the Morse Inequalities. If we choose a Riemannian metric on the manifold M, denoted gm , this implies that for all m M , we have an inner product gm (, ) on the tangent space T ( M ). For smooth vector fields on ...
... forms. We will also define the Hodge operator, which will be used in the proof of the Morse Inequalities. If we choose a Riemannian metric on the manifold M, denoted gm , this implies that for all m M , we have an inner product gm (, ) on the tangent space T ( M ). For smooth vector fields on ...
Transport properties of quantum-classical systems
... operators and sampling over the quantum-classical equilibrium density. More general expressions for time correlation functions have been derived by taking the quantum-classical limit of the quantum correlation function.14 The evaluation of these correlation functions involves forward and backward qu ...
... operators and sampling over the quantum-classical equilibrium density. More general expressions for time correlation functions have been derived by taking the quantum-classical limit of the quantum correlation function.14 The evaluation of these correlation functions involves forward and backward qu ...
Statistical Physics (PHY831), Part 2 - Exact results and solvable models
... Counting of degrees of freedom is often used to understand even complex systems such as glasses and biological structures. It is also relevant to problems such as polyatomic gases where there are rotational and internal harmonic degrees of freedom. Measurments of specific heat are often assessed in ...
... Counting of degrees of freedom is often used to understand even complex systems such as glasses and biological structures. It is also relevant to problems such as polyatomic gases where there are rotational and internal harmonic degrees of freedom. Measurments of specific heat are often assessed in ...
Mixed quantum–classical dynamics
... limitations as well, of course. The need for accurate multidimensional force Ðelds remains the primary focus. But as the methodology for “ on the Ñy Ï ab initio calculation of forces improves,2 we need to turn our attention to the more fundamental limitations of MD. Conventional MD is based on two u ...
... limitations as well, of course. The need for accurate multidimensional force Ðelds remains the primary focus. But as the methodology for “ on the Ñy Ï ab initio calculation of forces improves,2 we need to turn our attention to the more fundamental limitations of MD. Conventional MD is based on two u ...
Chapter 3 - Higher Education | Kendall Hunt Publishing
... A liquid has a definite volume but does not have its own shape since it takes the shape of the container in which it is placed. Its particles cohere firmly, but not rigidly, so the particles of a liquid have a great deal of mobility while maintaining close contact with one another. A gas has no fixe ...
... A liquid has a definite volume but does not have its own shape since it takes the shape of the container in which it is placed. Its particles cohere firmly, but not rigidly, so the particles of a liquid have a great deal of mobility while maintaining close contact with one another. A gas has no fixe ...
Read PDF - Physics (APS)
... In a ground-breaking work building on recent progress in invariant theory and representation theory, Klyachko exhibited an algorithm for computing all such Pauli-like constraints [4,8]. In fact, his work is part of a more general effort in quantum information theory addressing the quantum marginal p ...
... In a ground-breaking work building on recent progress in invariant theory and representation theory, Klyachko exhibited an algorithm for computing all such Pauli-like constraints [4,8]. In fact, his work is part of a more general effort in quantum information theory addressing the quantum marginal p ...
ATOMIC THEORY
... relatively slow-moving compared with other types of radiation. Thus, alpha particles are not very ________________________ - a single sheet of paper stops alpha particles. A beta particle is a veryfast moving ______________________ that has been emitted from a neutron of an unstable nucleus. Beta pa ...
... relatively slow-moving compared with other types of radiation. Thus, alpha particles are not very ________________________ - a single sheet of paper stops alpha particles. A beta particle is a veryfast moving ______________________ that has been emitted from a neutron of an unstable nucleus. Beta pa ...