Anyons and the quantum Hall effect— A pedagogical
... This paper is aimed at reviewing the physics of Anyons, particles whose statistics is neither fermionic not bosonic, and the way it is manifested in the quantum Hall effect. We will start with introducing the basic characters of this play—the Quantum Hall effect, the Aharonov–Bohm effect [7] and (more ...
... This paper is aimed at reviewing the physics of Anyons, particles whose statistics is neither fermionic not bosonic, and the way it is manifested in the quantum Hall effect. We will start with introducing the basic characters of this play—the Quantum Hall effect, the Aharonov–Bohm effect [7] and (more ...
TB-85 Dirt Trap for Boilers
... required when the boiler is installed to an existing heating system. Use of a Y strainer is not permitted as a substitute for a dirt trap. A dirt trap is a critical piece of equipment when using brazed plate heat exchangers in the E series boilers. The small passageways inside brazed plate heat exch ...
... required when the boiler is installed to an existing heating system. Use of a Y strainer is not permitted as a substitute for a dirt trap. A dirt trap is a critical piece of equipment when using brazed plate heat exchangers in the E series boilers. The small passageways inside brazed plate heat exch ...
Lecture Notes for Ph219/CS219: Quantum Information and Computation Chapter 2 John Preskill
... These five axioms provide a complete mathematical formulation of quantum mechanics. We immediately notice some curious features. One oddity is that the Schrödinger equation is linear, while we are accustomed to nonlinear dynamical equations in classical physics. This property seems to beg for an ex ...
... These five axioms provide a complete mathematical formulation of quantum mechanics. We immediately notice some curious features. One oddity is that the Schrödinger equation is linear, while we are accustomed to nonlinear dynamical equations in classical physics. This property seems to beg for an ex ...
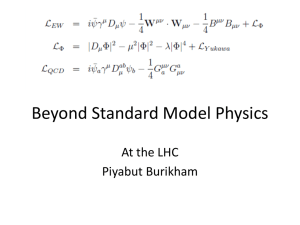
Beyond_Standard_Model_Physics
... • Quantum gravity suffers loop complications. Each order of loops is worse than the previous. unrenormalizable. • Loops induce anomalies (= breaking of classical sym by quantum effects). • Pheno level: loop corrections to scalar mass proportional to Λ^2 fine tuning problem. • SUSY ensures loop c ...
... • Quantum gravity suffers loop complications. Each order of loops is worse than the previous. unrenormalizable. • Loops induce anomalies (= breaking of classical sym by quantum effects). • Pheno level: loop corrections to scalar mass proportional to Λ^2 fine tuning problem. • SUSY ensures loop c ...