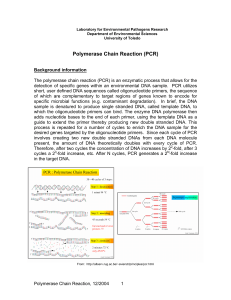
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) - Department of Environmental
... Low MgCl2 concentrations can help to eliminate non-specific priming and background PCR products and are desirable when fidelity of DNA synthesis is critical. At the same time however, too few Mg2+ ions can result in a low yield of PCR product. High MgCl2 concentrations can help to stabilize interact ...
... Low MgCl2 concentrations can help to eliminate non-specific priming and background PCR products and are desirable when fidelity of DNA synthesis is critical. At the same time however, too few Mg2+ ions can result in a low yield of PCR product. High MgCl2 concentrations can help to stabilize interact ...
The use of amplified fragment length polymorphism (AFLP) in the
... a DNA-based test. Despite its strengths, a DNA test can only be used if a sex-linked marker has been identified. The availability of sex-specific DNA is dictated by the relative contribution of genotype and environment in sex determination (Charlesworth 1991). Even if this has moved to the point whe ...
... a DNA-based test. Despite its strengths, a DNA test can only be used if a sex-linked marker has been identified. The availability of sex-specific DNA is dictated by the relative contribution of genotype and environment in sex determination (Charlesworth 1991). Even if this has moved to the point whe ...
Meiosis activity
... actually manipulate the chromosomes and draw the results. In thinking about how meiosis works, it is easiest to think about just a few chromosomes in a human cell, rather than all the chromosomes. So, for today’s exercise, imagine you are exploring the inheritance of two of the most common genetic d ...
... actually manipulate the chromosomes and draw the results. In thinking about how meiosis works, it is easiest to think about just a few chromosomes in a human cell, rather than all the chromosomes. So, for today’s exercise, imagine you are exploring the inheritance of two of the most common genetic d ...
Chromosomal Microarray (CGH+SNP)
... features and family history to determine whether mutation testing of individual genes is warranted. Test Limitations Balanced translocations, insertions, and inversions cannot be detected by microarray analysis as these do not generally lead to a gain or loss of genetic information. Chromosome an ...
... features and family history to determine whether mutation testing of individual genes is warranted. Test Limitations Balanced translocations, insertions, and inversions cannot be detected by microarray analysis as these do not generally lead to a gain or loss of genetic information. Chromosome an ...
Student`s guide -
... restriction enzymes. They are so called because they are made by bacteria to restrict the proliferation of viruses that attack them (the enzymes do this by cutting up the viral DNA). Restriction enzymes take their names from the bacterial species that produce them. For example, BamHI is obtained fro ...
... restriction enzymes. They are so called because they are made by bacteria to restrict the proliferation of viruses that attack them (the enzymes do this by cutting up the viral DNA). Restriction enzymes take their names from the bacterial species that produce them. For example, BamHI is obtained fro ...
Genetics and Genomics of Core Short Tandem Repeat Loci
... these variant alleles may contain partial repeats or insertions/deletions in the flanking region close to the repeat ...
... these variant alleles may contain partial repeats or insertions/deletions in the flanking region close to the repeat ...
Gene Mutations Caused by Radiation
... upon thermally activated reactions follows, for one thing, from the calculations and data presented by Muller and Mott-Smith (56), later confirmed by others, which showed that natural radiation is entirely inadequate in amount to be an important cause of spontaneous mutations in Drosophila at the ra ...
... upon thermally activated reactions follows, for one thing, from the calculations and data presented by Muller and Mott-Smith (56), later confirmed by others, which showed that natural radiation is entirely inadequate in amount to be an important cause of spontaneous mutations in Drosophila at the ra ...
unit – vi genetics - Sakshieducation.com
... 1) Sickle – cell anaemia: It is an autosomal recessive genetic disorder, characterized by rigid, sickle – shaped red blood cells in hypoxia conditions. Sickle cell anaemia is due to point mutation in the DNA that codes for β - globin polypeptide chain of haemoglobin molecule, causing the replacement ...
... 1) Sickle – cell anaemia: It is an autosomal recessive genetic disorder, characterized by rigid, sickle – shaped red blood cells in hypoxia conditions. Sickle cell anaemia is due to point mutation in the DNA that codes for β - globin polypeptide chain of haemoglobin molecule, causing the replacement ...
Meiosis II
... • Most organisms are diploid. Humans have 23 sets of chromosomes… therefore humans have 46 total chromosomes….. The diploid number for humans is 46 (46 chromosomes per cell). ...
... • Most organisms are diploid. Humans have 23 sets of chromosomes… therefore humans have 46 total chromosomes….. The diploid number for humans is 46 (46 chromosomes per cell). ...
The Fifties and the Renaissance in Human and
... rat and opossum (referring to 1959 and 1960 papers of OHNOet al. ) . In 1962, LYON gavea fuller discussion of the various components of her powerful hypothesis,with particular reference to human disease phenotypes. In this paper, she tried to share some credit, pointing out that, simultaneously with ...
... rat and opossum (referring to 1959 and 1960 papers of OHNOet al. ) . In 1962, LYON gavea fuller discussion of the various components of her powerful hypothesis,with particular reference to human disease phenotypes. In this paper, she tried to share some credit, pointing out that, simultaneously with ...
The replication of DNA
... placement of sliding camp on DNA. These enzyme couple ATP binding and hydrolysis to the placement of sliding clamp around primer template junction, every time that this junction is present in the cell. The clamp loaders also remove the slide clamp from DNA once all of the enzymes that interact with ...
... placement of sliding camp on DNA. These enzyme couple ATP binding and hydrolysis to the placement of sliding clamp around primer template junction, every time that this junction is present in the cell. The clamp loaders also remove the slide clamp from DNA once all of the enzymes that interact with ...
chromosomes
... Staining procedures have been developed in the past two decades and these techniques help to study the karyotype in plants and animals. 1. Q banding: The Q bands are the fluorescent bands observed after quinacrine mustard staining and observation with UV light. The distal ends of each chromatid are ...
... Staining procedures have been developed in the past two decades and these techniques help to study the karyotype in plants and animals. 1. Q banding: The Q bands are the fluorescent bands observed after quinacrine mustard staining and observation with UV light. The distal ends of each chromatid are ...
Huntingtin grabs a hammer: DNA repair in HD
... less efficient. To test this, she worked with normal and mutant skin cells donated by HD patients and their spouses. It turns out that mobility was not the issue – mutant huntingtin navigated to sites of DNA damage just like normal huntingtin. However, the DNA damage was more dire and more persisten ...
... less efficient. To test this, she worked with normal and mutant skin cells donated by HD patients and their spouses. It turns out that mobility was not the issue – mutant huntingtin navigated to sites of DNA damage just like normal huntingtin. However, the DNA damage was more dire and more persisten ...
Snímek 1
... (5) meiotic elimination in some species is counter-balanced by processes of drive at mitosis, mainly in the gametophytes, and less frequently at meiosis (equilibrium frequencies in populations) (6) neutral effects; negative and quantitative effects on the phenotype when present in high numbers (redu ...
... (5) meiotic elimination in some species is counter-balanced by processes of drive at mitosis, mainly in the gametophytes, and less frequently at meiosis (equilibrium frequencies in populations) (6) neutral effects; negative and quantitative effects on the phenotype when present in high numbers (redu ...
Identification of a Novel Streptococcal Gene
... elements pose a major threat to public health and motivate studies of SOS-like mechanisms in pathogenic bacteria (28). Several antibiotics, such as ciprofloxacin (50), trimethoprim (32), rifamycins (14), and -lactams (39), are known to induce an SOS response that increases mutations and accelerates ...
... elements pose a major threat to public health and motivate studies of SOS-like mechanisms in pathogenic bacteria (28). Several antibiotics, such as ciprofloxacin (50), trimethoprim (32), rifamycins (14), and -lactams (39), are known to induce an SOS response that increases mutations and accelerates ...
BASIC Role of Genes – 07/02/2012
... Only a small group of mutations directly associated with cancer risk are inherited from the parents Other (i.e., “most”) mutations are acquired over the life span Multiple injuries occur to the same cell to evolve or result in cancer “Injuries” can be from alcohol abuse, exposure to commercial tobac ...
... Only a small group of mutations directly associated with cancer risk are inherited from the parents Other (i.e., “most”) mutations are acquired over the life span Multiple injuries occur to the same cell to evolve or result in cancer “Injuries” can be from alcohol abuse, exposure to commercial tobac ...
Gel electrophoresis of restriction digest
... for the size of DNA fragments to be separated; (2) the DNA samples are loaded into the sample wells and the gel is run at a volatage and for a time period that will achieve optimal separation; and (3) the gel is stained or, if ethidium bromide has been incorporated into the gel and electrophoresis b ...
... for the size of DNA fragments to be separated; (2) the DNA samples are loaded into the sample wells and the gel is run at a volatage and for a time period that will achieve optimal separation; and (3) the gel is stained or, if ethidium bromide has been incorporated into the gel and electrophoresis b ...
Meiosis
... • Gametes have half the number of chromosomes • Meiosis is similar to mitosis with some chromosomal differences ...
... • Gametes have half the number of chromosomes • Meiosis is similar to mitosis with some chromosomal differences ...
Nucleotide Sequence Preservation of Human
... mutations in human leukemic cells. With the exception of 3 clones, we found no evidence of mtDNA nucleotide sequence divergence in 387 independently isolated mtDNA clones isolated from the leukemic cells of 4 patients. The small amount of nucleotide sequence divergence identified in the mtDNAs of 4 ...
... mutations in human leukemic cells. With the exception of 3 clones, we found no evidence of mtDNA nucleotide sequence divergence in 387 independently isolated mtDNA clones isolated from the leukemic cells of 4 patients. The small amount of nucleotide sequence divergence identified in the mtDNAs of 4 ...
Replication origin plasticity, Taylor-made: inhibition vs
... investigators went on to inhibit the checkpoint-signaling pathway with caffeine, which is known to inhibit at least two critical mediators of the S-phase checkpoint cascade. This caused a dramatic increase in the density of newly fired replication origins, whether or not aphidicolin was present. App ...
... investigators went on to inhibit the checkpoint-signaling pathway with caffeine, which is known to inhibit at least two critical mediators of the S-phase checkpoint cascade. This caused a dramatic increase in the density of newly fired replication origins, whether or not aphidicolin was present. App ...
Krebs, RA and AG Fasolo.
... The recessive X chromosome alleles all produce distinctive phenotypes: white eyes (w, 10.1), miniature wings (m, 36.1), and forked bristles (f, 56.7). T(2;3;)Al-W has multiple inversions superimposed on a translocation between the second and third chromosomes. This translocation is homozygous lethal ...
... The recessive X chromosome alleles all produce distinctive phenotypes: white eyes (w, 10.1), miniature wings (m, 36.1), and forked bristles (f, 56.7). T(2;3;)Al-W has multiple inversions superimposed on a translocation between the second and third chromosomes. This translocation is homozygous lethal ...
Cell Division (Meiosis)
... Meiosis II • No interphase II (or very short - no more DNA replication) • Remember: Meiosis II is similar to mitosis ...
... Meiosis II • No interphase II (or very short - no more DNA replication) • Remember: Meiosis II is similar to mitosis ...
Mutagen
In genetics, a mutagen is a physical or chemical agent that changes the genetic material, usually DNA, of an organism and thus increases the frequency of mutations above the natural background level. As many mutations can cause cancer, mutagens are therefore also likely to be carcinogens. Not all mutations are caused by mutagens: so-called ""spontaneous mutations"" occur due to spontaneous hydrolysis, errors in DNA replication, repair and recombination.