In recent years, a cost effective Wireless Mesh Networks ( WMNs
... network access to both the mesh and conventional clients. While, the mesh clients are either stationary or mobile, and form a client mesh network among themselves and with other mesh routers. In WMN, each node operates not only as host but also as a router, forwarding packets on behalf of other node ...
... network access to both the mesh and conventional clients. While, the mesh clients are either stationary or mobile, and form a client mesh network among themselves and with other mesh routers. In WMN, each node operates not only as host but also as a router, forwarding packets on behalf of other node ...
Love - Computing Science - Thompson Rivers University
... Reliable data delivery between two end applications or protocol entities It includes error recovery and packet loss recovery routines. How to send TCP packets to the destination through the jungle of computers on the Internet? There are other similar protocols, e.g., UDP, in the same level, which is ...
... Reliable data delivery between two end applications or protocol entities It includes error recovery and packet loss recovery routines. How to send TCP packets to the destination through the jungle of computers on the Internet? There are other similar protocols, e.g., UDP, in the same level, which is ...
Integrate Services Digital Network (ISDN) and SS7
... 30 x 64 kbit/s digital channels (B channels) 64 kbit/s channel for signaling (D channel) concatenation of B channels possible ...
... 30 x 64 kbit/s digital channels (B channels) 64 kbit/s channel for signaling (D channel) concatenation of B channels possible ...
QoS Protocols & Architectures
... 4 classes, 3 drop-precedences within each class Traffic that exceeds the traffic profile is not delivered with ...
... 4 classes, 3 drop-precedences within each class Traffic that exceeds the traffic profile is not delivered with ...
Chapter_1_V6.1 - Rose
... They’re in PowerPoint form so you see the animations; and can add, modify, and delete slides (including this one) and slide content to suit your needs. They obviously represent a lot of work on our part. In return for use, we only ask the following: If you use these slides (e.g., in a class) that ...
... They’re in PowerPoint form so you see the animations; and can add, modify, and delete slides (including this one) and slide content to suit your needs. They obviously represent a lot of work on our part. In return for use, we only ask the following: If you use these slides (e.g., in a class) that ...
The OSI Model
... Path Vector Routing Each entry in the routing table contains the destination network, the next router, and the path to reach the destination The path is usually defined as an ordered list of autonomous systems that a packet should travel through to reach the destination ...
... Path Vector Routing Each entry in the routing table contains the destination network, the next router, and the path to reach the destination The path is usually defined as an ordered list of autonomous systems that a packet should travel through to reach the destination ...
Document
... 3. The foreign agent contacts the mobile host’s home agent and says: “One of your hosts is over here.” The message from the foreign agent to the home agent contains the foreign agent’s network address. It also includes the security information, to convince the home agent that the mobile host is ...
... 3. The foreign agent contacts the mobile host’s home agent and says: “One of your hosts is over here.” The message from the foreign agent to the home agent contains the foreign agent’s network address. It also includes the security information, to convince the home agent that the mobile host is ...
Connecting In-Body Nano Communication with Body Area Networks
... above, we have to derive a network architecture which is technically feasible and takes these requirements into account. When we say technically feasible, we have to keep in mind that Body Area Networks have been deeply investigated and have become reality already. In-Body Networks, however, are sti ...
... above, we have to derive a network architecture which is technically feasible and takes these requirements into account. When we say technically feasible, we have to keep in mind that Body Area Networks have been deeply investigated and have become reality already. In-Body Networks, however, are sti ...
universitatea din craiova școala doctorală de facultatea de
... In the structure overlay network Chord it’s implemented for make management and discover of resources in the network. The Hashing in Chord is one of important adopted mechanisms; the hash will be at the IP address and produce the key this will attend with nodes. The hashing depends of load balance w ...
... In the structure overlay network Chord it’s implemented for make management and discover of resources in the network. The Hashing in Chord is one of important adopted mechanisms; the hash will be at the IP address and produce the key this will attend with nodes. The hashing depends of load balance w ...
IP: Datagram and Addressing
... LENGTH: gives length of option as it appears in IP datagram INTERNET ADDRESS: denotes the area reserved for internet addresses. This region is initially empty. Each router along the datagram path enters its address on the list POINTER: points to next available internet address slot in the option. Wh ...
... LENGTH: gives length of option as it appears in IP datagram INTERNET ADDRESS: denotes the area reserved for internet addresses. This region is initially empty. Each router along the datagram path enters its address on the list POINTER: points to next available internet address slot in the option. Wh ...
4th Edition: Chapter 1
... Residential, company and university ISPs Access ISPs in turn must be interconnected So that any two hosts can send packets to each other Resulting network of networks is very complex Evolution was driven by economics and national policies Let’s take a stepwise approach to describe current Inte ...
... Residential, company and university ISPs Access ISPs in turn must be interconnected So that any two hosts can send packets to each other Resulting network of networks is very complex Evolution was driven by economics and national policies Let’s take a stepwise approach to describe current Inte ...
Chapter 6
... • TCP/IP is considered the language of the Internet • It is the most widely used protocol today • It is a suite, or stack, of small, specialized protocols • Because of its routing ability, TCP/IP has become the protocol of choice for many LANs, as well as the basis for the Internet, making it the st ...
... • TCP/IP is considered the language of the Internet • It is the most widely used protocol today • It is a suite, or stack, of small, specialized protocols • Because of its routing ability, TCP/IP has become the protocol of choice for many LANs, as well as the basis for the Internet, making it the st ...
Remote Access Protection
... secure access to applications and network resources, thereby eliminating security/performance tradeoffs. • A single network-wide view for identification, mitigation and reporting on complex attacks, which eliminates false positives by using a highly advanced correlation system that enables IT and s ...
... secure access to applications and network resources, thereby eliminating security/performance tradeoffs. • A single network-wide view for identification, mitigation and reporting on complex attacks, which eliminates false positives by using a highly advanced correlation system that enables IT and s ...
Lecture 6 - Aerobic Suspended Growth
... IEEE 802.3 = Ethernet (10 Mbps, 100 Mbps, 10 Gbps) Ring networks: IEEE 802.5 = IBM Token Ring (4 and 16 Mbps), FDDI (Fiber Distributed Data Interface) Gbps. ...
... IEEE 802.3 = Ethernet (10 Mbps, 100 Mbps, 10 Gbps) Ring networks: IEEE 802.5 = IBM Token Ring (4 and 16 Mbps), FDDI (Fiber Distributed Data Interface) Gbps. ...
Introduction to Classless Routing
... – Supporting route aggregation (summarization), also known as supernetting, where thousands of routes could be represented by a single route in the routing table. • Route aggregation also helps prevent route flapping on Internet routers using BGP. Flapping routes can be a serious concern with Intern ...
... – Supporting route aggregation (summarization), also known as supernetting, where thousands of routes could be represented by a single route in the routing table. • Route aggregation also helps prevent route flapping on Internet routers using BGP. Flapping routes can be a serious concern with Intern ...
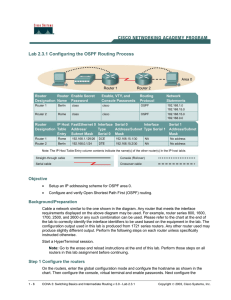
Lab 2.3.1 Configuring the OSPF Routing Process Objective
... In order to find out exactly how the router is configured, look at the interfaces. This will identify what type and how many interfaces the router has. There is no way to effectively list all of the combinations of configurations for each router class. What is provided are the identifiers for the po ...
... In order to find out exactly how the router is configured, look at the interfaces. This will identify what type and how many interfaces the router has. There is no way to effectively list all of the combinations of configurations for each router class. What is provided are the identifiers for the po ...
Internet QoS
... – The whole Internet – Q-BGP (= QoS-Enhanced Border Gateway Protocol) – Application-layer QoS routing – Performance-based routing: best routes selected by monitoring the ...
... – The whole Internet – Q-BGP (= QoS-Enhanced Border Gateway Protocol) – Application-layer QoS routing – Performance-based routing: best routes selected by monitoring the ...
A Predictive QoS Routing Scheme for Broadband Low Earth Orbit
... inter-satellite links, which connect the satellite to its neighboring satellites both in the adjacent orbital plane and in the same orbital plane. It is assumed that the inter-satellite links are reliable and exist for the complete duration of the satellite’s orbital revolution. This assumption resu ...
... inter-satellite links, which connect the satellite to its neighboring satellites both in the adjacent orbital plane and in the same orbital plane. It is assumed that the inter-satellite links are reliable and exist for the complete duration of the satellite’s orbital revolution. This assumption resu ...
COMPARATIVE STUDY OF TABLE DRIVEN ROUTING Mr. Pradip A. Chougule
... 3.1.1. Normalized routing overhead: This is the number of routing packets transmitted per delivery of a data packet. Each hop transmission of a routing packet is counted as one transmission. This factor also tells us something about the scalability of the routing protocol. If routing overhead increa ...
... 3.1.1. Normalized routing overhead: This is the number of routing packets transmitted per delivery of a data packet. Each hop transmission of a routing packet is counted as one transmission. This factor also tells us something about the scalability of the routing protocol. If routing overhead increa ...
Chapter 4 Network Layer Intro & Unicast Routing
... Priority: identify priority among datagrams in flow Flow Label: identify datagrams in same “flow.” (concept of“flow” not well defined). Next header: identify upper layer protocol for data ...
... Priority: identify priority among datagrams in flow Flow Label: identify datagrams in same “flow.” (concept of“flow” not well defined). Next header: identify upper layer protocol for data ...
4th Edition: Chapter 1
... at center: small # of well-connected large networks “tier-1” commercial ISPs (e.g., Level 3, Sprint, AT&T, NTT), national & international coverage content provider network (e.g, Google): private network that connects it data centers to Internet, often bypassing tier-1, regional ISPs Introduction ...
... at center: small # of well-connected large networks “tier-1” commercial ISPs (e.g., Level 3, Sprint, AT&T, NTT), national & international coverage content provider network (e.g, Google): private network that connects it data centers to Internet, often bypassing tier-1, regional ISPs Introduction ...
slides
... environment (offered traffic, QoS cubes supported, N-1 DIFs). – Connectivity graph, addressing, routing, data transfer, delimiting, resource allocation, relaying and multiplexing, authentication, authorization, SDU protection, etc ...
... environment (offered traffic, QoS cubes supported, N-1 DIFs). – Connectivity graph, addressing, routing, data transfer, delimiting, resource allocation, relaying and multiplexing, authentication, authorization, SDU protection, etc ...
ppt - Computer Science Division - University of California, Berkeley
... Properties of Routing Algorithms • Routing algorithm: – R: N x N -> C, which at each switch maps the destination node nd to the next channel on the route – which of the possible paths are used as routes? ...
... Properties of Routing Algorithms • Routing algorithm: – R: N x N -> C, which at each switch maps the destination node nd to the next channel on the route – which of the possible paths are used as routes? ...
Brief Tutorial on Networks and Communications
... Networks and Communications CS-4513 Distributed Systems (Slides include materials from Operating System Concepts, 7th ed., by Silbershatz, Galvin, & Gagne, Distributed Systems: Principles & Paradigms, 2nd ed. By Tanenbaum and Van Steen, and Distributed Systems: Concepts and Design, 4th ed., by Coulo ...
... Networks and Communications CS-4513 Distributed Systems (Slides include materials from Operating System Concepts, 7th ed., by Silbershatz, Galvin, & Gagne, Distributed Systems: Principles & Paradigms, 2nd ed. By Tanenbaum and Van Steen, and Distributed Systems: Concepts and Design, 4th ed., by Coulo ...
CCNA3 Chapter 2 Single Area OSPF
... • Routers send Link State Advertisements to other routers informing them of their links • All routers add Link State Advertisements to their topological database • Shortest Path algorithm calculates best route to each network • When link states change LSA update sent to all routers which recalculate ...
... • Routers send Link State Advertisements to other routers informing them of their links • All routers add Link State Advertisements to their topological database • Shortest Path algorithm calculates best route to each network • When link states change LSA update sent to all routers which recalculate ...