Rock
... rocks with heat from the core c. Bottom of the ocean floor where the plates of the ocean floor have opened up and allowed material from the mantle to escape ...
... rocks with heat from the core c. Bottom of the ocean floor where the plates of the ocean floor have opened up and allowed material from the mantle to escape ...
DR 2.4
... 1. What is the Greek meaning of “metamorphism”? Meta=change morphos=shape 2. What characterizes a metamorphic rock? Meaning what is true of all metamorphic ...
... 1. What is the Greek meaning of “metamorphism”? Meta=change morphos=shape 2. What characterizes a metamorphic rock? Meaning what is true of all metamorphic ...
Do Rocks Have Holes?
... Water, oil and gas are trapped inside the rocks beneath our feet. Porous rocks, or “rocks with holes” are good reservoirs for oil, gas and water. Non-porous layers of rock act as caps or seals to trap the resources. What is permeability? ...
... Water, oil and gas are trapped inside the rocks beneath our feet. Porous rocks, or “rocks with holes” are good reservoirs for oil, gas and water. Non-porous layers of rock act as caps or seals to trap the resources. What is permeability? ...
Chapter 14: Sediment and Sedimentary Rocks
... Once a sediment is deposited, it becomes hardened, or lithified, by two processes, including compaction and cementation (Figure 14.6). Common sedimentary cements include calcium carbonate (calcite, CaCO3), iron oxide (hematite, Fe2O3), and silica (quartz; SiO2). Remember that iron oxide, silica, and ...
... Once a sediment is deposited, it becomes hardened, or lithified, by two processes, including compaction and cementation (Figure 14.6). Common sedimentary cements include calcium carbonate (calcite, CaCO3), iron oxide (hematite, Fe2O3), and silica (quartz; SiO2). Remember that iron oxide, silica, and ...
Metamorphic rocks - Wando High School
... Background: Rocks are naturally occurring solid combination of two or more minerals. Think of a rock as being like a chocolate chip cookie. The cookie is made of flour, butter, sugar & chocolate. The cookie is like a rock and the flour, butter, sugar & chocolate are like minerals that make up the ro ...
... Background: Rocks are naturally occurring solid combination of two or more minerals. Think of a rock as being like a chocolate chip cookie. The cookie is made of flour, butter, sugar & chocolate. The cookie is like a rock and the flour, butter, sugar & chocolate are like minerals that make up the ro ...
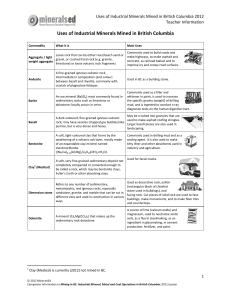
Uses of Industrial Minerals Mined in British Columbia
... rock; may have vesicles (trapped gas bubbles) like Larger basalt pieces are also used in pumice, but is very dense and heavy. landscaping. ...
... rock; may have vesicles (trapped gas bubbles) like Larger basalt pieces are also used in pumice, but is very dense and heavy. landscaping. ...
Quiz- Igneous and Sedimentary Rocks
... Which characteristic of an igneous rock provides the most information about how it formed? _texture__ ...
... Which characteristic of an igneous rock provides the most information about how it formed? _texture__ ...
Rock Cycle Crayon Lab
... Analyze and predict the sequence of events in the rock cycle. Represent the natural world using models and identify their limitations. ...
... Analyze and predict the sequence of events in the rock cycle. Represent the natural world using models and identify their limitations. ...
Chapter 7
... – Not common in glacial till formed from ground up sedimentary rocks – Common in soils with ultramafics – Not common in soils with lesser amounts of ultramafics – Sandy (common) clayey (uncommon) ...
... – Not common in glacial till formed from ground up sedimentary rocks – Common in soils with ultramafics – Not common in soils with lesser amounts of ultramafics – Sandy (common) clayey (uncommon) ...
Sedimentary rocks
... A variety of tests are used to identify the properties of minerals including: colour, hardness, luster and streak. The colour of a mineral is the first thing most people notice, but it can also be the least useful in identifying a mineral. Most minerals occur in more than one colour. The streak of a ...
... A variety of tests are used to identify the properties of minerals including: colour, hardness, luster and streak. The colour of a mineral is the first thing most people notice, but it can also be the least useful in identifying a mineral. Most minerals occur in more than one colour. The streak of a ...
What are igneous rocks?
... • Texture = size of the rock’s mineral crystals • Large crystals- slow cooling time – Intrusive rocks commonly have large crystals ...
... • Texture = size of the rock’s mineral crystals • Large crystals- slow cooling time – Intrusive rocks commonly have large crystals ...
Rock posters - metamorphic - EAL Nexus
... • It is formed under pressure. • It has alternating bands of colours. • It is rough to touch. • It sparkles. ...
... • It is formed under pressure. • It has alternating bands of colours. • It is rough to touch. • It sparkles. ...
Rock posters - metamorphic PDF - EAL Nexus
... • It is formed under pressure. • It has alternating bands of colours. • It is rough to touch. • It sparkles. ...
... • It is formed under pressure. • It has alternating bands of colours. • It is rough to touch. • It sparkles. ...
Minerals and Rocks - Ms. Lewis and Mr. Shumaker
... millions of years ago as magma cooled beneath Earth’s surface Mountain building pushed rock to and above surface Weathering and erosion wear away granite forming sand Streams carry sand to ocean Sand piles up and becomes compacted forming sandstone (sedimentary ...
... millions of years ago as magma cooled beneath Earth’s surface Mountain building pushed rock to and above surface Weathering and erosion wear away granite forming sand Streams carry sand to ocean Sand piles up and becomes compacted forming sandstone (sedimentary ...
Pertemuan 4 - Sri Atmaja P. Rosyidi
... or sand and containing silt-clay (minus 75 µm) material. Binder (Soil Binder): Portion of soil passing a 425 µm sieve. Stone: Crushed or naturally angular particles of rock which will pass a 75 mm sieve and be retained on a 2.00 mm sieve. Gravel: Rounded particles of rock which will pass a 75 mm sie ...
... or sand and containing silt-clay (minus 75 µm) material. Binder (Soil Binder): Portion of soil passing a 425 µm sieve. Stone: Crushed or naturally angular particles of rock which will pass a 75 mm sieve and be retained on a 2.00 mm sieve. Gravel: Rounded particles of rock which will pass a 75 mm sie ...
Marine Sediments
... • Mainly consists of sand, silt and clay within graded bedding • Continentally derived, but classified as transitional-deep sediment • Primarily transported and deposited by turbidity current processes ...
... • Mainly consists of sand, silt and clay within graded bedding • Continentally derived, but classified as transitional-deep sediment • Primarily transported and deposited by turbidity current processes ...
Rock posters - EAL Nexus
... Sandstone is made of sand-sized minerals or rock grains. Sandstone comes in many colours such as brown, yellow, red, grey, pink, white and black, but is usually a reddish-brown. The surface of sandstone is rough. Sandstone wears away easily in the rain and cold. ...
... Sandstone is made of sand-sized minerals or rock grains. Sandstone comes in many colours such as brown, yellow, red, grey, pink, white and black, but is usually a reddish-brown. The surface of sandstone is rough. Sandstone wears away easily in the rain and cold. ...
sedimentary, igneous - EAL Nexus
... Sandstone is made of sand-sized minerals or rock grains. Sandstone comes in many colours such as brown, yellow, red, grey, pink, white and black, but is usually a reddish-brown. The surface of sandstone is rough. ...
... Sandstone is made of sand-sized minerals or rock grains. Sandstone comes in many colours such as brown, yellow, red, grey, pink, white and black, but is usually a reddish-brown. The surface of sandstone is rough. ...
Marine environments - LSU Geology & Geophysics
... • Trace fossils, too, may be characteristic of particular environments • Trace fossils, of course, are not transported from their original place of origin ...
... • Trace fossils, too, may be characteristic of particular environments • Trace fossils, of course, are not transported from their original place of origin ...
Sedimentary Rocks T. Perron – 12.001 – 16 February 16, 2010 We
... Different source material (rock) Different pathways through the process we just sketched out Knowing the names & categories that have been devised to describe sed rocks is less important than knowing how a rock records different parts of this pathway, especially: 1. Which transport agent(s)? How ...
... Different source material (rock) Different pathways through the process we just sketched out Knowing the names & categories that have been devised to describe sed rocks is less important than knowing how a rock records different parts of this pathway, especially: 1. Which transport agent(s)? How ...
Type of Rock: Igneous
... visible, each layer in a foliated metamorphic rock appears to be made of the same mineral throughout, whereas sedimentary rocks will often have different layers of varying types of minerals, rocks, shells, etc. ...
... visible, each layer in a foliated metamorphic rock appears to be made of the same mineral throughout, whereas sedimentary rocks will often have different layers of varying types of minerals, rocks, shells, etc. ...
Rock Key tables c
... Igneous: A frozen melt without layering, if crystals are visible they are at random orientations; mostly black (basaltic) , gray (andesitic) , or white and pink granitic minerals ; may be course grained like granite or have no visible crystals, like basalt. Igneous rocks are always hard. ...
... Igneous: A frozen melt without layering, if crystals are visible they are at random orientations; mostly black (basaltic) , gray (andesitic) , or white and pink granitic minerals ; may be course grained like granite or have no visible crystals, like basalt. Igneous rocks are always hard. ...
Rock Candy
... 1. Lay out your samples of candy and determine which are models of a mineral and which are models of rocks. Use the information below to help you decide: ROCKS are made of one or more minerals. This means that the material that makes up an individual rock or several samples of the same kind of rock ...
... 1. Lay out your samples of candy and determine which are models of a mineral and which are models of rocks. Use the information below to help you decide: ROCKS are made of one or more minerals. This means that the material that makes up an individual rock or several samples of the same kind of rock ...
Mudrock

Mudrocks are a class of fine grained siliciclastic sedimentary rocks. The varying types of mudrocks include: siltstone, claystone, mudstone, slate, and shale. Most of the particles are less than 0.0625 mm (1/16th mm or 0.0025 inches) and are too small to study readily in the field. At first sight the rock types look quite similar; however, there are important differences in composition and nomenclature. There has been a great deal of disagreement involving the classification of mudrocks. There are a few important hurdles to classification, including:Mudrocks are the least understood, and one of the most understudied sedimentary rocks to dateIt is difficult to study mudrock constituents, due to their diminutive size and susceptibility to weathering on outcropsAnd most importantly, there is more than one classification scheme accepted by scientistsMudrocks make up fifty percent of the sedimentary rocks in the geologic record, and are easily the most widespread deposits on Earth. Fine sediment is the most abundant product of erosion, and these sediments contribute to the overall omnipresence of mudrocks. With increased pressure over time the platey clay minerals may become aligned, with the appearance of fissility or parallel layering. This finely bedded material that splits readily into thin layers is called shale, as distinct from mudstone. The lack of fissility or layering in mudstone may be due either to original texture or to the disruption of layering by burrowing organisms in the sediment prior to lithification. From the beginning of civilization, when pottery and mudbricks were made by hand, to now, mudrocks have been important. The first book on mudrocks, Geologie des Argils by Millot, was not published until 1964; however, scientists, engineers, and oil producers have understood the significance of mudrocks since the discovery of the Burgess Shale and the relatedness of mudrocks and oil. Literature on the elusive yet omnipresent rock-type has been increasing in recent years, and technology continues to allow for better analysis.