Mineral Discovery Kit
... Mineral Discovery Kit 1. Purpose: A. Show difference between Minerals and Rocks B. Conduct tests used to determine the identity of a mineral 2. Age Group: Primary grades 1 – 6 3. What is a mineral A. Minerals have the same chemical make up where ever they are found Quartz (SI02) is quartz no mater w ...
... Mineral Discovery Kit 1. Purpose: A. Show difference between Minerals and Rocks B. Conduct tests used to determine the identity of a mineral 2. Age Group: Primary grades 1 – 6 3. What is a mineral A. Minerals have the same chemical make up where ever they are found Quartz (SI02) is quartz no mater w ...
Second Hour Exam, Fall, 2006
... chemical weathering of minerals is a. calcium d. magnesium b. iron e. nitrogen c. potassium f. sulfur 17. If Brucium were a radioactive isotope that had a half-life of 250 years, how much of 100 grams of Brucium would still exist after 1000 years? a. none c. 6.25 grams e. you can't say c. 50 grams d ...
... chemical weathering of minerals is a. calcium d. magnesium b. iron e. nitrogen c. potassium f. sulfur 17. If Brucium were a radioactive isotope that had a half-life of 250 years, how much of 100 grams of Brucium would still exist after 1000 years? a. none c. 6.25 grams e. you can't say c. 50 grams d ...
Surficial materials of Pennsylvania
... Stratified sand and gravel includes flat-surfaced deposits in valley bottoms and hummocky deposits along valley sides. The valley-bottom deposits comprise clay, silt, sand, and gravel arranged in distinct layers, which are approximately parallel to the surface. The range of grain size within any lay ...
... Stratified sand and gravel includes flat-surfaced deposits in valley bottoms and hummocky deposits along valley sides. The valley-bottom deposits comprise clay, silt, sand, and gravel arranged in distinct layers, which are approximately parallel to the surface. The range of grain size within any lay ...
Chapter 2 Reading landscapes: how landscapes contain evidence
... attacked by acid chemical weathering, because the new compounds formed by chemical breakdown are usually of different colours. Any discolouration of rock or building stone surfaces is usually the result of chemical weathering. When the new compounds produced by chemical weathering are carried away i ...
... attacked by acid chemical weathering, because the new compounds formed by chemical breakdown are usually of different colours. Any discolouration of rock or building stone surfaces is usually the result of chemical weathering. When the new compounds produced by chemical weathering are carried away i ...
Metamorphic and Igneous
... There are a number of environments in which metamorphism occurs. Most are in the vicinity of plate margins, and many are associated with igneous activity. Contact or thermal metamorphism occurs when rocks immediately surrounding a molten igneous body are “baked” and therefore altered from their orig ...
... There are a number of environments in which metamorphism occurs. Most are in the vicinity of plate margins, and many are associated with igneous activity. Contact or thermal metamorphism occurs when rocks immediately surrounding a molten igneous body are “baked” and therefore altered from their orig ...
Finding Out – WALT: Investigate, explore and gather new
... of other rocks, parts of dead animals and shells. in a process called erosion sediment gets pushed down into the water and is held there for thousands even millions of years building up and getting squashed together and growing harder to form sedimentary rock. Metamorphic rock is made from old igneo ...
... of other rocks, parts of dead animals and shells. in a process called erosion sediment gets pushed down into the water and is held there for thousands even millions of years building up and getting squashed together and growing harder to form sedimentary rock. Metamorphic rock is made from old igneo ...
Type of Rock
... Sometimes, when lava cools very fast, there is not enough time for crystals to form. These rocks are smooth, like glass. These rocks are considered to have a glassy texture (Fig 5). Sometimes, rocks deep in earth’s surface take thousands of years to cool and harden. As this happens, the minerals coo ...
... Sometimes, when lava cools very fast, there is not enough time for crystals to form. These rocks are smooth, like glass. These rocks are considered to have a glassy texture (Fig 5). Sometimes, rocks deep in earth’s surface take thousands of years to cool and harden. As this happens, the minerals coo ...
Metamorphic Rocks
... The term "metamorphic" means "to change form." Any rock (igneous, sedimentary, or metamorphic) can become a metamorphic rock. If rocks are buried deep in the Earth at high temperatures and pressures, they form new minerals and textures all without melting ...
... The term "metamorphic" means "to change form." Any rock (igneous, sedimentary, or metamorphic) can become a metamorphic rock. If rocks are buried deep in the Earth at high temperatures and pressures, they form new minerals and textures all without melting ...
Chapter 3
... • A Combination of Minerals 1. The SIX most common minerals in igneous rocks are Quartz, Mica, Amphibole, Feldspar, Olivine, & Pyroxene ...
... • A Combination of Minerals 1. The SIX most common minerals in igneous rocks are Quartz, Mica, Amphibole, Feldspar, Olivine, & Pyroxene ...
Petroleum and Gas Engineering Exploration
... The clastic reservoirs are aggregates of particles, fragments of minerals, or fragments of older rocks. They are also called clastic or detrital rocks because they consist of minerals and rock particles washed from areas that have been eroded. Most clastic sedimentary rocks consist of grains that ar ...
... The clastic reservoirs are aggregates of particles, fragments of minerals, or fragments of older rocks. They are also called clastic or detrital rocks because they consist of minerals and rock particles washed from areas that have been eroded. Most clastic sedimentary rocks consist of grains that ar ...
Practice07w
... mineral bands of alternating felsic and mafic minerals. 4. _________ metamorphism occurs when rocks are overlain by more than 10 km of rocks or sediments. 5. Minerals stable in a narrow range of temperatures and pressures are called ________ minerals. 6. _____________ plate interactions form most dy ...
... mineral bands of alternating felsic and mafic minerals. 4. _________ metamorphism occurs when rocks are overlain by more than 10 km of rocks or sediments. 5. Minerals stable in a narrow range of temperatures and pressures are called ________ minerals. 6. _____________ plate interactions form most dy ...
Quiz # 1 Chapters 1 and 2
... mineral bands of alternating felsic and mafic minerals. 4. _________ metamorphism occurs when rocks are overlain by more than 10 km of rocks or sediments. 5. Minerals stable in a narrow range of temperatures and pressures are called ________ minerals. 6. _____________ plate interactions form most dy ...
... mineral bands of alternating felsic and mafic minerals. 4. _________ metamorphism occurs when rocks are overlain by more than 10 km of rocks or sediments. 5. Minerals stable in a narrow range of temperatures and pressures are called ________ minerals. 6. _____________ plate interactions form most dy ...
CEE 437 Engineering Geology
... between shells that are filled in with clear sparry calcite that was likely deposited in porous voids after burial. Limestones like this are major aquifers and oil reservoirs depending on how much porosity remains. You can also see some cavities that have not filled completely leaving small, well-fo ...
... between shells that are filled in with clear sparry calcite that was likely deposited in porous voids after burial. Limestones like this are major aquifers and oil reservoirs depending on how much porosity remains. You can also see some cavities that have not filled completely leaving small, well-fo ...
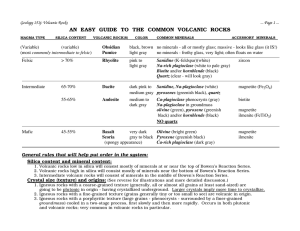
Volcanic Rock chart
... Glassy textures result from rapid cooling. There are few if any mineral grains; the rock is chiefly or entirely comprised of natural volcanic glass, or obsidian. Most obsidian is felsic (high in silica), but it also forms from other magma types as well. (For example, in Hawai'i, basaltic lavas flow ...
... Glassy textures result from rapid cooling. There are few if any mineral grains; the rock is chiefly or entirely comprised of natural volcanic glass, or obsidian. Most obsidian is felsic (high in silica), but it also forms from other magma types as well. (For example, in Hawai'i, basaltic lavas flow ...
Rock songs and carols
... hardening of compressed seashells composed of carbonate minerals and silica. Minerals become crystallized in solution (as in sea water), (Example: limestone made of calcite and dolomite). This group is known as chemical sedimentary rock. Particles carried by streams also build deposits. With multipl ...
... hardening of compressed seashells composed of carbonate minerals and silica. Minerals become crystallized in solution (as in sea water), (Example: limestone made of calcite and dolomite). This group is known as chemical sedimentary rock. Particles carried by streams also build deposits. With multipl ...
Whack-A-Mole Game -Rocks and Minerals Unit 2
... This type of rock was once another type of rock deep in the earth's surface. Heat and pressure caused it to change. What type of rock is formed this way? ...
... This type of rock was once another type of rock deep in the earth's surface. Heat and pressure caused it to change. What type of rock is formed this way? ...
Lesson 2 Types of rocks
... sedimentary rocks. The rocks are under tons of pressure, which causes heat build up, and this causes them to change. ...
... sedimentary rocks. The rocks are under tons of pressure, which causes heat build up, and this causes them to change. ...
Activity Description/Assignment
... determine grain size and maturity of the sandstone sample. The weathering products of typical igneous minerals are an integral part of the exercise. The metamorphic rock exercise includes a study of foliation, mineral content, degree of metamorphism, comparing the strength of quartzite and marble as ...
... determine grain size and maturity of the sandstone sample. The weathering products of typical igneous minerals are an integral part of the exercise. The metamorphic rock exercise includes a study of foliation, mineral content, degree of metamorphism, comparing the strength of quartzite and marble as ...
ES083 Rocks Assignment When early geologists looked at rocks
... footprints, tracks and trails, can also be present. Sediments are deposited only at or near the earth’s surface (the latter generally limited to caverns), and living things are basically limited to this realm as well. Fragments of pre-existing rocks (themselves containing smaller pieces of rock and/ ...
... footprints, tracks and trails, can also be present. Sediments are deposited only at or near the earth’s surface (the latter generally limited to caverns), and living things are basically limited to this realm as well. Fragments of pre-existing rocks (themselves containing smaller pieces of rock and/ ...
Unit 3 Lesson 3 Rock Cycle
... mineral because if the mineral is strongly colored, it may mask this property. Other Properties of Minerals Specific gravity - measure of each mineral's own unique density and how it compares to the density of water. The mineral's density is what makes the mineral heavy or light. Some minerals are v ...
... mineral because if the mineral is strongly colored, it may mask this property. Other Properties of Minerals Specific gravity - measure of each mineral's own unique density and how it compares to the density of water. The mineral's density is what makes the mineral heavy or light. Some minerals are v ...
Sedimentary Rocks
... of solution as calcite and its many crystals grow together, limestone forms. • Limestone also can contain other minerals and sediments, but it must be at least 50 percent calcite. • Limestone usually is deposited on the bottom of lakes or shallow seas. ...
... of solution as calcite and its many crystals grow together, limestone forms. • Limestone also can contain other minerals and sediments, but it must be at least 50 percent calcite. • Limestone usually is deposited on the bottom of lakes or shallow seas. ...
igneous rocks reading, a supplement to the lab manual
... interlocking of all these individual minerals is what gives many plutonic rocks (such as granite) their strength. Remember, plutonic (or intrusive) is the rock type, phaneritic is the texture that plutonic (or intrusive) rocks exhibit. The exception to this situation (which is common in Hawai‘i, act ...
... interlocking of all these individual minerals is what gives many plutonic rocks (such as granite) their strength. Remember, plutonic (or intrusive) is the rock type, phaneritic is the texture that plutonic (or intrusive) rocks exhibit. The exception to this situation (which is common in Hawai‘i, act ...
Sedimentary Rocks
... • Large areas of the central United States have limestone bedrock because seas covered much of the country for millions of years. • It is hard to imagine South Dakota being covered by ocean water, but it has happened several times throughout geological history. ...
... • Large areas of the central United States have limestone bedrock because seas covered much of the country for millions of years. • It is hard to imagine South Dakota being covered by ocean water, but it has happened several times throughout geological history. ...
Mudrock

Mudrocks are a class of fine grained siliciclastic sedimentary rocks. The varying types of mudrocks include: siltstone, claystone, mudstone, slate, and shale. Most of the particles are less than 0.0625 mm (1/16th mm or 0.0025 inches) and are too small to study readily in the field. At first sight the rock types look quite similar; however, there are important differences in composition and nomenclature. There has been a great deal of disagreement involving the classification of mudrocks. There are a few important hurdles to classification, including:Mudrocks are the least understood, and one of the most understudied sedimentary rocks to dateIt is difficult to study mudrock constituents, due to their diminutive size and susceptibility to weathering on outcropsAnd most importantly, there is more than one classification scheme accepted by scientistsMudrocks make up fifty percent of the sedimentary rocks in the geologic record, and are easily the most widespread deposits on Earth. Fine sediment is the most abundant product of erosion, and these sediments contribute to the overall omnipresence of mudrocks. With increased pressure over time the platey clay minerals may become aligned, with the appearance of fissility or parallel layering. This finely bedded material that splits readily into thin layers is called shale, as distinct from mudstone. The lack of fissility or layering in mudstone may be due either to original texture or to the disruption of layering by burrowing organisms in the sediment prior to lithification. From the beginning of civilization, when pottery and mudbricks were made by hand, to now, mudrocks have been important. The first book on mudrocks, Geologie des Argils by Millot, was not published until 1964; however, scientists, engineers, and oil producers have understood the significance of mudrocks since the discovery of the Burgess Shale and the relatedness of mudrocks and oil. Literature on the elusive yet omnipresent rock-type has been increasing in recent years, and technology continues to allow for better analysis.