TESTS FOR GROUNDING IN MODULE 1
... a) recessive, linked with a sex, which arises in X-chromosome; b) recessive, which arises in autosomes; c) dominant autosomal mutation CORRECT d) all of these avove 8. A human has galactosemia — a disease of accumulation. Which genetic method can we use to diagnose the case? a) Cytogenetic. b) Bioc ...
... a) recessive, linked with a sex, which arises in X-chromosome; b) recessive, which arises in autosomes; c) dominant autosomal mutation CORRECT d) all of these avove 8. A human has galactosemia — a disease of accumulation. Which genetic method can we use to diagnose the case? a) Cytogenetic. b) Bioc ...
Diverse Adaptations of an Ancestral Gill: A Common Evolutionary
... on the morphology and physiology of an organism. One of these changes is the evolutionary transition from aquatic to terrestrial life, leading to adaptations in locomotion, breathing, reproduction, and mechanisms for food capture. We have shown previously that insects’ wings most likely originated f ...
... on the morphology and physiology of an organism. One of these changes is the evolutionary transition from aquatic to terrestrial life, leading to adaptations in locomotion, breathing, reproduction, and mechanisms for food capture. We have shown previously that insects’ wings most likely originated f ...
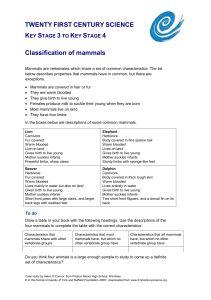
worksheet: classifying mammals
... characteristics which are determined by genes. We human beings have about 30,000 genes, but simpler organisms have a lot fewer genes. The more genes that humans have in common, the more similar they are. It follows that the more genes two different animals have in common, the more similar they are. ...
... characteristics which are determined by genes. We human beings have about 30,000 genes, but simpler organisms have a lot fewer genes. The more genes that humans have in common, the more similar they are. It follows that the more genes two different animals have in common, the more similar they are. ...
Child Development | Chapter 4
... females. These 22 pairs provide genetic information for both males and females, such as height and eye color. The chromosomes that make up the twenty-third pair are different for females and males. This pair is called the sex chromosomes. The sex of a child, however, is determined by this whole chro ...
... females. These 22 pairs provide genetic information for both males and females, such as height and eye color. The chromosomes that make up the twenty-third pair are different for females and males. This pair is called the sex chromosomes. The sex of a child, however, is determined by this whole chro ...
21 Learning About Pregnancy and Childbirth
... fertilizes an ovum, the resulting cell will have an XX pair of sex chromosomes. A fertilized ovum with an XX set of chromosomes develops into a female. If a sperm with a Y chromosome fertilizes an ovum, the resulting cell will have an XY pair of sex chromosomes. A fertilized ovum with an XY set of c ...
... fertilizes an ovum, the resulting cell will have an XX pair of sex chromosomes. A fertilized ovum with an XX set of chromosomes develops into a female. If a sperm with a Y chromosome fertilizes an ovum, the resulting cell will have an XY pair of sex chromosomes. A fertilized ovum with an XY set of c ...
Document
... 2- A form of inheritance in which no genes dominate over the opposite one, but they interact forming new trait 3- chemical substances which exist on the surfaces of red blood cells, they play an important role in blood transfusion process. 4- A kind of antigens whose inheritance is controlled by thr ...
... 2- A form of inheritance in which no genes dominate over the opposite one, but they interact forming new trait 3- chemical substances which exist on the surfaces of red blood cells, they play an important role in blood transfusion process. 4- A kind of antigens whose inheritance is controlled by thr ...
Chapter 14.
... 1 in 1000 live male births extra Y chromosome slightly taller than average more active normal intelligence, slight learning disabilities delayed emotional maturity normal sexual development ...
... 1 in 1000 live male births extra Y chromosome slightly taller than average more active normal intelligence, slight learning disabilities delayed emotional maturity normal sexual development ...
Syllabus
... or Cell Biology course. These include Molecular Biology of the Cell, Alberts et al, 5th edition, Chapters 4, 5 or Genetics: From Genes to Genomes, Hartwell et al, 3rd edition, Chapters 4, 13, 14, 18, 20. The 4th edition of Alberts is also available on line at pub med. You can search the text using t ...
... or Cell Biology course. These include Molecular Biology of the Cell, Alberts et al, 5th edition, Chapters 4, 5 or Genetics: From Genes to Genomes, Hartwell et al, 3rd edition, Chapters 4, 13, 14, 18, 20. The 4th edition of Alberts is also available on line at pub med. You can search the text using t ...
module-3-genetics-an-dd
... o Duplications: A portion of the chromosome is duplicated, resulting in extra genetic material. o Translocations: A portion of one chromosome is transferred to another chromosome. There are two main types of translocation. In a reciprocal translocation, segments from two different chromosomes have b ...
... o Duplications: A portion of the chromosome is duplicated, resulting in extra genetic material. o Translocations: A portion of one chromosome is transferred to another chromosome. There are two main types of translocation. In a reciprocal translocation, segments from two different chromosomes have b ...
Week 1 - Speyside High School
... Mutations are completely random and relatively rare They give rise to new alleles and are therefore a source of variation The rate of mutation can be increased by chemical agents or irradiation (X-rays & UV light etc.) These are called mutagenic agents There are two main types of mutation, ...
... Mutations are completely random and relatively rare They give rise to new alleles and are therefore a source of variation The rate of mutation can be increased by chemical agents or irradiation (X-rays & UV light etc.) These are called mutagenic agents There are two main types of mutation, ...
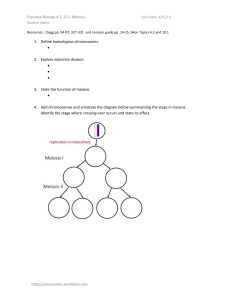
Directed Reading 11.2 - Blair Community Schools
... _____________________ 6. The centromeres divide, and the chromatids move to opposite poles of the cell. _____________________ 7. The homologous chromosomes separate. The chromosomes of each pair are pulled to opposite poles of the cell by the spindle fibers. The chromatids do not separate at their c ...
... _____________________ 6. The centromeres divide, and the chromatids move to opposite poles of the cell. _____________________ 7. The homologous chromosomes separate. The chromosomes of each pair are pulled to opposite poles of the cell by the spindle fibers. The chromatids do not separate at their c ...
chromosomes
... comes from the mother (called a maternal chromosome) and one comes from the father (paternal chromsosome). Homologous chromosomes are similar but not identical. Each carries the same genes in the same order, but the alleles (alternative form of a gene) for each trait may not be the same. Excepti ...
... comes from the mother (called a maternal chromosome) and one comes from the father (paternal chromsosome). Homologous chromosomes are similar but not identical. Each carries the same genes in the same order, but the alleles (alternative form of a gene) for each trait may not be the same. Excepti ...
ANSWERS on Inheritance File
... 6. continue process / repeat / further selective breeding / eq ; ...
... 6. continue process / repeat / further selective breeding / eq ; ...
BIO EXAM NOTES
... Chordata – fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds, mammals ENDOSYMBIOSIS - one cell engulfs a different type of cell survives and becomes an internal part of the engulfing cell - suggests that mitochondria and chloroplasts were once prokaryotes - they were engulfed by other larger cells and remained inta ...
... Chordata – fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds, mammals ENDOSYMBIOSIS - one cell engulfs a different type of cell survives and becomes an internal part of the engulfing cell - suggests that mitochondria and chloroplasts were once prokaryotes - they were engulfed by other larger cells and remained inta ...
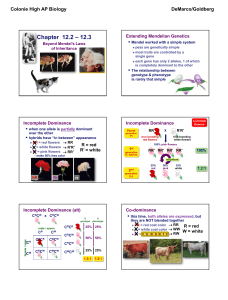
Lecture 030 - Beyond Mendel
... peas are genetically simple most traits are controlled by a single gene each gene has only 2 alleles, 1 of which is completely dominant to the other ...
... peas are genetically simple most traits are controlled by a single gene each gene has only 2 alleles, 1 of which is completely dominant to the other ...
genetics 2-2
... Color blindness- sex-linked genes in humans They are attached only to the Y chromosomes Hemophilia- a bleeders disease, sex-linked, attached only to the Y chromosome When you cross a horse and a mule -> a “sterile donkey” (Jackass) A germ mutation occurred in a reproduction cell and is transmitted t ...
... Color blindness- sex-linked genes in humans They are attached only to the Y chromosomes Hemophilia- a bleeders disease, sex-linked, attached only to the Y chromosome When you cross a horse and a mule -> a “sterile donkey” (Jackass) A germ mutation occurred in a reproduction cell and is transmitted t ...
Sex Chromosome Biology in the Mammalian Kingdom All biological
... million years ago, the X and Y chromosomes were very similar, but since then the Y chromosome has lost most of its genes, whereas the present X chromosome contains more than 1000 genes. Hence, the dosage of X-encoded genes needs to be equalized between female (XX) and male (XY) cells. This is achiev ...
... million years ago, the X and Y chromosomes were very similar, but since then the Y chromosome has lost most of its genes, whereas the present X chromosome contains more than 1000 genes. Hence, the dosage of X-encoded genes needs to be equalized between female (XX) and male (XY) cells. This is achiev ...
Dosage compensation

Dosage Compensation is the equalization of gene expression between the males and females of a species. Because sex chromosomes contain different numbers of genes, different species of organisms have developed different mechanisms to cope with this inequality. Replicating the actual gene is impossible; thus organisms instead equalize the expression from each gene. In humans, the females (XX) silence the transcription of one X chromosome of each pair, and transcribe all information from the other, expressed X chromosome. Thus, human females have the same number of expressed X-linked genes as do human males (XY), both genders having essentially one X chromosome per cell, from which to transcribe and express genes.