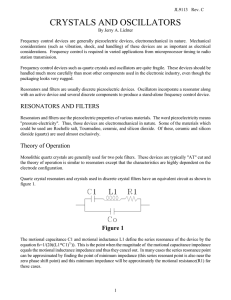
EXERCISES RESONAT CIRCUITS 5.21 The resonant circuit of the
... Knowing that the quality factor of the coil (L with internal resistance r) in the circuit of the Figure 1 at 0=1Mrad/s is Qb=50, and that the antiresonant circuit receives the maximum power at this frequency, obtain: a) Values of r, L and C. b) Value of the current through the coil if the frequency ...
... Knowing that the quality factor of the coil (L with internal resistance r) in the circuit of the Figure 1 at 0=1Mrad/s is Qb=50, and that the antiresonant circuit receives the maximum power at this frequency, obtain: a) Values of r, L and C. b) Value of the current through the coil if the frequency ...
Flag Antenna Construction
... box showed a deeper null (but, more often, not). Previous Kaz and Pennant tests (with the Mini-Circuits based feedpoint box) showed somewhat shallower average designzone nulls: 14.9 dB Pennant, 16.6 dB Kaz. Some nulls exceeded 30 dB. For many stations on southwesterly bearings, a 25 dB null was not ...
... box showed a deeper null (but, more often, not). Previous Kaz and Pennant tests (with the Mini-Circuits based feedpoint box) showed somewhat shallower average designzone nulls: 14.9 dB Pennant, 16.6 dB Kaz. Some nulls exceeded 30 dB. For many stations on southwesterly bearings, a 25 dB null was not ...
VI Characteristics – signal diode
... Explain the advantage of the full-wave over the half-wave rectifier in making a stable power supply. In fact, neither supply is very good. Both are unregulated. Regulated power supplies will be studied in a later lab. The Zener Diode Use the measuring setup of Part 1 above to measure the V-I charact ...
... Explain the advantage of the full-wave over the half-wave rectifier in making a stable power supply. In fact, neither supply is very good. Both are unregulated. Regulated power supplies will be studied in a later lab. The Zener Diode Use the measuring setup of Part 1 above to measure the V-I charact ...
AC Circuits - faculty at Chemeketa
... 4) Use three multi-meters configured as AC voltmeters to measure ΔVr, ΔVc, and E0 for an extremely large range of frequencies in an approximately geometric series. The frequency range should be large enough to measure several large potential differences (>0.8* E0), several small potential difference ...
... 4) Use three multi-meters configured as AC voltmeters to measure ΔVr, ΔVc, and E0 for an extremely large range of frequencies in an approximately geometric series. The frequency range should be large enough to measure several large potential differences (>0.8* E0), several small potential difference ...
60Apretest - De Anza College
... a. Open the circuit an connect the meter in series between the two ends b. Open the circuit at the positive and negative terminals of the battery c. Connect the meter across the battery or load d. Open the circuit at one point an connect the meter to one end 15. If a circuit has 12 volts and 4 amps ...
... a. Open the circuit an connect the meter in series between the two ends b. Open the circuit at the positive and negative terminals of the battery c. Connect the meter across the battery or load d. Open the circuit at one point an connect the meter to one end 15. If a circuit has 12 volts and 4 amps ...
Passive-Optical Person Detector
... will therefore even work in a darkened room. Gradual changes in illumination are ignored, while rapid changes are greeted with an acoustic alarm. However, direct sunlight is not good for the sensitivity of the circuit: it is better to use indirect lighting, reflected from other objects in the enviro ...
... will therefore even work in a darkened room. Gradual changes in illumination are ignored, while rapid changes are greeted with an acoustic alarm. However, direct sunlight is not good for the sensitivity of the circuit: it is better to use indirect lighting, reflected from other objects in the enviro ...
Document
... current IT and the common parallel voltage VA. Less parallel XL allows more IL to make the circuit more inductive, with a larger negative phase angle for IT with respect to VA. ...
... current IT and the common parallel voltage VA. Less parallel XL allows more IL to make the circuit more inductive, with a larger negative phase angle for IT with respect to VA. ...
Feed lines
... one made of a slightly lighter weight material than the last, until the ball nearest us is almost the same mass as the cue ball. Now the speeding cue ball will stop dead when it hits the row of balls, and the steel ball will slowly move off down the table, having absorbed all of the energy. When you ...
... one made of a slightly lighter weight material than the last, until the ball nearest us is almost the same mass as the cue ball. Now the speeding cue ball will stop dead when it hits the row of balls, and the steel ball will slowly move off down the table, having absorbed all of the energy. When you ...
Feed lines
... one made of a slightly lighter weight material than the last, until the ball nearest us is almost the same mass as the cue ball. Now the speeding cue ball will stop dead when it hits the row of balls, and the steel ball will slowly move off down the table, having absorbed all of the energy. When you ...
... one made of a slightly lighter weight material than the last, until the ball nearest us is almost the same mass as the cue ball. Now the speeding cue ball will stop dead when it hits the row of balls, and the steel ball will slowly move off down the table, having absorbed all of the energy. When you ...
Crystal radio
A crystal radio receiver, also called a crystal set or cat's whisker receiver, is a very simple radio receiver, popular in the early days of radio. It needs no other power source but that received solely from the power of radio waves received by a wire antenna. It gets its name from its most important component, known as a crystal detector, originally made from a piece of crystalline mineral such as galena. This component is now called a diode.Crystal radios are the simplest type of radio receiver and can be made with a few inexpensive parts, such as a wire for an antenna, a coil of copper wire for adjustment, a capacitor, a crystal detector, and earphones. They are distinct from ordinary radios as they are passive receivers, while other radios use a separate source of electric power such as a battery or the mains power to amplify the weak radio signal so as to make it louder. Thus, crystal sets produce rather weak sound and must be listened to with sensitive earphones, and can only receive stations within a limited range.The rectifying property of crystals was discovered in 1874 by Karl Ferdinand Braun, and crystal detectors were developed and applied to radio receivers in 1904 by Jagadish Chandra Bose, G. W. Pickard and others.Crystal radios were the first widely used type of radio receiver, and the main type used during the wireless telegraphy era. Sold and homemade by the millions, the inexpensive and reliable crystal radio was a major driving force in the introduction of radio to the public, contributing to the development of radio as an entertainment medium around 1920.After about 1920, crystal sets were superseded by the first amplifying receivers, which used vacuum tubes (Audions), and became obsolete for commercial use. They, however, continued to be built by hobbyists, youth groups, and the Boy Scouts as a way of learning about the technology of radio. Today they are still sold as educational devices, and there are groups of enthusiasts devoted to their construction who hold competitions comparing the performance of their home-built designs.Crystal radios receive amplitude modulated (AM) signals, and can be designed to receive almost any radio frequency band, but most receive the AM broadcast band. A few receive shortwave bands, but strong signals are required. The first crystal sets received wireless telegraphy signals broadcast by spark-gap transmitters at frequencies as low as 20 kHz.