148155
... circuit is operated at much higher frequency (in the range of 100 kHz) the input voltage, in spite of being unregulated, may be considered to have a constant magnitude during any high frequency cycle. A fast switching device („S‟), like a MOSFET, is used with fast dynamic control over switch duty ra ...
... circuit is operated at much higher frequency (in the range of 100 kHz) the input voltage, in spite of being unregulated, may be considered to have a constant magnitude during any high frequency cycle. A fast switching device („S‟), like a MOSFET, is used with fast dynamic control over switch duty ra ...
Ultra-low Jitter LVCMOS Fanout Buffer/Level Translator w/ Universal
... Differential Voltage Measurement Terminology The differential voltage of a differential signal can be described by two different definitions causing confusion when reading datasheets or communicating with other engineers. This section will address the measurement and description of a differential si ...
... Differential Voltage Measurement Terminology The differential voltage of a differential signal can be described by two different definitions causing confusion when reading datasheets or communicating with other engineers. This section will address the measurement and description of a differential si ...
Link Budget and Fade Margin
... approximately 1.7 dB at an operating frequency of 170 Mhz. One should note that this is the loss of the coaxial cable only and does not include the additional loss of any connectors used to construct a finished cable assembly. For the purposes of a link budget, the insertion loss for connectors can ...
... approximately 1.7 dB at an operating frequency of 170 Mhz. One should note that this is the loss of the coaxial cable only and does not include the additional loss of any connectors used to construct a finished cable assembly. For the purposes of a link budget, the insertion loss for connectors can ...
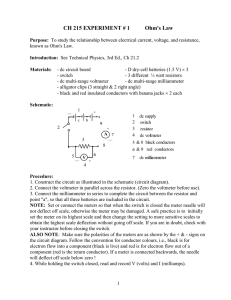
CH 215 EXPERIMENT # 1 Ohm`s Law
... 2. Construct the circuit as shown in the schematic with the voltmeter connected in parallel and the milliammeter connected in series (with correct polarity). 3. Note that the 200 resistor is connected in series with the battery to reduce the amount of current which will flow in the circuit to a sa ...
... 2. Construct the circuit as shown in the schematic with the voltmeter connected in parallel and the milliammeter connected in series (with correct polarity). 3. Note that the 200 resistor is connected in series with the battery to reduce the amount of current which will flow in the circuit to a sa ...
12. Transformers, Impedance Matching and Maximum Power Transfer
... Maximum Power Transfer Introduction The transformer is a device that takes AC at one voltage and transforms it into another voltage either higher or lower than the original voltage. Alternatively, a transformer can be used to do the same thing with current. Transformers only work with AC (and they d ...
... Maximum Power Transfer Introduction The transformer is a device that takes AC at one voltage and transforms it into another voltage either higher or lower than the original voltage. Alternatively, a transformer can be used to do the same thing with current. Transformers only work with AC (and they d ...
ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS LAB #1
... Most diodes use an identification number starting with the prefix “1N”. Locate a 1N4004 or a 1N4005 from your lab kit. It is a small resistor sized component…black…with a white stripe at the negative (cathode…N material) end. The other lead is the positive (anode… p type material) lead. ...
... Most diodes use an identification number starting with the prefix “1N”. Locate a 1N4004 or a 1N4005 from your lab kit. It is a small resistor sized component…black…with a white stripe at the negative (cathode…N material) end. The other lead is the positive (anode… p type material) lead. ...
High Sensitivity Photoreceiver Design
... power. They exhibit perfect signal to noise performance. However, the photon detectors require thermoelectric and cryogenic cooling. The second class of infrared detectors is composed of thermal detectors. Thermal effects are generally wavelength independent; the signal depends upon the radiant powe ...
... power. They exhibit perfect signal to noise performance. However, the photon detectors require thermoelectric and cryogenic cooling. The second class of infrared detectors is composed of thermal detectors. Thermal effects are generally wavelength independent; the signal depends upon the radiant powe ...
Outline of Content - College of Micronesia
... 2. Explain the purpose and identify the various types of resistors and their symbols. Identify the value, power rating and tolerance of resistors using various types of industry codes. 3. Describe the purpose and types of switches, fuses and circuit breakers and identify their schematic symbols. 4. ...
... 2. Explain the purpose and identify the various types of resistors and their symbols. Identify the value, power rating and tolerance of resistors using various types of industry codes. 3. Describe the purpose and types of switches, fuses and circuit breakers and identify their schematic symbols. 4. ...
Crystal radio
A crystal radio receiver, also called a crystal set or cat's whisker receiver, is a very simple radio receiver, popular in the early days of radio. It needs no other power source but that received solely from the power of radio waves received by a wire antenna. It gets its name from its most important component, known as a crystal detector, originally made from a piece of crystalline mineral such as galena. This component is now called a diode.Crystal radios are the simplest type of radio receiver and can be made with a few inexpensive parts, such as a wire for an antenna, a coil of copper wire for adjustment, a capacitor, a crystal detector, and earphones. They are distinct from ordinary radios as they are passive receivers, while other radios use a separate source of electric power such as a battery or the mains power to amplify the weak radio signal so as to make it louder. Thus, crystal sets produce rather weak sound and must be listened to with sensitive earphones, and can only receive stations within a limited range.The rectifying property of crystals was discovered in 1874 by Karl Ferdinand Braun, and crystal detectors were developed and applied to radio receivers in 1904 by Jagadish Chandra Bose, G. W. Pickard and others.Crystal radios were the first widely used type of radio receiver, and the main type used during the wireless telegraphy era. Sold and homemade by the millions, the inexpensive and reliable crystal radio was a major driving force in the introduction of radio to the public, contributing to the development of radio as an entertainment medium around 1920.After about 1920, crystal sets were superseded by the first amplifying receivers, which used vacuum tubes (Audions), and became obsolete for commercial use. They, however, continued to be built by hobbyists, youth groups, and the Boy Scouts as a way of learning about the technology of radio. Today they are still sold as educational devices, and there are groups of enthusiasts devoted to their construction who hold competitions comparing the performance of their home-built designs.Crystal radios receive amplitude modulated (AM) signals, and can be designed to receive almost any radio frequency band, but most receive the AM broadcast band. A few receive shortwave bands, but strong signals are required. The first crystal sets received wireless telegraphy signals broadcast by spark-gap transmitters at frequencies as low as 20 kHz.