Volcanoes
... A type of volcano often formed on or near another active volcano. Magma rises just under the crust and cools. ...
... A type of volcano often formed on or near another active volcano. Magma rises just under the crust and cools. ...
Geology Without Limits Investigation of Lithosphere Deep
... 1- Hispaniola, Puerto Rico, Virgin Islands. Crustal thickness ~30 km. Jurassic Cretaceous arc and oceanic rocks diachronously (west – east) emplaced northwards. Bounded south and north by the Muertos Trough and North Hispaniola-Puerto Rico Trench subduction zones. Major zone of sinistral displacemen ...
... 1- Hispaniola, Puerto Rico, Virgin Islands. Crustal thickness ~30 km. Jurassic Cretaceous arc and oceanic rocks diachronously (west – east) emplaced northwards. Bounded south and north by the Muertos Trough and North Hispaniola-Puerto Rico Trench subduction zones. Major zone of sinistral displacemen ...
The Big MELT
... ore than 95 percent of the earth’s volcanic magma is generated beneath the seafloor at mid-ocean ridges. As the oceanic plates move apart at spreading ridges, hot mantle rock rises from deep in the earth’s interior to replace material dragged away by the plates. This ascent releases pressure that ha ...
... ore than 95 percent of the earth’s volcanic magma is generated beneath the seafloor at mid-ocean ridges. As the oceanic plates move apart at spreading ridges, hot mantle rock rises from deep in the earth’s interior to replace material dragged away by the plates. This ascent releases pressure that ha ...
Hazardous Earth - The Student Room
... Qatar has the lowest disaster risk (at 0.1%) whilst Philippines has the highest (at 27.5%) out of 170 countries. The disaster risk equation helps explain why similar hazards cause disasters of different degrees. For instance both Izmit (Turkey) and Kashmir (Pakistan) had a similar sized earthqua ...
... Qatar has the lowest disaster risk (at 0.1%) whilst Philippines has the highest (at 27.5%) out of 170 countries. The disaster risk equation helps explain why similar hazards cause disasters of different degrees. For instance both Izmit (Turkey) and Kashmir (Pakistan) had a similar sized earthqua ...
Into Earth
... prediction. The broad geographic coverage will permit quantitative understanding of tantalizing connections observed between activity in different regions. Complementary geological ...
... prediction. The broad geographic coverage will permit quantitative understanding of tantalizing connections observed between activity in different regions. Complementary geological ...
Aquatic Science Where do Oceans come from?
... Google Image “Plate Tectonic map” On your globe, label the 3 types of boundaries. Label the plates. Draw arrows to indicate plate direction. Show me for grade. On paper, answer the following with complete sentences – What type of plate boundary appears mostly on the ocean floor? Why is this? – How d ...
... Google Image “Plate Tectonic map” On your globe, label the 3 types of boundaries. Label the plates. Draw arrows to indicate plate direction. Show me for grade. On paper, answer the following with complete sentences – What type of plate boundary appears mostly on the ocean floor? Why is this? – How d ...
Layers of the Earth Notes
... Earth’s Layers by Composition • Core – Below the mantle; at the center of Earth – Makes up 1/3 of Earth’s mass – Composed primarily of iron and nickel • Almost no oxygen, silicon, aluminum, or magnesium ...
... Earth’s Layers by Composition • Core – Below the mantle; at the center of Earth – Makes up 1/3 of Earth’s mass – Composed primarily of iron and nickel • Almost no oxygen, silicon, aluminum, or magnesium ...
39 Final Exam Review 2012 Revised KC
... 66. d. Convection currents are mainly due to radioactive isotopes in the mantle. It gets REALLY HOT! ...
... 66. d. Convection currents are mainly due to radioactive isotopes in the mantle. It gets REALLY HOT! ...
Minerals and Rocks
... Continental crust comprises the major landmasses on Earth that are exposed to the atmosphere. It is less dense (2.7 g/cm3) and much thicker than oceanic crust. Where continental crust extends to very high elevations, such as in mountain ranges, it also descends to great depths below the surface. Con ...
... Continental crust comprises the major landmasses on Earth that are exposed to the atmosphere. It is less dense (2.7 g/cm3) and much thicker than oceanic crust. Where continental crust extends to very high elevations, such as in mountain ranges, it also descends to great depths below the surface. Con ...
Geology and Nonrenewable Minerals
... Subduction – continental plate rides up over the denser oceanic plate and pushes it down into the mantle Subduction zone – the area where the collision and subduction take place Trench – forms at the boundary between the two converging plates ...
... Subduction – continental plate rides up over the denser oceanic plate and pushes it down into the mantle Subduction zone – the area where the collision and subduction take place Trench – forms at the boundary between the two converging plates ...
ES 106 Laboratory # 4 - Western Oregon University
... basins are geologically young, ephemeral features. Based upon this discovery, a revolutionary theory called plate tectonics has been developed that helps to explain and interrelate earthquakes, mountain building, and other geologic events and processes. The theory of plate tectonics is the foundatio ...
... basins are geologically young, ephemeral features. Based upon this discovery, a revolutionary theory called plate tectonics has been developed that helps to explain and interrelate earthquakes, mountain building, and other geologic events and processes. The theory of plate tectonics is the foundatio ...
Mr. Lee – Layers of the Earth rap
... Yeah, uh huh, you know what it is Crust moving ‘cause of plate tectonics Yeah, mantle’s like plastic And the core is really dense and metallic Memorize this song and you’ll know everything about the Crust and mantle, crust and mantle, crust and mantle, crust and mantle Moving on down there are two m ...
... Yeah, uh huh, you know what it is Crust moving ‘cause of plate tectonics Yeah, mantle’s like plastic And the core is really dense and metallic Memorize this song and you’ll know everything about the Crust and mantle, crust and mantle, crust and mantle, crust and mantle Moving on down there are two m ...
Activity 5
... that the continents of the Earth have moved during geologic time.Two features of the Earth were the subject of intense study in the late 1800s— the discovery of similar fossils on continents that are now separated widely by oceans, and the origin of mountain ranges. Both played a part in the early s ...
... that the continents of the Earth have moved during geologic time.Two features of the Earth were the subject of intense study in the late 1800s— the discovery of similar fossils on continents that are now separated widely by oceans, and the origin of mountain ranges. Both played a part in the early s ...
Ocean-Ocean Subduction Zones System
... • petrological-thermomechanical models including water transport and melting ...
... • petrological-thermomechanical models including water transport and melting ...
Geography How Tectonic Movement Shapes the Earth 2010
... discovered that the lithosphere is broken into huge pieces called tectonic plates. ...
... discovered that the lithosphere is broken into huge pieces called tectonic plates. ...
Teach the Earth Layers Song to the tune of Shortnin` Bread. Inner
... Inner core, outer core, mantle, crust. The Earth is made of rocks and dust. The inner core is in the middle, the inner core is very hot! Inner core, outer core, mantle, crust. The Earth is made of rocks and dust. The outer core is moving slowly all around the inner core. Inner core, outer core, mant ...
... Inner core, outer core, mantle, crust. The Earth is made of rocks and dust. The inner core is in the middle, the inner core is very hot! Inner core, outer core, mantle, crust. The Earth is made of rocks and dust. The outer core is moving slowly all around the inner core. Inner core, outer core, mant ...
Name: Planet Earth in Cross Section Objective: Devise a model of
... the Earth. These rocks actually flow, moving in response to the stresses placed upon them by the churning motions of the deep interior of the Earth. The flowing asthenosphere carries the lithosphere of the Earth, including the continents, on its back Lithosphere – The solid outer portion of the Eart ...
... the Earth. These rocks actually flow, moving in response to the stresses placed upon them by the churning motions of the deep interior of the Earth. The flowing asthenosphere carries the lithosphere of the Earth, including the continents, on its back Lithosphere – The solid outer portion of the Eart ...
Review Game
... Differentiation is heat generated by the energy released as dense objects fall toward the center of a planet during the formation of the core of a planet. Radioactive decay generates heat by releasing nuclear energy when an unstable (radioactive) isotope decays into a more stable element. 46. A cons ...
... Differentiation is heat generated by the energy released as dense objects fall toward the center of a planet during the formation of the core of a planet. Radioactive decay generates heat by releasing nuclear energy when an unstable (radioactive) isotope decays into a more stable element. 46. A cons ...
Plate Tectonic Theory
... Hot spots are places in the earth’s mantle where the hot rock or magma, continually rises and melts through a plate.. You won’t find a hot spot between the boundary of 2 different plates. You find hot spots breaking through the middle of a plate, whether that is in the middle of a continental plate ...
... Hot spots are places in the earth’s mantle where the hot rock or magma, continually rises and melts through a plate.. You won’t find a hot spot between the boundary of 2 different plates. You find hot spots breaking through the middle of a plate, whether that is in the middle of a continental plate ...
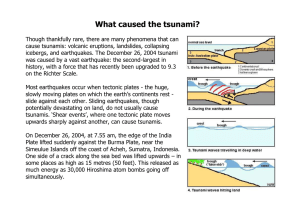
What caused the tsunami
... Though thankfully rare, there are many phenomena that can cause tsunamis: volcanic eruptions, landslides, collapsing icebergs, and earthquakes. The December 26, 2004 tsunami was caused by a vast earthquake: the second-largest in history, with a force that has recently been upgraded to 9.3 on the Ric ...
... Though thankfully rare, there are many phenomena that can cause tsunamis: volcanic eruptions, landslides, collapsing icebergs, and earthquakes. The December 26, 2004 tsunami was caused by a vast earthquake: the second-largest in history, with a force that has recently been upgraded to 9.3 on the Ric ...
Day 5 Subduction Trenches
... http://www2.wwnorton.com/college/geo/egeo/flash/2_9.swf Watch Blue planet video on deep ocean trench life: http://video.google.com/videoplay?docid=6616117576614575795 &q=deep+sea+creatures&total=945&start=0&num=10&so=0&type=se arch&plindex=1 ...
... http://www2.wwnorton.com/college/geo/egeo/flash/2_9.swf Watch Blue planet video on deep ocean trench life: http://video.google.com/videoplay?docid=6616117576614575795 &q=deep+sea+creatures&total=945&start=0&num=10&so=0&type=se arch&plindex=1 ...
Printer-friendly Version - Solid Earth Discussions
... topography calculation method we did a number of simple point load calculations which were compared to published solutions. Although I have no problem with explaining the Qom basin as a fairly passive (i.e. driven by far field forces, since there is no known tectonics in that region at that age) I a ...
... topography calculation method we did a number of simple point load calculations which were compared to published solutions. Although I have no problem with explaining the Qom basin as a fairly passive (i.e. driven by far field forces, since there is no known tectonics in that region at that age) I a ...
Chapter 10: Plate Tectonics
... these changes, shown in Figure 4, took place. The idea suggested that lower-density, continental material somehow had to plow through higher-density, ocean-floor material. The force behind this plowing was thought to be the spin of Earth on its axis—a notion that was quickly rejected by physicists. ...
... these changes, shown in Figure 4, took place. The idea suggested that lower-density, continental material somehow had to plow through higher-density, ocean-floor material. The force behind this plowing was thought to be the spin of Earth on its axis—a notion that was quickly rejected by physicists. ...
Interior of the earth
... a sharp increase downward in the speed of earthquake waves there. The explanation for the increase at the Moho is presumed to be a change in rock types. Drill holes to penetrate the Moho have been proposed, and a Soviet hole on the Kola Peninsula has been drilled to a depth of 12 kilometers, but dri ...
... a sharp increase downward in the speed of earthquake waves there. The explanation for the increase at the Moho is presumed to be a change in rock types. Drill holes to penetrate the Moho have been proposed, and a Soviet hole on the Kola Peninsula has been drilled to a depth of 12 kilometers, but dri ...
Plate tectonics
Plate tectonics (from the Late Latin tectonicus, from the Greek: τεκτονικός ""pertaining to building"") is a scientific theory that describes the large-scale motion of Earth's lithosphere. This theoretical model builds on the concept of continental drift which was developed during the first few decades of the 20th century. The geoscientific community accepted the theory after the concepts of seafloor spreading were later developed in the late 1950s and early 1960s.The lithosphere, which is the rigid outermost shell of a planet (on Earth, the crust and upper mantle), is broken up into tectonic plates. On Earth, there are seven or eight major plates (depending on how they are defined) and many minor plates. Where plates meet, their relative motion determines the type of boundary; convergent, divergent, or transform. Earthquakes, volcanic activity, mountain-building, and oceanic trench formation occur along these plate boundaries. The lateral relative movement of the plates typically varies from zero to 100 mm annually.Tectonic plates are composed of oceanic lithosphere and thicker continental lithosphere, each topped by its own kind of crust. Along convergent boundaries, subduction carries plates into the mantle; the material lost is roughly balanced by the formation of new (oceanic) crust along divergent margins by seafloor spreading. In this way, the total surface of the globe remains the same. This prediction of plate tectonics is also referred to as the conveyor belt principle. Earlier theories (that still have some supporters) propose gradual shrinking (contraction) or gradual expansion of the globe.Tectonic plates are able to move because the Earth's lithosphere has greater strength than the underlying asthenosphere. Lateral density variations in the mantle result in convection. Plate movement is thought to be driven by a combination of the motion of the seafloor away from the spreading ridge (due to variations in topography and density of the crust, which result in differences in gravitational forces) and drag, with downward suction, at the subduction zones. Another explanation lies in the different forces generated by the rotation of the globe and the tidal forces of the Sun and Moon. The relative importance of each of these factors and their relationship to each other is unclear, and still the subject of much debate.