Chapter 13 - The Theory of Plate Tectonics
... continental drift. Convection is a vertical circulation pattern in a gas or liquid caused by hot material rising and cold material sinking occurs in the mantle when warm molten rock rises and cool magma ...
... continental drift. Convection is a vertical circulation pattern in a gas or liquid caused by hot material rising and cold material sinking occurs in the mantle when warm molten rock rises and cool magma ...
Sea-Floor Spreading - Madison County Schools
... • Using a submarine named Alvin, scientists were able to look into a rift valley and examine something called pillow lava, which is a special type of solid rock that only forms on the ocean floor when magma cools very rapidly. This proved that new molten material was being added to the ocean floor a ...
... • Using a submarine named Alvin, scientists were able to look into a rift valley and examine something called pillow lava, which is a special type of solid rock that only forms on the ocean floor when magma cools very rapidly. This proved that new molten material was being added to the ocean floor a ...
What landforms are at different plate boundaries?
... Fold mountains • Young fold mountains (formed over last 65 million years) are the highest areas in the world. • All peaks over 7000m are in central Asia, including Mt Everest at 8,850m. • Young fold mountains include ranges such as the Himalayas, the Rockies, the Andes and the Alps. • Fold mountai ...
... Fold mountains • Young fold mountains (formed over last 65 million years) are the highest areas in the world. • All peaks over 7000m are in central Asia, including Mt Everest at 8,850m. • Young fold mountains include ranges such as the Himalayas, the Rockies, the Andes and the Alps. • Fold mountai ...
Boundaries, Stresses, and Faults OH MY!
... • May work like a trash compactor smashing rock. – Rock goes crunches up to make folded mountains. – Rock goes down “under” @ subduction zone. ...
... • May work like a trash compactor smashing rock. – Rock goes crunches up to make folded mountains. – Rock goes down “under” @ subduction zone. ...
Modelling the initiation of sea floor spreading and formation of rifted
... industry and a sound understanding of the breakup process, the nature of the continent-ocean transition and heat flow history are of prime importance to oil industry exploration in these regions. However the recent observations of depth dependent (heterogeneous) stretching, where upper crustal exten ...
... industry and a sound understanding of the breakup process, the nature of the continent-ocean transition and heat flow history are of prime importance to oil industry exploration in these regions. However the recent observations of depth dependent (heterogeneous) stretching, where upper crustal exten ...
Unit 4 Chapter 11
... Subsidence- It is the apparent sinking of the ocean floor due to the deposition of mud, sand and gravel flowing from rivers. This deposition is occurring in the Gulf of Mexico at the mouth of the Mississippi River. Glaciers and Isostasy The weight of the ice makes the land sink the ocean floor rises ...
... Subsidence- It is the apparent sinking of the ocean floor due to the deposition of mud, sand and gravel flowing from rivers. This deposition is occurring in the Gulf of Mexico at the mouth of the Mississippi River. Glaciers and Isostasy The weight of the ice makes the land sink the ocean floor rises ...
Chapter 9 Planetary Geology: Agenda Ad Hoc Rover Update
... • Was Earth’s geology destined from birth? – Many of Earth’s features determined by size, distance from Sun, and rotation rate – Reason for plate tectonics still a mystery ...
... • Was Earth’s geology destined from birth? – Many of Earth’s features determined by size, distance from Sun, and rotation rate – Reason for plate tectonics still a mystery ...
GEO100 05 plate tectonics
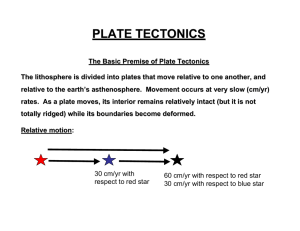
... The lithosphere is divided into plates that move relative to one another, and relative to the earth’s asthenosphere. Movement occurs at very slow (cm/yr) rates. As a plate moves, its interior remains relatively intact (but it is not totally ridged) while its boundaries become deformed. ...
... The lithosphere is divided into plates that move relative to one another, and relative to the earth’s asthenosphere. Movement occurs at very slow (cm/yr) rates. As a plate moves, its interior remains relatively intact (but it is not totally ridged) while its boundaries become deformed. ...
Notes For Chapter 9 - Folds, Faults, and Geologic Maps
... • Dominant displacement is horizontal and parallel to the strike of the fault • Types of strike-slip faults – Right-lateral – as you face the fault, the block on the opposite side of the fault moves to the right – Left-lateral – as you face the fault, the block on the opposite side of the fault move ...
... • Dominant displacement is horizontal and parallel to the strike of the fault • Types of strike-slip faults – Right-lateral – as you face the fault, the block on the opposite side of the fault moves to the right – Left-lateral – as you face the fault, the block on the opposite side of the fault move ...
PLATE TECTONICS Last time, we discussed the lithosphere, the
... Last time, we discussed the lithosphere, the outer rigid shell of the earth. The last major portion of this class is devoted to understanding the forces acting in the earth’s upper ~100 km Questions: a) Do portions of the earth’s surface move relative to each other? b) Why are there mountains, earth ...
... Last time, we discussed the lithosphere, the outer rigid shell of the earth. The last major portion of this class is devoted to understanding the forces acting in the earth’s upper ~100 km Questions: a) Do portions of the earth’s surface move relative to each other? b) Why are there mountains, earth ...
Sea Floor Spreading - Smyth County Schools
... • Ocean crust thin; continental crust thick & granitic • Rocks on continent varied, oldest 3.8 billion years old • Volcanoes & Earthquakes limited in locations • Atlantic & Pacific different topography from land and from each other ...
... • Ocean crust thin; continental crust thick & granitic • Rocks on continent varied, oldest 3.8 billion years old • Volcanoes & Earthquakes limited in locations • Atlantic & Pacific different topography from land and from each other ...
Plate tectonics
... underwater mountain range in the middle of the Atlantic Ocean. Hess’s original hypothesis was that convection currents deep inside the mantle caused spreading. If convection does occur within the Earth’s mantle, then rising hot magma can push up the thin oceanic crust to form a ridge crest. Oceanic ...
... underwater mountain range in the middle of the Atlantic Ocean. Hess’s original hypothesis was that convection currents deep inside the mantle caused spreading. If convection does occur within the Earth’s mantle, then rising hot magma can push up the thin oceanic crust to form a ridge crest. Oceanic ...
Geography 12
... Short movements along the fault that gradually release pressure. This creep an release of pressure means earthquakes are lower in magnitude and less destructive. ...
... Short movements along the fault that gradually release pressure. This creep an release of pressure means earthquakes are lower in magnitude and less destructive. ...
Lithosphere and Asthenosphere
... about 100 kilometers thick. How are crust and lithosphere different from each other? ...
... about 100 kilometers thick. How are crust and lithosphere different from each other? ...
Theory of Plate Tectonics and Convection Currents
... continents were once joined in a single landmass and gradually moved, or drifted, apart. For many years, people did not accept Wegener’s ideas. Not until the mid-1900s did scientists find new evidence that made them consider continental drift more seriously. Scientists now had proof that tectonic pl ...
... continents were once joined in a single landmass and gradually moved, or drifted, apart. For many years, people did not accept Wegener’s ideas. Not until the mid-1900s did scientists find new evidence that made them consider continental drift more seriously. Scientists now had proof that tectonic pl ...
No Plumes Along Mid-Ocean Ridges
... thermal convection regime that guides and helps maintain volcanism along spreading ridges. These plumes have been considered to be the main or even total (Yamamoto et al., 2007) source of thermal energy that drives plates. They would also provide the energy for enhanced lava production and locally h ...
... thermal convection regime that guides and helps maintain volcanism along spreading ridges. These plumes have been considered to be the main or even total (Yamamoto et al., 2007) source of thermal energy that drives plates. They would also provide the energy for enhanced lava production and locally h ...
Plate Tectonics
... • Earthquakes are a result of motion within the earth. • This only occurs where the earth is solid and therefore can only occur within about 100 miles of the surface • Earthquakes provide the best evidence regarding the interior structure of the Earth. ...
... • Earthquakes are a result of motion within the earth. • This only occurs where the earth is solid and therefore can only occur within about 100 miles of the surface • Earthquakes provide the best evidence regarding the interior structure of the Earth. ...
Plate Tectonics and Climate— Episodes of Extensive Glaciation and
... Effects on large-scale circulation. The distribution of mountains influences the large-scale circulation of the atmosphere. In the simplest form, this influence is analogous to that of a large rock in a stream. The rock acts as a barrier to the flow of the fluid, and the current pattern is modified ...
... Effects on large-scale circulation. The distribution of mountains influences the large-scale circulation of the atmosphere. In the simplest form, this influence is analogous to that of a large rock in a stream. The rock acts as a barrier to the flow of the fluid, and the current pattern is modified ...
Slide 1
... b) What can we learn from foreland basin deposits (i.e. climate vs tectonic) ? In a medial-distal part of a foreland basin high sediment accumulation rates coincide with fine-grained sediments and reflect an increase in subsidence due to tectonic loading Low sediment accumulation rates coincide with ...
... b) What can we learn from foreland basin deposits (i.e. climate vs tectonic) ? In a medial-distal part of a foreland basin high sediment accumulation rates coincide with fine-grained sediments and reflect an increase in subsidence due to tectonic loading Low sediment accumulation rates coincide with ...
Key Stage 3 unit: tectonic patterns and processes
... hazardous locations, human response to risk and the idea of preparedness for natural hazards. By investigating the location of these features pupils develop their skills in using a variety of atlases/online mapping tools and add to their developing framework of world knowledge. ...
... hazardous locations, human response to risk and the idea of preparedness for natural hazards. By investigating the location of these features pupils develop their skills in using a variety of atlases/online mapping tools and add to their developing framework of world knowledge. ...
Light: The Cosmic Messenger
... crust differs from thick continental crust • Dating of seafloor shows it is usually quite young ...
... crust differs from thick continental crust • Dating of seafloor shows it is usually quite young ...
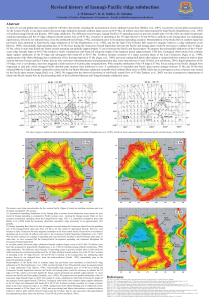
Revised history of Izanagi-Pacific ridge subduction
... for the western Pacific. In our plate model mid-ocean ridge subduction beneath southern Japan occurs at 60-55 Ma, 20 million years later than proposed for Kula-Pacific [Engebretson, et al., 1985] or Farallon-Izanagi [Onishi and Kimura, 1995] ridge subduction. The difference arises because Izanagi-Pa ...
... for the western Pacific. In our plate model mid-ocean ridge subduction beneath southern Japan occurs at 60-55 Ma, 20 million years later than proposed for Kula-Pacific [Engebretson, et al., 1985] or Farallon-Izanagi [Onishi and Kimura, 1995] ridge subduction. The difference arises because Izanagi-Pa ...
Lithosphere and Asthenosphere
... about 100 kilometers thick. How are crust and lithosphere different from each other? ...
... about 100 kilometers thick. How are crust and lithosphere different from each other? ...
Geography Knowledge Organiser 8.1.1
... - Scientists can currently forcast the likelihood of an earthquake in the long term (over years and decades). However, it is almost impossible to predict earthquakes in the short term. - However, there are ways that scientists can monitor tectonic activity to help them forcast earthquakes: - Scienti ...
... - Scientists can currently forcast the likelihood of an earthquake in the long term (over years and decades). However, it is almost impossible to predict earthquakes in the short term. - However, there are ways that scientists can monitor tectonic activity to help them forcast earthquakes: - Scienti ...
Plate tectonics
Plate tectonics (from the Late Latin tectonicus, from the Greek: τεκτονικός ""pertaining to building"") is a scientific theory that describes the large-scale motion of Earth's lithosphere. This theoretical model builds on the concept of continental drift which was developed during the first few decades of the 20th century. The geoscientific community accepted the theory after the concepts of seafloor spreading were later developed in the late 1950s and early 1960s.The lithosphere, which is the rigid outermost shell of a planet (on Earth, the crust and upper mantle), is broken up into tectonic plates. On Earth, there are seven or eight major plates (depending on how they are defined) and many minor plates. Where plates meet, their relative motion determines the type of boundary; convergent, divergent, or transform. Earthquakes, volcanic activity, mountain-building, and oceanic trench formation occur along these plate boundaries. The lateral relative movement of the plates typically varies from zero to 100 mm annually.Tectonic plates are composed of oceanic lithosphere and thicker continental lithosphere, each topped by its own kind of crust. Along convergent boundaries, subduction carries plates into the mantle; the material lost is roughly balanced by the formation of new (oceanic) crust along divergent margins by seafloor spreading. In this way, the total surface of the globe remains the same. This prediction of plate tectonics is also referred to as the conveyor belt principle. Earlier theories (that still have some supporters) propose gradual shrinking (contraction) or gradual expansion of the globe.Tectonic plates are able to move because the Earth's lithosphere has greater strength than the underlying asthenosphere. Lateral density variations in the mantle result in convection. Plate movement is thought to be driven by a combination of the motion of the seafloor away from the spreading ridge (due to variations in topography and density of the crust, which result in differences in gravitational forces) and drag, with downward suction, at the subduction zones. Another explanation lies in the different forces generated by the rotation of the globe and the tidal forces of the Sun and Moon. The relative importance of each of these factors and their relationship to each other is unclear, and still the subject of much debate.