Name - cloudfront.net
... In this part of the lab, you will measure some of the properties of wood floating in water and then compare it to processes happening in the earth’s crust and mantle. Choose two of the different types of wood, measure their mass (using the balance) and volume (using a ruler), and write your measurem ...
... In this part of the lab, you will measure some of the properties of wood floating in water and then compare it to processes happening in the earth’s crust and mantle. Choose two of the different types of wood, measure their mass (using the balance) and volume (using a ruler), and write your measurem ...
Plate Tectonics - North Coast Distance Education
... The theory of continental drift was proposed in the early 1900s and was supported by a variety of impressive geologic data. Lack of an understanding of the nature of the oceanic crust, however, prevented the development of a complete theory of Earth’s dynamics. The theory of plate tectonics wrought ...
... The theory of continental drift was proposed in the early 1900s and was supported by a variety of impressive geologic data. Lack of an understanding of the nature of the oceanic crust, however, prevented the development of a complete theory of Earth’s dynamics. The theory of plate tectonics wrought ...
example from the Australian plate
... • Low-angle subduction zones, great distance from trench to active arc. • Magmatic events produce large composite batholiths, with superunits and units which individually show mafic to acid (primitive to mature) compositional trends. • Very large volumes of magma are emplaced into the crust, and can ...
... • Low-angle subduction zones, great distance from trench to active arc. • Magmatic events produce large composite batholiths, with superunits and units which individually show mafic to acid (primitive to mature) compositional trends. • Very large volumes of magma are emplaced into the crust, and can ...
LLVSPs vs. LVAs - Do plumes exist?
... ridges are in the same places as they were when Pangea broke up & the antipodal Pacific plates reorganized & oceanic plateaus erupted. The surface expressions of ridges migrate but only within the confines of the ~2000-km wide LVAs associated with ridges at 150-200 km depth. ...
... ridges are in the same places as they were when Pangea broke up & the antipodal Pacific plates reorganized & oceanic plateaus erupted. The surface expressions of ridges migrate but only within the confines of the ~2000-km wide LVAs associated with ridges at 150-200 km depth. ...
plate tectonics and associated hazards
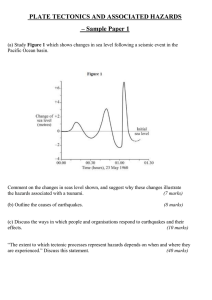
... Discuss the degree to which the theory of Plate Tectonics is supported by the distribution of volcanic and seismic activity across the globe. (40 marks) ...
... Discuss the degree to which the theory of Plate Tectonics is supported by the distribution of volcanic and seismic activity across the globe. (40 marks) ...
Plate Tectonics Review with Answers Rich Text
... 11. Plates slide past one another at ____. a. subduction zones b. transform boundaries ...
... 11. Plates slide past one another at ____. a. subduction zones b. transform boundaries ...
Sample Lesson 56 - Nancy Larson® Science
... • Discuss the “Use What You Have Learned” question with the children. • Allow children to use their geology booklets to answer the questions. • Circulate and assist children as they work. If children have difficulty reading, pair children and allow them to work with a partner to complete the lesson ...
... • Discuss the “Use What You Have Learned” question with the children. • Allow children to use their geology booklets to answer the questions. • Circulate and assist children as they work. If children have difficulty reading, pair children and allow them to work with a partner to complete the lesson ...
Unit 3 Review
... large landmass that they call Pangaea. • It’s important to understand that at one time scientists think that all the continents were connected and during millions of years the continents moved into their current locations. ...
... large landmass that they call Pangaea. • It’s important to understand that at one time scientists think that all the continents were connected and during millions of years the continents moved into their current locations. ...
Section 4 Deforming the Earth`s Crust
... • The process by which the shape of a rock changes because of stress is called deformation. • Rock layers bend when stress is placed on them. • When enough stress is placed on rocks, they can reach their elastic limit and break. ...
... • The process by which the shape of a rock changes because of stress is called deformation. • Rock layers bend when stress is placed on them. • When enough stress is placed on rocks, they can reach their elastic limit and break. ...
12585507_Chapter 2_The Physical Environment
... and are effectively 'rafted' on the yielding asthenosphere, they are also characterised by complex deformation and plate interactions along their margins. Here plates are created, deformed, and destroyed, giving rise to concentrated narrow belts of volcanic and earthquake activity. The plate boundar ...
... and are effectively 'rafted' on the yielding asthenosphere, they are also characterised by complex deformation and plate interactions along their margins. Here plates are created, deformed, and destroyed, giving rise to concentrated narrow belts of volcanic and earthquake activity. The plate boundar ...
1. The traditional divisions are physical and historical geology, often
... agents of erosion, and with how rocks deform, lands are uplifted or lowered, continents moved, and ocean basins opened and closed through tectonic forces and lithospheric plate movements. Historical geology places origins of rock masses, integrated effects of geologic processes, interpretations of a ...
... agents of erosion, and with how rocks deform, lands are uplifted or lowered, continents moved, and ocean basins opened and closed through tectonic forces and lithospheric plate movements. Historical geology places origins of rock masses, integrated effects of geologic processes, interpretations of a ...
Magnitude 7.7 MARIANA ISLANDS
... of subducting oceanic plates, 500 km rock in Earth’s mantle below about 100 km depth is viscoelastic and cannot rupture to produce Cross section created with the IRIS Earthquake Browser earthquakes. However, rapidly subducting cool oceanic plates can reach depths up to about 700 km into the hot mant ...
... of subducting oceanic plates, 500 km rock in Earth’s mantle below about 100 km depth is viscoelastic and cannot rupture to produce Cross section created with the IRIS Earthquake Browser earthquakes. However, rapidly subducting cool oceanic plates can reach depths up to about 700 km into the hot mant ...
Document
... Isostasy: the state of gravitational equilibrium between the Earth's lithosphere (analogous to iceberg) and asthenosphere (analogous to seawater). Tectonic plates ‘float’ at an elevation which depends on their thickness and relative density; thus high areas will have large lithospheric ‘roots’. Wher ...
... Isostasy: the state of gravitational equilibrium between the Earth's lithosphere (analogous to iceberg) and asthenosphere (analogous to seawater). Tectonic plates ‘float’ at an elevation which depends on their thickness and relative density; thus high areas will have large lithospheric ‘roots’. Wher ...
Revision Audit
... (determined from rocks, sediment or archaeological records). Convection In the mantle convection, heat produced by decay of radioactive elements in the earth’s core heats the lower mantle – creating convection currents. These hot, liquid magma currents are thought to move in circles in the asthenosp ...
... (determined from rocks, sediment or archaeological records). Convection In the mantle convection, heat produced by decay of radioactive elements in the earth’s core heats the lower mantle – creating convection currents. These hot, liquid magma currents are thought to move in circles in the asthenosp ...
Sea-Floor Spreading
... sound waves off under-water objects and then records the echoes of these sound waves. The time it takes for the echo to arrive indicates the distance to the object. ...
... sound waves off under-water objects and then records the echoes of these sound waves. The time it takes for the echo to arrive indicates the distance to the object. ...
World Tectonic Maps package as a pdf file
... The continental crusts are much more complex since they contain flaws from all the previous events over their long histories (more than 4000 million or 4 billion years). The oceanic plates are much simpler since they are just made at sea floor spreading centers, drift passively across the oceans, an ...
... The continental crusts are much more complex since they contain flaws from all the previous events over their long histories (more than 4000 million or 4 billion years). The oceanic plates are much simpler since they are just made at sea floor spreading centers, drift passively across the oceans, an ...
Tectonic controls on the distribution of large
... below thin crust of SE Asia. The oblique vector of this subduction results in the formation of an important dextral shear zone on Sumatra, the Sumatran Fault Zone. No significant porphyry systems are known in western Indonesia. The subducting oceanic plate in this region comprises cold Eocene crust, ...
... below thin crust of SE Asia. The oblique vector of this subduction results in the formation of an important dextral shear zone on Sumatra, the Sumatran Fault Zone. No significant porphyry systems are known in western Indonesia. The subducting oceanic plate in this region comprises cold Eocene crust, ...
baumgardner`s modeling of rapid plate tectonic motion
... cells, each with a variable value for its temperature, pressure, density, velocity, and material properties. These variables change through time in a calculation based on a small set of basic principles. TERRA is one of four models in the world capable of modeling Earth in a global manner. Results f ...
... cells, each with a variable value for its temperature, pressure, density, velocity, and material properties. These variables change through time in a calculation based on a small set of basic principles. TERRA is one of four models in the world capable of modeling Earth in a global manner. Results f ...
Modeling Seafloor Spreading
... 2. When the strips of paper are pulled out, what process does this represent? Pulling out the strips of paper represents the process of seafloor spreading 3. What does the magnet represent? The magnet represents the Earth’s magnetic field 4. What do the sections with arrows represent? (Why are ...
... 2. When the strips of paper are pulled out, what process does this represent? Pulling out the strips of paper represents the process of seafloor spreading 3. What does the magnet represent? The magnet represents the Earth’s magnetic field 4. What do the sections with arrows represent? (Why are ...
Word document - teachearthscience.org
... The process of seafloor spreading created the seafloor of the oceans. For example, in the Atlantic Ocean, North America and South America moved away from Europe and Africa and the resulting crack was filled by mantle material, which cooled and formed new lithosphere. The process continues today. Mol ...
... The process of seafloor spreading created the seafloor of the oceans. For example, in the Atlantic Ocean, North America and South America moved away from Europe and Africa and the resulting crack was filled by mantle material, which cooled and formed new lithosphere. The process continues today. Mol ...
Plate tectonics NB Name
... 2. What happened to the supercontinent Pangaea? _________________________________________________________________________________________________ 3. How did Alfred Wegener use FOSSILS to explain the Continental Drift theory? ___________________________________________________________________________ ...
... 2. What happened to the supercontinent Pangaea? _________________________________________________________________________________________________ 3. How did Alfred Wegener use FOSSILS to explain the Continental Drift theory? ___________________________________________________________________________ ...
The Ocean Floor
... mountains, valleys, hills, and plains! Some important features of the ocean floor include the continental shelf, the continental slope, the continental rise, the abyssal plain, and ocean trenches. ...
... mountains, valleys, hills, and plains! Some important features of the ocean floor include the continental shelf, the continental slope, the continental rise, the abyssal plain, and ocean trenches. ...
Seismic waves - Albert
... When two blocks of rock or two plates are rubbing against each other, they stick a little. They don't just slide smoothly; the rocks catch on each other. The rocks are still pushing against each other, but not moving. After a while, the rocks break because of all the pressure that's built up. When t ...
... When two blocks of rock or two plates are rubbing against each other, they stick a little. They don't just slide smoothly; the rocks catch on each other. The rocks are still pushing against each other, but not moving. After a while, the rocks break because of all the pressure that's built up. When t ...
Plate tectonics
Plate tectonics (from the Late Latin tectonicus, from the Greek: τεκτονικός ""pertaining to building"") is a scientific theory that describes the large-scale motion of Earth's lithosphere. This theoretical model builds on the concept of continental drift which was developed during the first few decades of the 20th century. The geoscientific community accepted the theory after the concepts of seafloor spreading were later developed in the late 1950s and early 1960s.The lithosphere, which is the rigid outermost shell of a planet (on Earth, the crust and upper mantle), is broken up into tectonic plates. On Earth, there are seven or eight major plates (depending on how they are defined) and many minor plates. Where plates meet, their relative motion determines the type of boundary; convergent, divergent, or transform. Earthquakes, volcanic activity, mountain-building, and oceanic trench formation occur along these plate boundaries. The lateral relative movement of the plates typically varies from zero to 100 mm annually.Tectonic plates are composed of oceanic lithosphere and thicker continental lithosphere, each topped by its own kind of crust. Along convergent boundaries, subduction carries plates into the mantle; the material lost is roughly balanced by the formation of new (oceanic) crust along divergent margins by seafloor spreading. In this way, the total surface of the globe remains the same. This prediction of plate tectonics is also referred to as the conveyor belt principle. Earlier theories (that still have some supporters) propose gradual shrinking (contraction) or gradual expansion of the globe.Tectonic plates are able to move because the Earth's lithosphere has greater strength than the underlying asthenosphere. Lateral density variations in the mantle result in convection. Plate movement is thought to be driven by a combination of the motion of the seafloor away from the spreading ridge (due to variations in topography and density of the crust, which result in differences in gravitational forces) and drag, with downward suction, at the subduction zones. Another explanation lies in the different forces generated by the rotation of the globe and the tidal forces of the Sun and Moon. The relative importance of each of these factors and their relationship to each other is unclear, and still the subject of much debate.