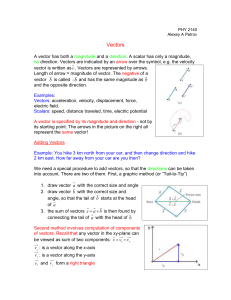
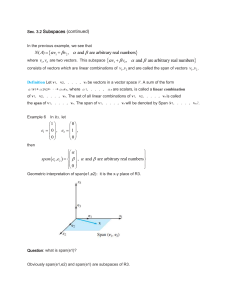
MATH 2030: MATRICES Introduction to Linear Transformations We
... The matrix in the proof of the last theorem is called the standard matrix of the linear transformation T. Example 0.7. Q: Show that a rotation about the origin through an angle θ defines a linear transformation from R2 to R2 and find its standard matrix. A: Let Rθ be the rotation, we will prove this ...
... The matrix in the proof of the last theorem is called the standard matrix of the linear transformation T. Example 0.7. Q: Show that a rotation about the origin through an angle θ defines a linear transformation from R2 to R2 and find its standard matrix. A: Let Rθ be the rotation, we will prove this ...
Apprentice Linear Algebra, 3rd day, 07/06/05
... • Skew projection onto a line. (This means choosing a direction along which the projection occurs; this direction is not necessarily perpendicular to the chosen line.) • Shearing. In coordinates, this is given by the transformation (x, y) 7→ (x + αy, y), where α is a given real number. This transfor ...
... • Skew projection onto a line. (This means choosing a direction along which the projection occurs; this direction is not necessarily perpendicular to the chosen line.) • Shearing. In coordinates, this is given by the transformation (x, y) 7→ (x + αy, y), where α is a given real number. This transfor ...
Ch3a-Systems of Linear Equations
... • Linear Equation: an equations where only the first exponent of the unknown is present • System of Linear Equations: the set of linear equations where there are more than one unknown For example 5x + 2y = -13 x - 2y = 1 is a system of two linear equations with two unknowns x and y. There may be cas ...
... • Linear Equation: an equations where only the first exponent of the unknown is present • System of Linear Equations: the set of linear equations where there are more than one unknown For example 5x + 2y = -13 x - 2y = 1 is a system of two linear equations with two unknowns x and y. There may be cas ...