18.03 LA.2: Matrix multiplication, rank, solving linear systems
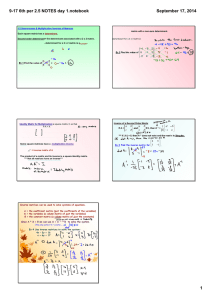
... the equation. Ax = b/ If b is in the plane, then there is a solution to the equation! All possible b ⇐⇒ all possible combinations Ax. In our case, this was a plane. We will call this plane, this subspace, the column space of the matrix A. If b is not on that plane, not in that column space, then the ...
... the equation. Ax = b/ If b is in the plane, then there is a solution to the equation! All possible b ⇐⇒ all possible combinations Ax. In our case, this was a plane. We will call this plane, this subspace, the column space of the matrix A. If b is not on that plane, not in that column space, then the ...
Matrix operations on the TI-82
... 4. Another approach is to define, instead of the above two functions, the single function Y1 = 2 cos x – x – 1, and then find its roots. Approximate roots may be found by tracing and zooming, and it is easy to see that the equation has three solutions. On the CALC menu, roots are found using . Use t ...
... 4. Another approach is to define, instead of the above two functions, the single function Y1 = 2 cos x – x – 1, and then find its roots. Approximate roots may be found by tracing and zooming, and it is easy to see that the equation has three solutions. On the CALC menu, roots are found using . Use t ...
Supporting Information S1.
... This Appendix summarizes theoretical results about measures of autocorrelation and variance as equation [1] approaches a critical transition. For readers who wish to skip the technical background, here are the key points. For many critical transitions of ecological interest, autocorrelation is one a ...
... This Appendix summarizes theoretical results about measures of autocorrelation and variance as equation [1] approaches a critical transition. For readers who wish to skip the technical background, here are the key points. For many critical transitions of ecological interest, autocorrelation is one a ...