Worksheet 5 (2
... 2. Apply distributive property to clear parentheses when appropriate. 3. Use the addition property of equality to collect terms containing the desired variable on one side and all other terms on the opposite side. 4. If two or more terms contain the desired variable on one side, use the distributive ...
... 2. Apply distributive property to clear parentheses when appropriate. 3. Use the addition property of equality to collect terms containing the desired variable on one side and all other terms on the opposite side. 4. If two or more terms contain the desired variable on one side, use the distributive ...
9. Change of basis/coordinates Theorem Let β and β be two ordered
... • Let T be a linear operator on a finite dimensional vector space V , let β and β 0 be ordered bases for V and let P be the change of coordinates from β 0 to β. Then [T ]β = P [T ]β 0 P −1. • Let T be a linear operator on a finite dimensional vector space V . Then for any ordered bases β and γ of V ...
... • Let T be a linear operator on a finite dimensional vector space V , let β and β 0 be ordered bases for V and let P be the change of coordinates from β 0 to β. Then [T ]β = P [T ]β 0 P −1. • Let T be a linear operator on a finite dimensional vector space V . Then for any ordered bases β and γ of V ...
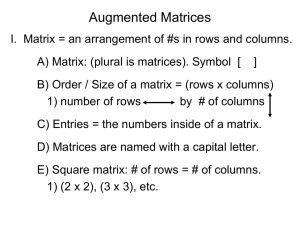
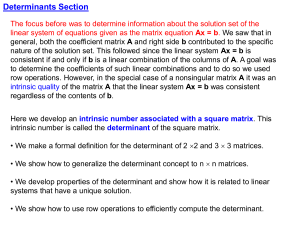
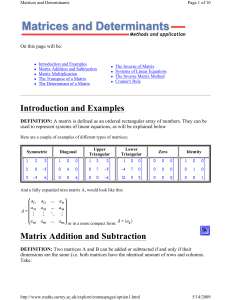
ULinear Algebra and Matrices
... Let A be an m n matrix and let B be an n k matrix. To find the element in the ith row and jth column of the product matrix AB, multiply each element in the ith row of A by the corresponding element in the jth column of B, and then add these products. The product matrix AB is an m k matrix. (The ...
... Let A be an m n matrix and let B be an n k matrix. To find the element in the ith row and jth column of the product matrix AB, multiply each element in the ith row of A by the corresponding element in the jth column of B, and then add these products. The product matrix AB is an m k matrix. (The ...
9_5 Solving Quadratic Equations by Graphing
... STEP 1 Write the equation in the standard for ax2 +bx + c = 0 STEP 2 Sketch the graph of the related quadratic function y = ax2 +bx + c STEP 3 Estimate the values of the x-intercepts, if any. The solutions, or roots, of ax2 +bx + c = 0 are the x-intercepts of the graph. ...
... STEP 1 Write the equation in the standard for ax2 +bx + c = 0 STEP 2 Sketch the graph of the related quadratic function y = ax2 +bx + c STEP 3 Estimate the values of the x-intercepts, if any. The solutions, or roots, of ax2 +bx + c = 0 are the x-intercepts of the graph. ...
a review sheet for test #FN
... Technique #2 for graphing a line: USE THE INTERCEPTS (uses the fact that you only need 2 points to draw a line) 1. Find the x-intercept (which is where the line crosses the x-axis) by setting y = 0 and solving for x. 2. Find the y-intercept (which is where the line crosses the y-axis) by setting x = ...
... Technique #2 for graphing a line: USE THE INTERCEPTS (uses the fact that you only need 2 points to draw a line) 1. Find the x-intercept (which is where the line crosses the x-axis) by setting y = 0 and solving for x. 2. Find the y-intercept (which is where the line crosses the y-axis) by setting x = ...